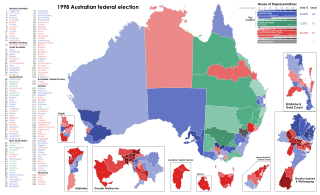
The 1998 Australian federal election was held to determine the members of the 39th Parliament of Australia. It was held on 3 October 1998. All 148 seats of the House of Representatives and 40 seats of the 76 seat Senate were up for election. The incumbent centre-right Liberal/National Coalition government led by Prime Minister John Howard of the Liberal Party and coalition partner Tim Fischer of the National Party defeated the centre-left Australian Labor Party opposition led by Opposition Leader Kim Beazley, despite losing the nationwide popular and two-party preferred vote. However, the Australian Labor Party gained seats compared to the previous election.

The 1996 Australian federal election was held to determine the members of the 38th Parliament of Australia. It was held on 2 March 1996. All 148 seats of the House of Representatives and 40 seats of the 76-seat Senate were up for election. The centre-right Liberal/National Coalition led by Opposition Leader John Howard of the Liberal Party and coalition partner Tim Fischer of the National Party defeated the incumbent centre-left Australian Labor Party government led by Prime Minister Paul Keating in a landslide victory. The Coalition won 94 seats in the House of Representatives, which is the largest number of seats held by a federal government to date, and only the second time a party had won over 90 seats at a federal election.

The Division of North Sydney is an Australian electoral division in the state of New South Wales.
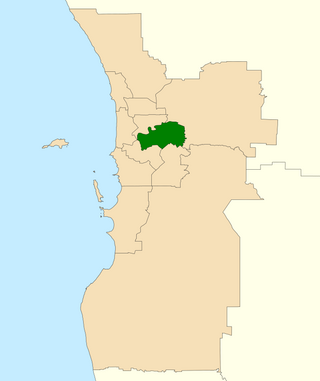
The Division of Swan is an Australian electoral division located in Western Australia.
The Division of Boothby is an Australian federal electoral division in South Australia. The division was one of the seven established when the former Division of South Australia was redistributed on 2 October 1903 and is named after William Boothby (1829–1903), the Returning Officer for the first federal election.
The Division of Mayo is an Australian electoral division located to the east and south of Adelaide, South Australia. Created in the state redistribution of 3 September 1984, the division is named after Helen Mayo, a social activist and the first woman elected to an Australian University Council. The 9,315 km2 rural seat covers an area from the Barossa Valley in the north to Cape Jervis in the south. Taking in the Adelaide Hills, Fleurieu Peninsula and Kangaroo Island regions, its largest population centre is Mount Barker. Its other population centres are Aldgate, Bridgewater, Littlehampton, McLaren Vale, Nairne, Stirling, Strathalbyn and Victor Harbor, and its smaller localities include American River, Ashbourne, Balhannah, Brukunga, Carrickalinga, Charleston, Cherry Gardens, Clarendon, Crafers, Cudlee Creek, Currency Creek, Delamere, Echunga, Forreston, Goolwa, Gumeracha, Hahndorf, Houghton, Inglewood, Kersbrook, Kingscote, Langhorne Creek, Lobethal, Macclesfield, McLaren Flat, Meadows, Middleton, Milang, Mount Compass, Mount Pleasant, Mount Torrens, Mylor, Myponga, Normanville, Norton Summit, Oakbank, Penneshaw, Piccadilly, Port Elliot, Second Valley, Springton, Summertown, Uraidla, Willunga, Woodchester, Woodside, Yankalilla, and parts of Birdwood, Old Noarlunga and Upper Sturt.
The Division of Sturt is an Australian electoral division in South Australia. It was proclaimed at the South Australian redistribution of 11 May 1949. Sturt was named for Captain Charles Sturt, a nineteenth century British Military officer and explorer.

The 1959 Manitoba general election was held on May 14, 1959 to elect 57 members to the Legislative Assembly of Manitoba, Canada. It resulted in a majority victory for the incumbent Progressive Conservatives under the leadership of Premier Dufferin Roblin. It was the first time since the 1914 election that the PCs won an outright majority in the province, when they were led by Dufferin Roblin's grandfather, Sir Rodmond Roblin.

Australian Greens SA is a green political party located in the Australian state of South Australia. It is a member of the federation of the Australian Greens party.
The term swing refers to the extent of change in voter support, typically from one election or opinion poll to another, expressed as a positive or negative percentage point. For the Australian House of Representatives and the lower or unicameral houses of the parliaments of all the states and territories except Tasmania and the ACT, as well as Tasmania's upper house, Australia employs preferential voting in single-member constituencies. Under the full-preference instant-runoff voting system, in each seat the candidate with the lowest vote is eliminated and their preferences are distributed, which is repeated until only two candidates remain. While every seat has a two-candidate preferred (TCP) result, seats where the major parties have come first and second are commonly referred to as having a two-party-preferred (TPP) result. The concept of "swing" in Australian elections is not simply a function of the difference between the votes of the two leading candidates, as it is in Britain. To know the majority of any seat, and therefore the swing necessary for it to change hands, it is necessary to know the preferences of all the voters, regardless of their first preference votes. It is not uncommon in Australia for candidates who have comfortable leads on the first count to fail to win the seat, because "preference flows" go against them.

In Australian politics, the two-party-preferred vote is the result of an election or opinion poll after preferences have been distributed to the highest two candidates, who in some cases can be independents. For the purposes of TPP, the Liberal/National Coalition is usually considered a single party, with Labor being the other major party. Typically the TPP is expressed as the percentages of votes attracted by each of the two major parties, e.g. "Coalition 50%, Labor 50%", where the values include both primary votes and preferences. The TPP is an indicator of how much swing has been attained/is required to change the result, taking into consideration preferences, which may have a significant effect on the result.

The 1954 Australian federal election were held in Australia on 29 May 1954. All 121 seats in the House of Representatives were up for election, but no Senate election took place. The incumbent Liberal–Country coalition led by Prime Minister Robert Menzies defeated the opposition Labor Party led by H. V. Evatt, despite losing the two-party preferred vote. Although the ALP won the two-party preferred vote, six Coalition seats were uncontested compared to one ALP seat. The Psephos blog makes clear that if all seats had been contested, the Coalition would have recorded a higher primary vote than the ALP and possibly also a higher two-party preferred vote.

The 1919 Australian federal election was held on 13 December 1919 to elect members to the Parliament of Australia. All 75 seats in the House of Representatives and 19 of the 36 seats in the Senate were up for election. The incumbent Nationalist Party government won re-election, with Prime Minister Billy Hughes continuing in office.

The 1917 Australian federal election was held in Australia on 5 May 1917. All 75 seats in the House of Representatives and 18 of the 36 seats in the Senate were up for election. The incumbent Nationalist Party, led by Prime Minister Billy Hughes, defeated the opposition Labor Party led by Frank Tudor in a landslide.

The 1913 Australian federal election was held in Australia on 31 May 1913. All 75 seats in the House of Representatives, and 18 of the 36 seats in the Senate were up for election. The incumbent Labor Party, led by Prime Minister Andrew Fisher, was defeated by the opposition Commonwealth Liberal Party under Joseph Cook, marking the second time an Australian Prime Minister was defeated at an election. The new government had a majority of just a single seat, and held a minority of seats in the Senate. It would last only 15 months, suffering defeat at the 1914 election.
The 1918 Swan by-election was a by-election for the Division of Swan in the Australian House of Representatives, following the death of the sitting member Sir John Forrest. Held on 26 October 1918, the by-election led to the election of the youngest person to be elected until 2010 to the Parliament of Australia, Edwin Corboy. It saw the conservative vote split between the Country Party and the Nationalist Party, which directly prompted the introduction of preferential voting in Australia.
This is a list of members of the Western Australian Legislative Assembly between the 1914 election and the 1917 election, together known as the Ninth Parliament. The re-election of Premier John Scaddan's Labor Government with a 26-24 majority in 1914 was tempered when, a year later, Labor member Joseph Gardiner's seat was declared vacant on account of his non-attendance and a Liberal was elected in his stead, and Labor became a minority government when on 18 December 1915, Edward Johnston resigned from the Labor Party and became an independent. On 27 July 1916, the Scaddan Ministry was defeated and the Liberals' Frank Wilson became the new Premier.

State elections were held in South Australia on 29 April 1944. All 39 seats in the South Australian House of Assembly were up for election. The incumbent Liberal and Country League government led by Premier of South Australia Thomas Playford IV defeated the opposition Australian Labor Party led by Leader of the Opposition Robert Richards.
A by-election was held for the Australian House of Representatives seat of Adelaide on 10 January 1914. This was triggered by the death of Labor Party MP Ernest Roberts.
The 5 September 1914 election was a double dissolution election which meant all 36 seats in the Senate were up for election, with each Australian states electing six members, with half to serve a six-year term and the rest to serve a three year term. Terms were taken to have commenced on 1 July 1914. The Senate resolved that in each State the three senators who received the most votes would sit for a six-year term, finishing on 30 June 1920 while the other half would sit for a three-year term, finishing on 30 June 1917.












