
The BBC World Service is an international broadcaster owned and operated by the BBC. It is the world's largest external broadcaster in terms of reception area, language selection and audience reach. It broadcasts radio news, speech and discussions in more than 40 languages to many parts of the world on analogue and digital shortwave platforms, internet streaming, podcasting, satellite, DAB, FM and MW relays. In 2015, the World Service reached an average of 210 million people a week. In November 2016, the BBC announced that it would start broadcasting in additional languages including Amharic and Igbo, in its biggest expansion since the 1940s.

Newsnight is the BBC's news and current affairs programme, providing in-depth investigation and analysis of the stories behind the day's headlines. The programme is broadcast on weekdays at 22:30 on BBC Two and the UK feed of BBC News channel; it is also available on BBC iPlayer.
The Hutton Inquiry was a 2003 judicial inquiry in the UK chaired by Lord Hutton, who was appointed by the Labour government to investigate the controversial circumstances surrounding the death of David Kelly, a biological warfare expert and former UN weapons inspector in Iraq.

Gregory Dyke is a British media executive, football administrator, journalist and broadcaster. Since the 1960s, Dyke has had a long career in the UK in print and then broadcast journalism. He is credited with introducing 'tabloid' television to British broadcasting, and reviving the ratings of TV-am. In the 1990s, he held chief executive positions at LWT Group, Pearson Television, and Channel 5.
Newsquest Media Group Limited is the second largest publisher of regional and local newspapers in the United Kingdom. It is owned by the American mass media holding company Gannett. It has 205 brands across the UK, publishing online and in print and reaches 28 million visitors a month online and 6.5 million readers a week in print. Based in London, Newsquest employs a total of more than 5,500 people across the UK. It also has a specialist arm that publishes both commercial and business-to-business (B2B) titles such as Insurance Times, The Strad and Boxing News.

Sir Mark John Thompson is a British media executive who is Chairman of the Board of Directors of Ancestry, the largest for-profit genealogy company in the world, and Chief Executive Officer of the Cable News Network (CNN). He is the former president and chief executive officer of The New York Times Company. From 2004 to 2012, he served as Director-General of the BBC, and before that was the Chief Executive of Channel 4. In 2009 Thompson was ranked as the 65th most powerful person in the world by Forbes magazine. He was elected to the American Philosophical Society in 2017.

BBC News is an operational business division of the British Broadcasting Corporation (BBC) responsible for the gathering and broadcasting of news and current affairs in the UK and around the world. The department is the world's largest broadcast news organisation and generates about 120 hours of radio and television output each day, as well as online news coverage. The service maintains 50 foreign news bureaus with more than 250 correspondents around the world. Deborah Turness has been the CEO of news and current affairs since September 2022.
This article outlines, in chronological order, the various controversies surrounding or involving the BBC.

The 2006 youth protests in France occurred during the months of February, March, and April as a result of opposition to a measure set to deregulate labour. Young people were the primary participants in the protests as the bill would have directly affected their future jobs in a way that they considered negative.
The BBC Trust was the governing body of the British Broadcasting Corporation (BBC) between 2007 and 2017. It was operationally independent of BBC management and external bodies, and its stated aim was to make decisions in the best interests of licence-fee payers. On 12 May 2016, it was announced in the House of Commons that, under the next royal charter, the regulatory functions of the BBC Trust were to be transferred to Ofcom.
The British Broadcasting Corporation (BBC) is a British public service broadcaster headquartered at Broadcasting House in London, England. Originally established in 1922 as the British Broadcasting Company, it evolved into its current state with its current name on New Year's Day 1927. The oldest and largest local and global broadcaster by stature and by number of employees, the BBC employs over 21,000 staff in total, of whom approximately 17,900 are in public-sector broadcasting.
The BBC Academy is an educational arm of the British Broadcasting Corporation which trains current and prospective broadcasting employees in the skills of the Broadcasting industry, in addition to training the corporation's own staff and prospects. A subsidiary of the academy, the BBC College of Journalism, functions as a free e-learning, online course series for all licence-fee payers.

The 2010 pension reform strikes in France were a series of general strikes and demonstrations which occurred in France throughout September and October 2010.

The Fight for $15 is an American political movement advocating for the minimum wage to be raised to USD$15 per hour. The federal minimum wage was last set at $7.25 per hour in 2009. The movement has involved strikes by child care, home healthcare, airport, gas station, convenience store, and fast food workers for increased wages and the right to form a labor union. The "Fight for $15" movement started in 2012, in response to workers' inability to cover their costs on such a low salary, as well as the stressful work conditions of many of the service jobs which pay the minimum wage.
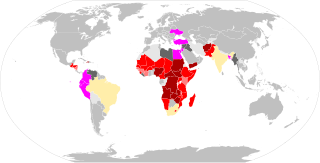
During the COVID-19 pandemic, food insecurity has intensified in many places – in the second quarter of 2020 there were multiple warnings of famine later in the year. In an early report, the Nongovernmental Organization (NGO) Oxfam-International talks about "economic devastation" while the lead-author of the UNU-WIDER report compared COVID-19 to a "poverty tsunami". Others talk about "complete destitution", "unprecedented crisis", "natural disaster", "threat of catastrophic global famine". The decision of WHO on March 11, 2020, to qualify COVID as a pandemic, that is "an epidemic occurring worldwide, or over a very wide area, crossing international boundaries and usually affecting a large number of people" also contributed to building this global-scale disaster narrative.
The economic impact of the global COVID-19 pandemic on the United Kingdom has been largely disruptive. It has adversely affected travel, financial markets, employment, a number of industries, and shipping.
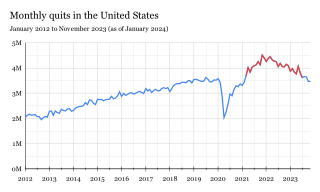
The Great Resignation, also known as the Big Quit and the Great Reshuffle, was a mainly American economic trend in which employees voluntarily resigned from their jobs en masse, beginning in early 2021 in the wake of the COVID-19 pandemic. Among the most cited reasons for resigning included wage stagnation amid rising cost of living, limited opportunities for career advancement, hostile work environments, lack of benefits, inflexible remote-work policies, and long-lasting job dissatisfaction. Most likely to quit were workers in hospitality, healthcare, and education.
Since late 2021, the prices for many essential goods in the United Kingdom began increasing faster than household incomes, resulting in a fall in real incomes. This is caused in part by a rise in inflation in both the UK and the world in general, as well as the economic impact of issues such as the COVID-19 pandemic, Russia's invasion of Ukraine, and Brexit. While all in the UK are affected by rising prices, it most substantially affects low-income persons. The British government has responded in various ways such as grants, tax rebates, and subsidies to electricity and gas suppliers.
The 2022–2024 United Kingdom railway strikes are an industrial dispute in the United Kingdom (UK). The UK has seen its largest incidence of industrial action since 1989, beginning in the second Johnson ministry and continuing through the Truss ministry and Sunak ministry. The railway strikes commenced on 21 June 2022 after members of the National Union of Rail, Maritime and Transport Workers (RMT) walked out over wages, planned changes to working practices – involving the removal of guards from trains, the reduction in the number of open ticket offices, and an increase in the age at which people could claim the young persons and senior citizen card – and the threat of redundancies. The disputes in Scotland and Wales were resolved by the RMT in December 2022, and by ASLEF in May 2023. In much of England the RMT dispute was resolved in November 2023. As of January 2024, the RMT dispute remains active in London, while the ASLEF dispute is active across all of England.

Starting in May 2022, postal workers in the United Kingdom undertook a series of strikes and industrial disputes. They principally involved members of Unite and the Communication Workers Union (CWU) at both Royal Mail and the Post Office. The Royal Mail strikes ended in July 2023 after workers agreed to a three-year pay deal with Royal Mail.











