Generally speaking, a calendar year begins on the New Year's Day of the given calendar system and ends on the day before the following New Year's Day, and thus consists of a whole number of days. A year can also be measured by starting on any other named day of the calendar, and ending on the day before this named day in the following year. This may be termed a "year's time", but not a "calendar year". To reconcile the calendar year with the astronomical cycle certain years contain extra days.
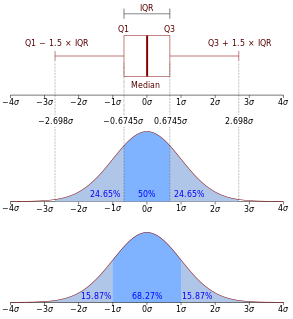
In descriptive statistics, the interquartile range (IQR), also called the midspread or middle 50%, or technically H-spread, is a measure of statistical dispersion, being equal to the difference between 75th and 25th percentiles, or between upper and lower quartiles, IQR = Q3 − Q1. In other words, the IQR is the first quartile subtracted from the third quartile; these quartiles can be clearly seen on a box plot on the data. It is a trimmed estimator, defined as the 25% trimmed range, and is a commonly used robust measure of scale.
RSA (Rivest–Shamir–Adleman) is one of the first public-key cryptosystems and is widely used for secure data transmission. In such a cryptosystem, the encryption key is public and it is different from the decryption key which is kept secret (private). In RSA, this asymmetry is based on the practical difficulty of the factorization of the product of two large prime numbers, the "factoring problem". The acronym RSA is made of the initial letters of the surnames of Ron Rivest, Adi Shamir, and Leonard Adleman, who first publicly described the algorithm in 1978. Clifford Cocks, an English mathematician working for the British intelligence agency Government Communications Headquarters (GCHQ), had developed an equivalent system in 1973, but this was not declassified until 1997.

Q fever is a disease caused by infection with Coxiella burnetii, a bacterium that affects humans and other animals. This organism is uncommon, but may be found in cattle, sheep, goats, and other domestic mammals, including cats and dogs. The infection results from inhalation of a spore-like small-cell variant, and from contact with the milk, urine, feces, vaginal mucus, or semen of infected animals. Rarely, the disease is tick-borne. The incubation period is 9–40 days. Humans are vulnerable to Q fever, and infection can result from even a few organisms. The bacterium is an obligate intracellular pathogenic parasite.
![Dead Sea Scrolls Ancient Jewish religious, mostly Hebrew, manuscripts found in the Qumran Caves in the West Bank] near the Dead Sea](https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d4/Flag_of_Israel.svg/320px-Flag_of_Israel.svg.png)
The Dead Sea Scrolls are ancient Jewish religious, mostly Hebrew, manuscripts found in the Qumran Caves in the West Bank near the Dead Sea. Scholarly consensus dates these scrolls from the last three centuries BCE and the first century CE. The texts have great historical, religious, and linguistic significance because they include the second-oldest known surviving manuscripts of works later included in the Hebrew Bible canon, along with deuterocanonical and extra-biblical manuscripts which preserve evidence of the diversity of religious thought in late Second Temple Judaism. Almost all of the Dead Sea Scrolls collection is currently under the ownership of the Government of the state of Israel, and housed in the Shrine of the Book on the grounds of the Israel Museum.

Capacitance is the ratio of the change in an electric charge in a system to the corresponding change in its electric potential. There are two closely related notions of capacitance: self capacitance and mutual capacitance. Any object that can be electrically charged exhibits self capacitance. A material with a large self capacitance holds more electric charge at a given voltage than one with low capacitance. The notion of mutual capacitance is particularly important for understanding the operations of the capacitor, one of the three elementary linear electronic components.
Q is a popular music magazine published monthly in the United Kingdom. It was founded in 1986 by the journalists and broadcasters Mark Ellen and David Hepworth, who were presenters of the BBC television music series Whistle Test.

Kamaal Ibn John Fareed, better known by his stage name Q-Tip, is an American rapper, record producer, singer, actor and DJ. Nicknamed The Abstract, he is noted for his innovative jazz-influenced style of hip hop production and his philosophical, esoteric and introspective lyrical themes. He embarked on his music career in the late 1980s, as an MC and main producer of the influential alternative hip hop group A Tribe Called Quest. In the mid-1990s, he co-founded the production team The Ummah, followed by the release of his gold-certified solo debut Amplified in 1999. In the 2000s, he released the Grammy Award-nominated album The Renaissance and the experimental album Kamaal the Abstract.

The DHC-8 Dash 8 is a series of turboprop-powered regional airliners, introduced by de Havilland Canada (DHC) in 1984. DHC was later bought by Boeing in 1988, then by Bombardier in 1992; the program is to be resold to Viking Air parent Longview Aviation Capital by late 2019. Powered by two Pratt & Whitney Canada PW100s, it was developed from the Dash 7 with improved cruise performance, lowered operational costs but worse STOL performance. Three sizes were offered: initially the 37-40 seat -100 until 2005 and the more powerful -200 from 1995, the stretched 50-56 seats -300 from 1989, both until 2009, and the 68-90 seats -400 from 1999, still in production. The Q Series are post-1997 variants with quieter cabins.

Avenue Q is a musical comedy featuring puppets and human actors with music and lyrics by Robert Lopez and Jeff Marx and book by Jeff Whitty. The show won Best Musical, Book, and Score at the 2004 Tony Awards. The show was directed by Jason Moore with puppets designed and built by original cast member Rick Lyon. Avenue Q has received many favorable reviews for its approach on topics like racism.

The Audi Q7 is a full-size luxury SUV made by the German manufacturer Audi, unveiled in September 2005 at the Frankfurt Motor Show. Production of this 7-seater SUV began in the autumn of 2005 at the Volkswagen Bratislava Plant in Bratislava, Slovakia. It was the first SUV offering from Audi and went on sale in 2006. Later, Audi's second SUV, the Q5, was unveiled as a 2009 model. Audi has since unveiled a third SUV model, the Q3, which went on sale in the 3rd quarter of 2011. The Q7 shares a Volkswagen Group MLB platform and chassis with the Bentley Bentayga, Lamborghini Urus, Porsche Cayenne and the Volkswagen Touareg

Electric potential energy, or electrostatic potential energy, is a potential energy that results from conservative Coulomb forces and is associated with the configuration of a particular set of point charges within a defined system. An object may have electric potential energy by virtue of two key elements: its own electric charge and its relative position to other electrically charged objects.
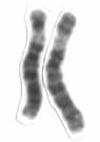
Chromosome 6 is one of the 23 pairs of chromosomes in humans. People normally have two copies of this chromosome. Chromosome 6 spans more than 170 million base pairs and represents between 5.5 and 6% of the total DNA in cells. It contains the Major Histocompatibility Complex, which contains over 100 genes related to the immune response, and plays a vital role in organ transplantation.
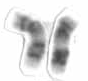
Chromosome 17 is one of the 23 pairs of chromosomes in humans. People normally have two copies of this chromosome. Chromosome 17 spans more than 83 million base pairs and represents between 2.5 and 3% of the total DNA in cells.
ICD-10 is an international statistical classification used in health care and related industries.

Margaret Denise Quigley, professionally known as Maggie Q, is an American actress, model, and animal rights activist. She is known for starring in the action films Mission: Impossible III and Live Free or Die Hard and played the title role of The CW's action-thriller series Nikita, airing from 2010 to 2013. In 2014, she portrayed Tori Wu in the film adaptation of Veronica Roth's novel Divergent, a role she reprised in its sequels, Insurgent and Allegiant. Currently, she stars in the role of FBI Agent Hannah Wells in the political drama Designated Survivor.

The Toyota iQ is a transverse engined, front-wheel-drive city car that was manufactured by Toyota and marketed in a single generation for Japan (2008–2016), Europe (2008–2015), and North America (2012–2015) where it was marketed as the Scion iQ. A rebadged variant was marketed in Europe as the Aston Martin Cygnet (2009–2013).

Coulomb's law, or Coulomb's inverse-square law, is a law of physics for quantifying Coulomb's force, or electrostatic force. Electrostatic force is the amount of force with which stationary, electrically charged particles either repel, or attract each other. This force and the law for quantifying it, represent one of the most basic forms of force used in the physical sciences, and were an essential basis to the study and development of the theory and field of classical electromagnetism. The law was first published in 1785 by French physicist Charles-Augustin de Coulomb.

C/2014 Q2 (Lovejoy) is a long-period comet discovered on 17 August 2014 by Terry Lovejoy using a 0.2-meter (8 in) Schmidt–Cassegrain telescope. It was discovered at apparent magnitude 15 in the southern constellation of Puppis. It is the fifth comet discovered by Terry Lovejoy. Its blue-green glow is the result of organic molecules and water released by the comet fluorescing under the intense UV and optical light of the Sun as it passes through space.






![Dead Sea Scrolls Ancient Jewish religious, mostly Hebrew, manuscripts found in the Qumran Caves in the West Bank] near the Dead Sea](https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d4/Flag_of_Israel.svg/320px-Flag_of_Israel.svg.png)









