The playoffs, play-offs, postseason or finals of a sports league are a competition played after the regular season by the top competitors to determine the league champion or a similar accolade. Depending on the league, the playoffs may be either a single game, a series of games, or a tournament, and may use a single-elimination system or one of several other different playoff formats. Playoff, in regard to international fixtures, is to qualify or progress to the next round of a competition or tournament.
A tournament is a competition involving at least three competitors, all participating in a sport or game. More specifically, the term may be used in either of two overlapping senses:
- One or more competitions held at a single venue and concentrated into a relatively short time interval.
- A competition involving a number of matches, each involving a subset of the competitors, with the overall tournament winner determined based on the combined results of these individual matches. These are common in those sports and games where each match must involve a small number of competitors: often precisely two, as in most team sports, racket sports and combat sports, many card games and board games, and many forms of competitive debating. Such tournaments allow large numbers to compete against each other in spite of the restriction on numbers in a single match.
The 1999 Rugby World Cup was the fourth Rugby World Cup, the quadrennial international rugby union championship. It was principally hosted by Wales, and was won by Australia. This was the first Rugby World Cup to be held in the sport's professional era.
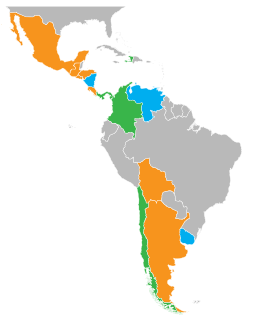
The Apertura[apeɾˈtuɾa] and Clausura[klawˈsuɾa] tournaments is a split season format for Spanish-speaking sports leagues. It is a relatively recent innovation for many Latin American football leagues in which the traditional association football season from August to May is divided in two sections per season, each with its own champion. Apertura and Clausura are the Spanish words for "opening" and "closing". In French-speaking Haiti, these are known as the Ouverture and the Fermeture, while in English-speaking Belize, they are respectively the Opening and Closing seasons. When used in the United States and Canada, they are known as the Spring and Fall seasons.
The FIFA U-17 World Cup, founded as the FIFA U-16 World Championship, later changed to U-17 in 1991 and to its current name in 2007, is the world championship of association football for male players under the age of 17 organized by Fédération Internationale de Football Association (FIFA). The current champion is Brazil, which won its fourth title at the 2019 tournament on home soil.
The Thomas Cup, sometimes called the World Men's Team Championships, is an international badminton competition among teams representing member nations of the Badminton World Federation (BWF), the sport's global governing body. The championships have been conducted every two years since the 1982 tournament, amended from being conducted every three years since the first tournament held in 1948–1949.
The 2006 FIFA World Cup qualification competition was a series of tournaments organised by the six FIFA confederations. Each confederation — the AFC (Asia), CAF (Africa), CONCACAF, CONMEBOL, OFC (Oceania), and UEFA (Europe) — was allocated a certain number of the 32 places at the tournament. A total of 197 teams entered the qualification process for the 2006 FIFA World Cup. In 2001 FIFA ended automatic qualification of the reigning champion, so that 2002 champions Brazil became first to participate in the qualifying tournament. The hosts (Germany) retained their automatic spot.
The 2002 FIFA World Cup qualification competition was a series of tournaments organised by the six FIFA confederations. Each confederation — the AFC (Asia), CAF (Africa), CONCACAF, CONMEBOL, OFC (Oceania), and UEFA (Europe) — was allocated a certain number of the 32 places at the tournament. 199 teams entered the tournament qualification rounds, competing for 32 spots in the final tournament. South Korea and Japan, as the co-hosts, and France, as the defending champions, qualified automatically, leaving 29 spots open for competition.
The 1994 FIFA World Cup qualification was a series of tournaments organised by the six FIFA confederations. The 1994 FIFA World Cup featured 24 teams with one place reserved for the host nation, United States, and one place for the defending champions, Germany. The remaining 22 places were determined by a qualification process, in which 147 teams, from the six FIFA confederations, competed. Most of the successful teams were determined within these confederations, with a limited number of inter-confederation play-offs occurring at the end of the process.
The 1998 FIFA World Cup qualification competition was a series of tournaments organised by the six FIFA confederations. Each confederation — the AFC (Asia), CAF (Africa), CONCACAF, CONMEBOL, OFC (Oceania), and UEFA (Europe) — was allocated a certain number of the 32 places at the tournament. A total of 174 teams entered the 1998 FIFA World Cup qualification rounds, competing for a total of 32 spots in the final tournament. The 1998 FIFA World Cup featured 32 teams, with two places reserved for France and Brazil as host nation and defending champions, respectively. The remaining 30 places were determined by a qualification process, in which the other 174 teams, from the six FIFA confederations, competed.
There are a number of formats used in various levels of competition in sports and games to determine an overall champion. Some of the most common are the single elimination, the best-of- series, the total points series more commonly known as on aggregate, and the round-robin tournament.
The FIFA World Cup qualification is the process that a national association football team goes through to qualify for the final tournament of the FIFA World Cup. The qualification reduces the large field of eligible entrants from 211 to just 32 for the finals as of the 2022 edition.
The 2007 Cricket World Cup was contested between 16 of the 97 countries that were members of the International Cricket Council at the time. The 11 teams with One-Day International status at the time of drafting qualified automatically for the World Cup. Meanwhile, the 86 other members of the ICC played off in a series of tournaments, forming the Cricket World Cup qualification process, to capture one of the remaining five spots in the World Cup.
The 2003 FIFA Women's World Cup qualification process decided the 15 teams which played at the 2003 FIFA Women's World Cup, with the host China qualifying automatically as the host nation. The qualification process for the 2003 FIFA Women's World Cup saw 99 teams from the six FIFA confederations compete for the 16 places in the tournament's finals. The places were divided as follows:
The 2018 FIFA World Cup qualification process was a series of tournaments organised by the six FIFA confederations to decide 31 of the 32 teams which would play in the 2018 FIFA World Cup, with Russia qualifying automatically as hosts. All 210 remaining FIFA member associations were eligible to enter the qualifying process, and for the first time in World Cup history, all eligible national teams registered for the preliminary competition, but Zimbabwe and Indonesia were disqualified before playing their first matches. Bhutan, South Sudan, Gibraltar and Kosovo made their FIFA World Cup qualification debuts.
21 teams entered in the 1966 FIFA World Cup qualification rounds for the African, Asian and Oceanian zone. The entries of Congo and the Philippines were rejected.

The men's qualification for the 2004 Olympic men's basketball tournament occurred from 2002–2003; all five FIBA zones sent in teams.
The 2002 Africa Cup was the third edition of highest level rugby union tournament in Africa Six teams participated to this tournament valid also as final round of African qualification for 2003 Rugby World Cup. For this reason, at the tournament participated the winner of first round, the Madadagascar. The teams were divided in two pools, with a final between the winner of each pool. A second division was also played
The 2004 Africa Cup was the fifth edition of top level rugby union tournament in Africa. Ten teams were admitted, but Tunisia withdrew.

The AFC Asian Cup qualification is the process that a national association football team goes through to qualify for the final tournament of AFC Asian Cup. The qualification reduces the large field of eligible entrants from 47 to just 24 for the finals.


