
The Yom Kippur War, also known as the Ramadan War, the October War, the 1973 Arab–Israeli War, or the Fourth Arab–Israeli War, was fought from 6 to 25 October 1973 between Israel and a coalition of Arab states led by Egypt and Syria. Most of the fighting occurred in the Sinai Peninsula and Golan Heights, territories occupied by Israel in 1967. Some combat also took place in Egypt and northern Israel. Egypt aimed to secure a foothold on the eastern bank of the Suez Canal and use it to negotiate the return of the Sinai Peninsula.

The Israeli Air Force operates as the aerial and space warfare branch of the Israel Defense Forces (IDF). It was founded on May 28, 1948, shortly after the Israeli Declaration of Independence. As of April 2022, Aluf Tomer Bar has been serving as the Air Force commander.

The War of Attrition involved fighting between Israel and Egypt, Jordan, the Palestine Liberation Organisation (PLO) and their allies from 1967 to 1970.
The history of the Israel Defense Forces (IDF) intertwines in its early stages with history of the Haganah.

The 1st "Golani" Brigade is an Israeli military infantry brigade. It is subordinated to the 36th Division and traditionally associated with the Northern Command. It is one of the five infantry brigades of the regular Israel Defense Forces (IDF), the others being the Paratroopers Brigade, the Nahal Brigade, the Givati Brigade and the Kfir Brigade. Its symbol is a green olive tree against a yellow background, with its soldiers wearing a brown beret. It is one of the most highly decorated infantry units in the IDF. The brigade consists of five battalions, including two which it kept from its inception, one transferred from the Givati Brigade (51st).

The 35th Paratroopers Brigade is an Israeli military airborne infantry brigade. It forms a major part of the Israeli Ground Forces' Infantry Corps, and has a history of carrying out special operations from the 1950s onwards. Soldiers of the brigade wear maroon berets with the Infantry Corps pin and russet boots.

The Bar-Lev Line was a chain of fortifications built by Israel along the eastern bank of the Suez Canal shortly after the 1967 Arab–Israeli War, during which Egypt lost the entire Sinai Peninsula. It was considered impenetrable by the Israeli military until it was overrun in less than two hours during Egypt's Operation Badr, which sparked the 1973 Arab–Israeli War.

Mohammed Aly Fahmy was an Egyptian field marshal, known as the "Father of the Egyptian Air Defense".

Zeev Almog, was the Commander In Chief (C.I.C.) of the Israeli Navy from 1979 to 1985. He was also General Manager of Israel Shipyards from 1986 to 1995.
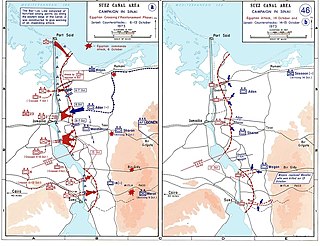
The Battle of the Sinai was one of the most consequential battles of the Yom Kippur war. An Egyptian attacking force that advanced beyond their line of defense at the Bar-Lev Line was repulsed with heavy losses by Israeli forces. This prompted the Israelis to launch Operation Abiray-Lev the next day, penetrating the Egyptian line of defense and crossing the Suez Canal.

The 114 Squadron of the Israeli Air Force, also known as the Night Leaders Squadron, is a helicopter squadron of CH-53-2000 Sea Stallions based at Tel Nof Airbase.

Avraham Botzer was the Commander of the Israeli Navy between 1968 and 1972.
Egyptian 25th Brigade ambush was a battle that occurred on October 17, 1973, the eleventh day of the Yom Kippur War, east of the Great Bitter Lake, in the Sinai Peninsula. The ambush was conducted by the Israel Defense Forces' 162nd Division, against the 25th Brigade of the Egyptian army. The Israelis' goal was the destruction of the brigade, which attempted to disrupt the Israeli crossing of the Suez Canal.

The October 22 Scud missile attack, which took place in the midst of the 1973 Yom Kippur War, was the first operational use of Scud missiles in the world. It witnessed Egypt launch three Scud missiles against Israeli targets. One of the missiles was fired at Arish and the others at the Israeli bridgehead on the western bank of the Suez Canal, near Deversoir.

El-Sa‘ka Forces is an Egyptian military commando force established in 1955 by Major General Jalal Mahmoud Fahmy Al-Haridi. High fitness is required and training is conducted at the El Sa‘ka Academy built by Major General Ahmed Ragai Ateya. Unit 777 and Unit 999 are divisions of the Sa'ka forces.

This article deals with the history and development of tanks of the Israeli Army, from their first use after World War II in the establishment of the State of Israel after the end of the British Mandate, and into the Cold War and what today is considered the modern era.

Operation Abirey-Halev or Operation Abirey-Lev also known as Operation Stouthearted Men and Operation Valiant, code-named Operation Gazelle, was an Israeli operation that took place in the center of the Suez Canal on 15–23 October 1973 during the Yom Kippur War.

Giora Lev was the 7th mayor of Petah Tikva (1989-1998) and Brigadier-general in the Israel Defense Forces.

Moshe Levy was a half-track commander in the Israeli Armored Corps, and was awarded the Medal of Valor for his fighting in Sinai during the Yom Kippur War.

Nabil Shukri was the commander of the El-Sa'ka Special Forces Corps during the War of Attrition and the Yom Kippur War; He joined the Military College in 1948 and graduated in 1950. He then joined the Sixth Infantry Battalion, then joined the Airborne Corps, then the El-Sa'ka Forces.


















