| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
All 30 seats for the Babil Governorate council | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The Babil governorate election of 2009 was held on 31 January 2009 alongside elections for all other governorates outside Iraqi Kurdistan and Kirkuk.
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
All 30 seats for the Babil Governorate council | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The Babil governorate election of 2009 was held on 31 January 2009 alongside elections for all other governorates outside Iraqi Kurdistan and Kirkuk.
A candidate for the State of Law Coalition, Shaykh Haitham Kadhim al-Husaini was shot dead by gunmen who attacked his car when he left a campaign rally in Jabala district, a mixed Sunni-Shiite area where he lived. His wife and four children had been killed in a separate attack at their home two years previously. [1] He was one of eight candidates across Iraq who were killed during the campaign.
In March, the Iraqi National Dialogue Front said they would form an alliance with the State of Law Coalition. [2]
| Coalition | Allied national parties | Seats (2005) | Seats (2009) | Change | Votes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| State of Law Coalition | Islamic Dawa Party | - | 8 | +8 | 60,914 |
| Al Mihrab Martyr List | Islamic Supreme Council of Iraq | 25 | 5 | -20 | 40,365 |
| Independent Free Movement List | Sadrist Movement | - | 3 | +3 | 30,119 |
| National Reform Trend | - | 3 | +3 | 21,055 | |
| Iraqi Commission for Independent Civil Society Organizations | - | 3 | +3 | 19,875 | |
| Independent Justice Society | - | 3 | +3 | 17,683 | |
| Iraqi National List | - | 3 | +3 | 17,017 | |
| Independent al-Ansar Bloc | - | 2 | +2 | 16,493 | |
| Association of Imam Ali | 6 | - | -6 | ||
| Al-Rasul Association | 6 | - | -6 | ||
| Security and reconstruction | 2 | - | -2 | ||
| Babel Independent Association | 2 | - | -2 | 8,328 | |
| Other Parties | 256,009 | ||||
| Total | 41 | 30 | -11 | 487,858 | |
| Sources: this article - [3] | |||||
The politics of Iraq take place in a framework of a federal parliamentary representative democratic republic. It is a multi-party system whereby the executive power is exercised by the Prime Minister of the Council of Ministers as the head of government, as well as the President of Iraq, and legislative power is vested in the Council of Representatives and the Federation Council.

Parliamentary elections were held in Iraq on 30 January 2005 to elect the new National Assembly, alongside governorate elections and a parliamentary election in Kurdistan Region. The 275-member legislature had been created under the Transitional Law during the international occupation. The newly elected body was given a mandate to write a new constitution and exercise legislative functions until the new constitution came into effect. The elections also led to the formation of the Iraqi Transitional Government.

The Council of Representatives is the unicameral legislature of the Republic of Iraq. As of 2020, it comprises 329 seats and meets in Baghdad inside the Green Zone.

Parliamentary elections were held in Iraq on 15 December 2005, following the approval of a new constitution in a referendum of 15 October.
The 2008 Nineveh campaign was a series of offensives and counter-attacks between insurgent and Coalition forces for control of the Nineveh Governorate in northern Iraq in early-to-mid-2008. Some fighting also occurred in the neighboring Kirkuk Governorate.

Governorate or provincial elections were held in Iraq on 31 January 2009, to replace the local councils in fourteen of the eighteen governorates of Iraq that were elected in the 2005 Iraqi governorate elections. 14,431 candidates, including 3,912 women, contested 440 seats. The candidates came from over 400 parties, 75% of which were newly formed.

Parliamentary elections were held in Iraq on 7 March 2010. The elections decided the 325 members of the Council of Representatives who would elect the prime minister and president. The elections resulted in a partial victory for the Iraqi National Movement, led by former Interim Prime Minister Ayad Allawi, which won 91 seats, making it the largest alliance in the Council. The State of Law Coalition, led by incumbent Prime Minister Nouri Al-Maliki, was the second largest grouping with 89 seats.
The Baghdad governorate election of 2009 was held on 31 January 2009 alongside elections for all other governorates outside Iraqi Kurdistan and Kirkuk.

The Diyala governorate election of 2009 was held on 31 January 2009 alongside elections for all other governorates outside Iraqi Kurdistan and Kirkuk.

The Nineveh Governorate election of 2009 was held on 31 January 2009 alongside elections for all other governorates outside Iraqi Kurdistan and Kirkuk Governorate.
The Saladin governorate election of 2009, was held on 31 January 2009 alongside elections for all other governorates outside Iraqi Kurdistan and Kirkuk Governorate.

The State of Law Coalition also known as Rule of Law Coalition is an Iraqi political coalition formed for the 2009 Iraqi governorate elections by the Prime Minister of Iraq at the time, Nouri al-Maliki, of the Islamic Dawa Party.
List of the Martyr al-Mehraab and the Independent Forces,, commonly known as the al-Mehraab Martyr List was a Shi'a Islamist, Iraqi political coalition formed for the 2009 Iraqi governorate elections by the Islamic Supreme Council of Iraq.

Governorate or provincial elections were held in Iraq on 20 April 2013, to replace the local councils in the governorates of Iraq that were elected in the Iraqi governorate elections of 2009. Elections took place in 12 of Iraq's 18 governorates. Elections didn't take place in the 3 governorates forming the Kurdistan Region or Kirkuk, Anbar, or Nineveh, meaning that a total of 378 provincial council seats were up for election.

The 2012–2013 Iraqi protests started on 21 December 2012 following a raid on the home of Sunni Finance Minister Rafi al-Issawi and the arrest of 10 of his bodyguards. Beginning in Fallujah, the protests afterwards spread throughout Sunni Arab parts of Iraq. The protests centered on the issue of the alleged sectarianism of Prime Minister Nouri al-Maliki. Pro-Maliki protests also took place throughout central and southern Iraq, where there is a Shia Arab majority. In April 2013, sectarian violence escalated after the 2013 Hawija clashes. The protests continued throughout 2013, and in December Maliki used security forces to forcefully close down the main protest camp in Ramadi, killing hundreds of civilian protesters in the process. Sunni groups, such as the Army of the Men of the Naqshbandi Order, took up arms in response, and joined forces with the General Military Council for Iraqi Revolutionaries (GMCIR), a militant group made up of former Ba'athists, to conduct a military campaign against the Iraqi government. The Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant (ISIL) would later grow out of this civil conflict, escalating into a full-scale war.
A wave of bombings and shootings across Iraq killed at least 75 people and injured more than 356 others on 15 April. The attacks came just days before the provincial elections which was held on 20 April.

Operation al-Shabah was launched in May 2013 by the Iraqi Army, with the stated aim of severing contact between the Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant and the al-Nusra Front in Syria by clearing militants from the border area with Syria and Jordan.

The 2013 Nineveh Governorate election in Iraq was held on 20 June with elections for the Al Anbar Governorate. Due to security problems, turnout was less than half that of the 2009 election. This election saw Sunni Arab parties lose a number of seats to minority parties.

Parliamentary elections were held in Iraq on 12 May 2018. The elections decided the 329 members of the Council of Representatives, the country's unicameral legislature, who in turn will elect the Iraqi President and Prime Minister. The Iraqi parliament ordered a manual recount of the results on 6 June 2018. On 10 June 2018, a storage site in Baghdad housing roughly half of the ballots from the May parliamentary election caught fire.
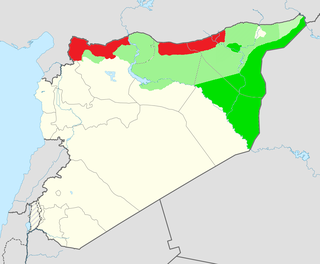
The Eastern Syria insurgency is an armed insurgency being waged by remnants of the Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant (ISIL) and both pro and anti-Syrian government Arab nationalist insurgents, against the Autonomous Administration of North and East Syria (AANES), its military, and their allies in the US-led Combined Joint Task Force – Operation Inherent Resolve (CJTF–OIR) coalition.