| |||||
| Decades: | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| See also: | |||||
The following lists events that happened during 2006 in Algeria.
| |||||
| Decades: | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| See also: | |||||
The following lists events that happened during 2006 in Algeria.

The president of the People's Democratic Republic of Algeria is the head of state and chief executive of Algeria, as well as the commander-in-chief of the Algerian People's National Armed Forces.

Abdelaziz Bouteflika was an Algerian politician and diplomat who served as the seventh president of Algeria from 1999 to his resignation in 2019.

The Movement of Society for Peace, sometimes known by its shortened form Hamas, is a Sunni Islamist party in Algeria, led by Mahfoud Nahnah until his death in 2003. Its current leader is Abderrazak Makri. It is an offshoot of the Muslim Brotherhood.

Abdelaziz Belkhadem is an Algerian politician who was Prime Minister of Algeria from 2006 to 2008. He was also Secretary-General of the National Liberation Front (FLN). Belkhadem served as Minister of Foreign Affairs from 2000 to 2005 and Personal Representative of President Abdelaziz Bouteflika from 2005 to 2006; after serving as Prime Minister from 2006 to 2008, he was again appointed as Personal Representative of the Head of State in 2008.

Mohamed Abdelaziz was the 3rd Secretary General of the Polisario Front, from 1976, and the 1st President of the Sahrawi Arab Democratic Republic from 1982, until his death in 2016.

Hassan Hattab, also known as Abu Hamza, is the founder and first leader of the Algerian Jihadist rebel group Salafist Group for Preaching and Combat (GSPC) from 1998 to 2003.
The Charter for Peace and National Reconciliation was a charter proposed by Algerian President Abdelaziz Bouteflika, in an attempt to bring closure to the Algerian Civil War by offering an amnesty for most violence committed in it. The referendum on it was held on September 29, 2005, passing with 97%, and the charter was implemented as law on February 28, 2006.
Ali Benhadj is an Algerian Islamist activist and preacher and cofounder of the Islamic Salvation Front (FIS) political party, the winner of the June 1990 local elections and the 1991 Algerian legislative election.
Abdelhak Layada, also known as Abu Adlane, is one of the founders of Algeria's militant Islamist group Armed Islamic Group (GIA) during the Algerian Civil War. He led the group after the death of Mohamed Allel.
The working conditions of journalists in Algeria have evolved since the 1962 independence. After 1990, the Code of Press was suppressed, allowing for greater freedom of press. However, with the civil war in the 1990s, more than 70 journalists were assassinated by terrorists. Sixty journalists were killed between 1993 and 1998 in Algeria.

The 2000s in Algeria emerged from the 'Black Decade' of the 1990s. The 'Black Decade' was characterised by a civil war beginning in 1991 and ending at the beginning of the following decade in 2002. President Abdelaziz Bouteflika, who is accredited with ending the civil war, continued to be in power throughout the 2000s following his election in 1999. Despite being in power for 20 years and being Algeria's longest running president, Bouteflika's politics have been widely opposed and contested, with accusations from the BBC “of widespread corruption and state repression”. In April 2019 Bouteflika officially resigned from his position as president after months of public protest and loss of the army's support. The 82 Year old President was widely considered unfit for the role after experiencing a stroke in 2013. His resignation was reported by the BBC to have been met with "huge celebrations".

Relations between Algeria and Pakistan are excellent. Pakistan was one of the first countries to recognize the Provisional Government of Algerian Republic and its mission was opened in Karachi, the then capital of Pakistan in 1958. Both sides have convergence of views on issues of international importance. Both countries have also been supporting each other in various multilateral forums including UN, OIC and NAM. Algeria has an embassy in Islamabad and Pakistan has an embassy in Algiers.

The 2005 Algerian national reconciliation referendum took place in Algeria on 29 September 2005. The referendum was held on a Charter for Peace and National Reconciliation which had been drawn up to try to bring closure to the Algerian Civil War. The official results showed an overwhelming vote in favour on a high turnout.

Algeria has an embassy in Kuala Lumpur, and Malaysia has an embassy in Algiers.
The following lists events that happened during 2014 in Algeria.

Abdelmadjid Tebboune is an Algerian politician currently serving as the President of Algeria since December 2019 and as Minister of Defence.
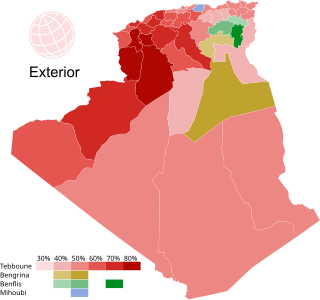
Presidential elections were held in Algeria on 12 December 2019. The election had originally been scheduled for 18 April, but was postponed due to sustained weekly protests against plans by the incumbent president Abdelaziz Bouteflika to run for a fifth term. Bouteflika resigned on 2 April and Abdelkader Bensalah was elected acting president by parliament a week later. On 10 April the election was rescheduled for 4 July. On 2 June the Constitutional Council postponed the elections again, citing a lack of candidates. A new electoral authority, Autorité nationale indépendante des élections (ANIE), was created in mid-September as an alternative to the existing Haute instance indépendante de surveillance des élections (HIISE) defined by the 2016 constitution. The election was rescheduled for 12 December 2019 and ANIE, of disputed constitutional validity, announced five valid candidates on 2 November. In their 200000 strong protest on 1 November, Algerian protestors rejected the 12 December election and called for a radical change in the system to take place first. The Forces of the Democratic Alternative (FDA) alliance and the Justice and Development Front also called for boycotting the 12 December election, and the FDA called for creating a constituent assembly.
Events from 2019 in Algeria.

Abdelaziz Djerad is an Algerian politician and diplomat who served as Prime Minister of Algeria from 28 December 2019 to 30 June 2021. In September 2021, he was appointed ambassador to Sweden.
Events from 2021 in Algeria.