| History of Angola | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 | ||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||
| Post-war Angola’s | ||||||||||||||||
| See also | ||||||||||||||||
| Years in Angola | ||||||||||||||||
This is a list of events in 2010s in Angola :
| History of Angola | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 | ||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||
| Post-war Angola’s | ||||||||||||||||
| See also | ||||||||||||||||
| Years in Angola | ||||||||||||||||
This is a list of events in 2010s in Angola :

The current political regime in Angola is presidentialism, in which the President of the Republic is also head of state and government; it is advised by a Council of Ministers, which together with the President form the national executive power. Legislative power rests with the 220 parliamentarians elected to the National Assembly. The President of the Republic, together with the parliament, appoints the majority of the members of the two highest bodies of the judiciary, that is, the Constitutional Court and the Supreme Court. The judiciary is still made up of the Court of Auditors and the Supreme Military Court.
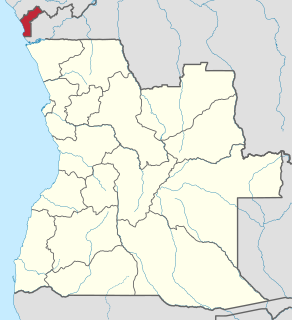
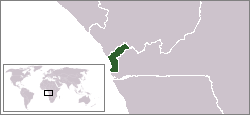
Cabinda is an exclave and province of Angola in Africa, a status that has been disputed by several political organizations in the territory. The capital city is also called Cabinda, known locally as Tchiowa, Tsiowa or Kiowa. The province is divided into four municipalities—Belize, Buco-Zau, Cabinda and Cacongo.

José Eduardo dos Santos was the president of Angola from 1979 to 2017. As president, dos Santos was also the commander-in-chief of the Angolan Armed Forces (FAA) and president of the People's Movement for the Liberation of Angola (MPLA), the party that has ruled Angola since it won independence in 1975. He was the second-longest-serving president in Africa, surpassed only by Teodoro Obiang Nguema Mbasogo of Equatorial Guinea.

The Front for the Liberation of the Enclave of Cabinda is a guerrilla and political movement fighting for the independence of the Angolan province of Cabinda. Formerly under Portuguese administration, with the independence of Angola from Portugal in 1975, the territory became an exclave province of the newly independent Angola. The FLEC fights the Cabinda War in the region occupied by the former kingdoms of Kakongo, Loango and N'Goyo.

The Togo national football team represents Togo in international football and is controlled by the Togolese Football Federation. The national football team of Togo made their debut in the FIFA World Cup in 2006. Their team bus underwent a fatal attack in Angola prior to the 2010 Africa Cup of Nations. They withdrew and were subsequently banned from the following two tournaments by the Confederation of African Football (CAF). In 2013 for the first time in history, Togo reached the quarter-finals of the Africa Cup of Nations. The team represents both FIFA and Confederation of African Football (CAF).
The Angolan Civil War was a civil war in Angola, beginning in 1975 and continuing, with interludes, until 2002. The war immediately began after Angola became independent from Portugal in November 1975. The war was a power struggle between two former anti-colonial guerrilla movements, the communist People's Movement for the Liberation of Angola (MPLA) and the turned anti-communist National Union for the Total Independence of Angola (UNITA). The war was used as a surrogate battleground for the Cold War by rival states such as the Soviet Union, Cuba, South Africa, and the United States.
Kodjovi Dodji Akanava Obilalé is a Togolese former footballer who played as a goalkeeper. His last club was the French amateur club GSI Pontivy. His career was cut short after he was severely injured in a bus attack against the Togolese team that took place in the Cabinda Province, Angola, just days before the start of the 2010 African Cup of Nations.

The 2010 Africa Cup of Nations, also known as the Orange Africa Cup of Nations for sponsorship reasons, was the 27th Africa Cup of Nations, the biennial football championship of Africa (CAF). It was held in Angola, where it began on 10 January 2010 and concluded on 31 January.

The Republic of Cabinda was an unrecognized state located in what is presently Angola's Cabinda Province. The Front for the Liberation of the State of Cabinda-Exército de Cabinda (FLEC) claims sovereignty from Angola and proclaimed the Republic of Cabinda as an independent country in 1975. The government of this entity operates in exile, with offices located in Paris, France, and Pointe Noire, Congo-Brazzaville.

Legislative elections were held in Angola on 5 and 6 September 2008, as announced by President José Eduardo dos Santos on 27 December 2007. They were the first since the 1992 general elections, which had led to the outbreak of the second phase of the Angolan Civil War, which continued until 2002.
The Alvor Agreement, signed on 15 January 1975 in Alvor, Portugal, granted Angola independence from Portugal on 11 November and formally ended the 13-year-long Angolan War of Independence.

Since its independence from Portugal in 1975, Angola has had three constitutions. The first came into force in 1975 as an "interim" measure; the second was approved in a 1992 referendum, and the third one was instituted in 2010.
Democratic Front of Cabinda is a separatist rebel group that fights for the independence of Cabinda province from Angola.

Henrique N'zita Tiago was President of the Armed Forces of Cabinda, a rebel group that fights for the independence of Cabinda from Angola. He died in Paris on 3 June 2016. It was reported that Tiago was 88 years old when he died, and that he was buried in France – as Cabinda was not independent at the time of his death.
In the 1990s in Angola, the last decade of the Angolan Civil War (1975–2002), the Angolan government transitioned from a nominally communist state to a nominally democratic one, a move made possible by political changes abroad and military victories at home. Namibia's declaration of independence, internationally recognized on April 1, eliminated the southwestern front of combat as South African forces withdrew to the east. The MPLA abolished the one-party system in June and rejected Marxist-Leninism at the MPLA's third Congress in December, formally changing the party's name from the MPLA-PT to the MPLA. The National Assembly passed law 12/91 in May 1991, coinciding with the withdrawal of the last Cuban troops, defining Angola as a "democratic state based on the rule of law" with a multi-party system.
The Togo national football team bus attack was a terrorist attack that occurred on 8 January 2010 as the Togo national football team traveled through the Angolan province of Cabinda on the way to the 2010 Africa Cup of Nations tournament, two days before it began. A little-known offshoot of the Front for the Liberation of the Enclave of Cabinda (FLEC), a group promoting independence for the province of Cabinda, known as the Front for the Liberation of the Enclave of Cabinda – Military Position (FLEC-PM), claimed responsibility for the attack. Bus driver Mário Adjoua, the team's assistant manager Améleté Abalo, and media officer Stanislas Ocloo were killed, with several others injured. Secretary General of the FLEC-PM Rodrigues Mingas, currently exiled in France, claimed the attack was not aimed at the Togolese players but at the Angolan forces at the head of the convoy. Authorities reported two suspects were detained in connection with the attacks.
Pascal Amélété Abalo Dosseh was the assistant coach of the Togo national football team and manager of ASKO Kara.
Rodrigues Mingas is the leader of the Front for the Liberation of the Enclave of Cabinda-Military Position, a guerrilla independence movement fighting since 1975 for the total independence of Cabinda, one of Angola's 14 provinces which is rich with oil reserves.

The Cabinda War is an ongoing separatist insurgency, waged by the Front for the Liberation of the Enclave of Cabinda (FLEC) against the government of Angola. FLEC aims at the restoration of the self-proclaimed Republic of Cabinda, located within the borders of the Cabinda province of Angola.

General elections were held in Angola on 31 August 2012 to elect the President and National Assembly. During campaigning, the opposition UNITA and its offshoot CASA-CE accused and criticised the government of corruption and called for greater transparency; this also led to protests and arrests the day before the election. These were the first elections after the new 2010 constitution was instituted.