
The demographic characteristics of the population of Bolivia are known from censuses, with the first census undertaken in 1826 and the most recent in 2024. The National Institute of Statistics of Bolivia (INE) has performed this task since 1950. The population of Bolivia in 2024 reached 11 million for the first time in history. The population density is 11.36 inhabitants per square kilometer, and the overall life expectancy in Bolivia at birth is 68.2 years. The population has steadily risen from the late 1800s to the present time. The natural growth rate of the population is positive, which has been a continuing trend since the 1950s; in 2012, Bolivia's birth rate continued to be higher than the death rate. Bolivia is in the third stage of demographic transition. In terms of age structure, the population is dominated by the 15–64 segment. The median age of the population is 23.1, and the gender ratio of the total population is 0.99 males per female.

Bolivia is a town in Brunswick County, North Carolina, United States. The population was 149 at the 2020 census. It is the county seat of Brunswick County.

Cochabamba, from Quechua qucha or qhucha, meaning "lake", pampa meaning "plain", is one of the nine departments of Bolivia. It is known to be the "granary" of the country because of its variety of agricultural products from its geographical position. It has an area of 55,631 km2. Its population in the 2024 census was 2,005,373. Its capital is the city of Cochabamba, known as the "City of Eternal Spring" and "The Garden City" because of its spring-like temperatures all year.

The La Paz Department of Bolivia comprises 133,985 square kilometres (51,732 sq mi) with a 2024 census population of 3,022,566 inhabitants. It is situated at the western border of Bolivia, sharing Lake Titicaca with the neighboring Peru. It contains the Cordillera Real mountain range, which reaches altitudes of 6.6 kilometers (22,000 ft). Northeast of the Cordillera Real are the Yungas, the steep eastern slopes of the Andes Mountains that make the transition to the Amazon River basin to the northeast. The capital of the department is the city of La Paz and is the administrative city and seat of government/national capital of Bolivia.

Abel Iturralde is one of the twenty provinces of the Bolivian La Paz Department. It is situated in its northern part. Its name honors Abel Iturralde Palacios, a Bolivian politician. Madidi National Park is partially in this province.

Aroma is one of the twenty provinces of the Bolivian La Paz Department. It is situated in the southern parts of the department. Its seat is Sica Sica.

Alonso de Ibáñez is a province in the northern parts of the Bolivian Potosí Department. Its capital is Sacaca.

Carangas is a province in the northern parts of the Bolivian department of Oruro.
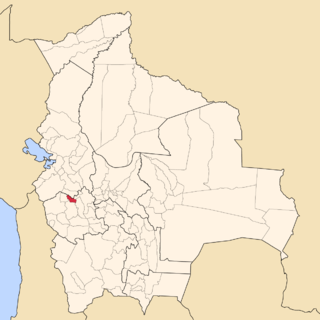
Nor Carangas is a province in the northern parts of the Bolivian department of Oruro. Its seat is Huayllamarca.
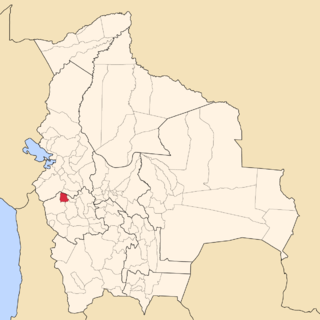
San Pedro de Totora is a province in the northern parts of the Bolivian department of Oruro.
Capinota is a small town in the Bolivian Department of Cochabamba and capital of the Capinota Province.

Ayopaya or Independencia is a town in the Cochabamba Department, Bolivia. It is the capital of the Ayopaya Province and Ayopaya Municipality. At the time of census 2001 it had a population of 2,014.

Punata is the capital of Punata Province and Punata Municipality in Cochabamba Department, Bolivia. At the time of census 2012 it had a population of 19,559 inhabitants and at the census 2012 the populations rose to 28.707 inhabitants. People from Punata and surrounding areas used to be called “Vallunos” meaning coming from the valleys of Punata and other surrounding small towns. Punata is renowned for its wonderful agricultural market held every Tuesday where people from surrounding towns and rural villages come to sell and buy.
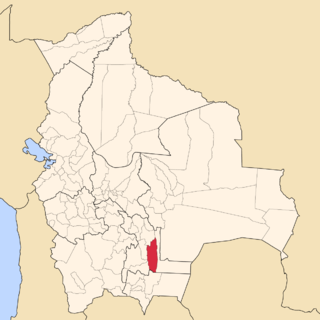
Hernando Siles is a province of the department of Chuquisaca, Bolivia. In the 2024 census it had a population of 31,688. It covers an area of 5,473 km², giving it a population density of 6.67/km². Its capital is Monteagudo.

Villa Tunari or Tunari is a location in the department of Cochabamba, Bolivia. It is the seat of the Villa Tunari Municipality, the third municipal section of the Chapare Province. According to the census 2012 the population was 3,213 in the town which is an increment from 2,510 registered during the 2001 census.

Ñuflo de Chávez is one of the fifteen provinces of the Bolivian Santa Cruz Department and is situated in the northern and central parts of the department. The name of the province honors the conquistador Ñuflo de Chaves (1518–1556) who founded the city of Santa Cruz de la Sierra. Its capital is Concepción. The province was created by law of September 16, 1915, during the presidency of Ismael Montes. Originally it was part of the Chiquitos Province.

Ignacio Warnes is one of the fifteen provinces of the Bolivian Santa Cruz Department and is situated in the department's central parts. The province name honors Colonel Ignacio Warnes (1772–1816), a military leader in the South American war of independence.

Manuel María Caballero Province is one of the fifteen provinces of the Bolivian Santa Cruz Department and is situated in the department's western parts. The province name honors deputy Manuel María Caballero from Vallegrande, one of the signatories of the Bolivian constitution of 5 August 1861.
Anzaldo is a location in the Cochabamba Department in central Bolivia. It is the seat of the Anzaldo Municipality, the second municipal section of the Esteban Arce Province.

Bolivians are people identified with the country of Bolivia. This connection may be residential, legal, historical or cultural. For most Bolivians, several of these connections exist and are collectively the source of their being Bolivian.


















