Related Research Articles

John Quincy Adams was the sixth president of the United States, serving from 1825 to 1829. He previously served as the eighth United States secretary of state from 1817 to 1825. During his long diplomatic and political career, Adams served as an ambassador and also as a member of the United States Congress representing Massachusetts in both chambers. He was the eldest son of John Adams, who served as the second president of the United States from 1797 to 1801, and First Lady Abigail Adams. Initially a Federalist like his father, he won election to the presidency as a member of the Democratic-Republican Party, and later, in the mid-1830s, became affiliated with the Whig Party.

Sir John Major is a British former politician who served as Prime Minister of the United Kingdom and Leader of the Conservative Party from 1990 to 1997. He previously held Cabinet positions under prime minister Margaret Thatcher, his last as chancellor of the Exchequer from 1989 to 1990. Major was Member of Parliament (MP) for Huntingdon, formerly Huntingdonshire, from 1979 to 2001. Since stepping down as an MP in 2001, Major has focused on writing and his business, sporting and charity work, and has occasionally commented on political developments in the role of an elder statesman.

The 2000 United States presidential election was the 54th quadrennial presidential election, held on Tuesday, November 7, 2000. The Republican nominee, Governor George W. Bush of Texas, the eldest son of George H. W. Bush, narrowly defeated incumbent Democratic Vice President Al Gore. It was the fourth of five U.S. presidential elections, and the first since 1888, in which the winning candidate lost the popular vote, and is considered one of the closest U.S. presidential elections, with long-standing controversy about the result. Gore conceded the election on December 13.

The 1796 United States presidential election was the third quadrennial presidential election of the United States. It was held from Friday, November 4 to Wednesday, December 7, 1796. It was the first contested American presidential election, the first presidential election in which political parties played a dominant role, and the only presidential election in which a president and vice president were elected from opposing tickets. Incumbent vice president John Adams of the Federalist Party defeated former secretary of state Thomas Jefferson of the Democratic-Republican Party.

The 1824 United States presidential election was the tenth quadrennial presidential election. It was held from Tuesday, October 26 to Thursday, December 2, 1824. Andrew Jackson, John Quincy Adams, Henry Clay and William Crawford were the primary contenders for the presidency. The result of the election was inconclusive, as no candidate won a majority of the electoral vote. In the election for vice president, John C. Calhoun was elected with a comfortable majority of the vote. Because none of the candidates for president garnered an electoral vote majority, the U.S. House of Representatives, under the provisions of the Twelfth Amendment, held a contingent election. On February 9, 1825, the House voted to elect John Quincy Adams as president, ultimately giving the election to him.

The 1860 United States presidential election was the 19th quadrennial presidential election, held on Tuesday, November 6, 1860. In a four-way contest, the Republican Party ticket of Abraham Lincoln and Hannibal Hamlin won a national popular plurality, a popular majority in the North where states had already abolished slavery, and a national electoral majority comprising only Northern electoral votes. Lincoln's election thus served as the main catalyst of the states that would become the Confederacy seceding from the Union. This marked the first time that a Republican was elected president. It was also the first presidential election in which both major party candidates were registered in the same home state; the others have been in 1904, 1920, 1940, 1944, and 2016.
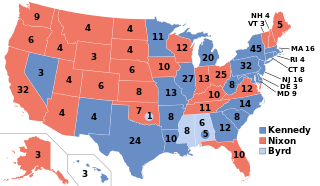
The 1960 United States presidential election was the 44th quadrennial presidential election, held on Tuesday, November 8, 1960. The Democratic ticket of Senator John F. Kennedy and his running mate, Senate Majority Leader Lyndon B. Johnson, narrowly defeated the Republican ticket of incumbent Vice President Richard Nixon and his running mate, U.N. Ambassador Henry Cabot Lodge Jr. This was the first election in which 50 states participated, marking the first participation of Alaska and Hawaii, and the last in which the District of Columbia did not. This made it the only presidential election where the threshold for victory was 269 electoral votes. It was also the first election in which an incumbent president—in this case, Dwight D. Eisenhower—was ineligible to run for a third term because of the term limits established by the 22nd Amendment.

The 1972 United States presidential election was the 47th quadrennial presidential election held on Tuesday, November 7, 1972. Incumbent Republican President Richard Nixon defeated Democratic Senator George McGovern in a landslide victory. With 60.7% of the popular vote, Richard Nixon won the largest share of the popular vote for the Republican Party in any presidential election.

The 1980 United States presidential election was the 49th quadrennial presidential election, held on November 4, 1980. The Republican nominee, former California governor Ronald Reagan, defeated incumbent Democratic President Jimmy Carter in a landslide victory. This was the first election since 1932 in which an elected incumbent president was defeated, as well as the first election since 1888 that saw the defeat of an incumbent Democratic president.

In the United States, the Electoral College is the group of presidential electors that is formed every four years during the presidential election for the sole purpose of voting for the president and vice president. The process is described in Article II of the U.S. Constitution. The number of electoral votes a state has equals its number of Senators (2) plus its number of Representatives in the House of Representatives, the latter being dependent on the Census's reported population. Each state appoints electors using legal procedures determined by its legislature, equal in number to its congressional delegation totaling 535 electors in the 50 states. The Twenty-third Amendment from 1961 granted the federal District of Columbia three electors, bringing the total number of electors to 538. Federal office holders, including senators and representatives, cannot be electors. Of the current 538 electors, a simple majority of 270 or more electoral votes is required to elect the president and vice president. If no candidate achieves a majority there, a contingent election is held by the House of Representatives to elect the president and by the Senate to elect the vice president.

The 2008 United States presidential election was the 56th quadrennial presidential election, held on Tuesday, November 4, 2008. The Democratic ticket of Barack Obama, the junior senator from Illinois, and Joe Biden, the senior senator from Delaware, defeated the Republican ticket of John McCain, the senior senator from Arizona, and Sarah Palin, the governor of Alaska. Obama became the first African American to be elected to the presidency, as well as being only the third sitting United States senator elected president, joining Warren G. Harding and John F. Kennedy. Meanwhile, this was only the second successful all-senator ticket since the 1960 election and is the only election where both major party nominees were sitting senators. This was the first election since 1952 in which neither the incumbent president nor vice president was on the ballot, as well as the first election since 1928 in which neither ran for the nomination.
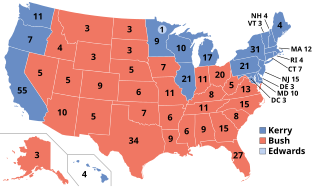
The 2004 United States presidential election was the 55th quadrennial presidential election, held on Tuesday, November 2, 2004. The Republican ticket of incumbent President George W. Bush and his running mate incumbent Vice President Dick Cheney was re-elected to a second term. They narrowly defeated the Democratic ticket of John Kerry, a senator from Massachusetts and his running mate John Edwards, a senator from North Carolina.

The 2002 United States House of Representatives elections were held on November 5, 2002, in the middle of President George W. Bush's first term, to elect U.S. Representatives to serve in the 108th United States Congress. This was the first congressional election using districts drawn up during the 2000 United States redistricting cycle on the basis of the 2000 census.
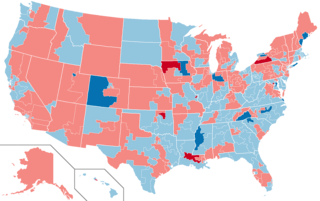
The 1986 United States House of Representatives elections was held on November 4, 1986, to elect U.S. Representatives to serve in the 100th United States Congress. They occurred in the middle of President Ronald Reagan's second term in office, while he was still relatively popular with the American public. As in most mid-term elections, the president's party — in this case, the Republican Party — lost seats, with the Democratic Party gaining a net of five seats and cementing its majority. These results were not as dramatic as those in the Senate, where the Republicans lost control of the chamber to the Democrats.

The 2016 United States presidential election was the 58th quadrennial presidential election, held on Tuesday, November 8, 2016. The Republican ticket, businessman Donald Trump and Indiana governor Mike Pence, defeated the Democratic ticket of former secretary of state and First Lady of the United States Hillary Clinton and the junior senator from Virginia, Tim Kaine, in what was considered one of the biggest political upsets in American history. It was the fifth and most recent presidential election in which the winning candidate lost the popular vote. It was also the sixth and most recent presidential election in U.S. history in which both major party candidates were registered in the same home state; the others have been in 1860, 1904, 1920, 1940, and 1944.

The 2024 United States elections are scheduled to be held on Tuesday, November 5, 2024. During this presidential election year, the president and vice president will be elected. In addition, all 435 seats in the United States House of Representatives and 34 of the 100 seats in the United States Senate will be contested to determine the membership of the 119th United States Congress. Thirteen state and territorial governorships and numerous other state and local elections will also be contested.

The 2024 United States Senate elections are scheduled to be held on November 5, 2024, as part of the 2024 United States elections. Thirty-three of the 100 seats in the U.S. Senate will be contested in regular elections. Senators are divided into three classes whose six-year terms are staggered so that a different class is elected every two years. Class 1 senators will face election in 2024.

The 2026 United States Senate elections are scheduled to be held on November 3, 2026, with 33 of the 100 seats in the Senate being contested in regular elections, the winners of which will serve 6-year terms in the United States Congress from January 3, 2027, to January 3, 2033. Senators are divided into 3 groups, or classes, whose terms are staggered so that a different class is elected every 2 years. Class 2 senators were last elected in 2020, and will be up for election in 2032.
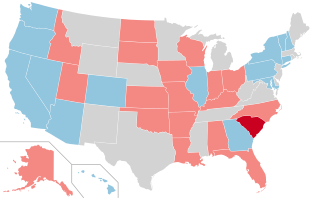
The 2028 United States Senate elections will be held on November 7, 2028, with 34 of the 100 seats in the Senate being contested in regular elections, the winners of which will serve 6-year terms in the United States Congress from January 3, 2029, to January 3, 2035. Senators are divided into 3 groups or classes whose terms are staggered so that a different class is elected every 2 years. Class 3 senators were last elected in 2022, and will be up for election again in 2028. These elections will run concurrently with the 2028 United States presidential election.
References
- ↑ "By-Elections 1958-1961". Psephos. Archived from the original on 3 August 2008.