Plurality voting refers to electoral systems in which a candidate who polls more than any other is elected. In systems based on single-member districts, it elects just one member per district and may also be referred to as first-past-the-post (FPTP), single-member plurality (SMP/SMDP), single-choice voting, simple plurality or relative majority. A system that elects multiple winners elected at once with the plurality rule and where each voter casts multiple X votes in a multi-seat district is referred to as plurality block voting. A semi-proportional system that elects multiple winners elected at once with the plurality rule and where each voter casts just one vote in a multi-seat district is known as single non-transferable voting.

Politics of Norfolk Island takes place in a framework of a parliamentary representative democratic entity. Norfolk Island is the only non-mainland Australian territory to have achieved self-governance. The Norfolk Island Act 1979, passed by the Parliament of Australia in 1979, is the Act under which the island is governed.
Mixed-member proportional representation is a mixed electoral system in which votes are cast for both local elections and also for overall party vote tallies, which are used to allocate additional members to produce or deepen overall proportional representation.
Electoral systems of the Australian states and territories are broadly similar to the electoral system used in federal elections in Australia.
The parliaments of the Australian states and territories are legislative bodies within the federal framework of the Commonwealth of Australia.
Canada holds elections for legislatures or governments in several jurisdictions: for the federal (national) government, provincial and territorial governments, and municipal governments. Elections are also held for self-governing First Nations and for many other public and private organizations including corporations and trade unions. Municipal elections can also be held for both upper-tier and lower-tier governments.

Romania elects on a national level a head of state – the president – and a legislature. The president is elected for a five-year term by the people. The Romanian Parliament has two chambers. The Chamber of Deputies has currently 330 members, elected for a four-year term by party-list proportional representation on closed lists. The Senate has currently 136 members, elected for a four-year term by party-list proportional representation on closed lists.

Elections in Portugal are free, fair, and regularly held, in accordance with election law.

The National Assembly is the unicameral legislative house of the Parliament of Mauritania. The legislature currently has 176 members, elected for five-year terms in electoral districts or nationwide proportional lists.

The Politics of British Columbia involves not only the governance of British Columbia, Canada, and the various political factions that have held or vied for legislative power, but also a number of experiments or attempts at political and electoral reform.
Electoral districts go by different names depending on the country and the office being elected.
Electoral reform is a change in electoral systems which alters how public desires are expressed in election results.

The Falkland Islands general election of 2001 was held on Thursday 22 November 2001 to elect members to the Legislative Council through universal suffrage using block voting. Chief Executive Michael Blanch acted as Chief Counting Officer.
A non-binding referendum on electoral reform was held in the Canadian province of Prince Edward Island between 27 October – 7 November 2016. This was the second electoral reform referendum to be held in Prince Edward Island, following a vote to maintain the status quo in 2005. The referendum asked which of five voting systems residents would prefer to use in electing members to the Legislative Assembly of Prince Edward Island. The referendum involved four instant run-off counts and indicated mixed member proportional representation was the majority choice with 55.03% support on the final ballot, with support of 52.42% of votes cast.

A referendum on electoral reform took place by mail-in ballot between October 22 and December 7, 2018, in the Canadian province of British Columbia. 61.3 percent of voters supported maintaining the first-past-the-post voting system rather than switching to a proportional representation voting system, which was supported by 38.7 percent of voters. This was British Columbia's third referendum on electoral reform, following ones in 2005 and 2009.

Rural–urban proportional representation (RUP), also called flexible district PR, is a mixed electoral system which combines the use of single- and multi-member constituencies in a lower tier and top-up seats in an upper tier to meet the different needs of both rural and urban areas, while protecting the objective of proportionality. The term was coined by Fair Vote Canada, which devised a rural–urban system with the intention of meeting the special challenges of Canada's geography, which includes wide-flung, sparsely populated areas.
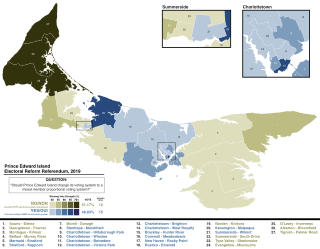
A referendum on electoral reform was held on April 23, 2019, in the Canadian province of Prince Edward Island – simultaneously with the 2019 provincial election – to determine if the province should adopt a mixed-member proportional representation voting system (MMP). A narrow majority voted to keep the existing first-past-the-post system. However, the referendum was not binding, as neither the yes or no side received majority support in 60% or more of the province's 27 electoral districts.

A referendum on reforming the electoral system was held in the Falkland Islands on 24 September 2020, after being postponed from 26 March 2020 following the Coronavirus pandemic. Voters were asked if they wanted to replace the two existing electoral constituencies with a single constituency for the whole of the Islands. Although a majority of those who voted supported the change, the required two-thirds majority in both of the islands' constituencies was not achieved.
An electoral system referendum was held in Norfolk Island on 1 December 1982 to decide whether the electoral system for the Norfolk Island Legislative Assembly should be changed from proportional representation to a new cumulative voting system.
The 1979 Norfolk Island legislative election was held on 10 August 1979 to elect the 1st Norfolk Island Legislative Assembly, the prime legislative body of Norfolk Island.








