A cartridge or a round is a type of pre-assembled firearm ammunition packaging a projectile, a propellant substance and an ignition device (primer) within a metallic, paper, or plastic case that is precisely made to fit within the barrel chamber of a breechloading gun, for the practical purpose of convenient transportation and handling during shooting. Although in popular usage the term "bullet" is often informally used to refer to a complete cartridge, it is correctly used only to refer to the projectile.

A centerfire cartridge is a firearm metallic cartridge whose primer is located at the center of the base of its casing. Unlike rimfire cartridges, the centerfire primer is typically a separate component seated into a recessed cavity in the case head and is replaceable by reloading.

Rimfire ammunition is a type of firearm metallic cartridge whose primer is located within a hollow circumferential rim protruding from the base of its casing. When fired, the gun's firing pin will strike and crush the rim against the edge of the barrel breech, sparking the primer compound within the rim, and in turn ignite the propellant within the case. Invented in 1845, by Louis-Nicolas Flobert, the first rimfire metallic cartridge was the .22 BB Cap cartridge, which consisted of a percussion cap with a bullet attached to the top. While many other different cartridge priming methods have been tried since the 19th century, only rimfire and the later centerfire cartridges survive to the present day with regular usages. The .22 Long Rifle rimfire cartridge, introduced in 1887, is by far the most common ammunition in the world today in terms of units sold.

.32 ACP is a centerfire pistol cartridge. It is a semi-rimmed, straight-walled cartridge developed by firearms designer John Browning, initially for use in the FN M1900 semi-automatic pistol. It was introduced in 1899 by Fabrique Nationale, and is also known as the 7.65×17mmSR Browning or 7.65 mm Browning Short.

The .25 ACP (6.35×16mmSR) is a semi-rimmed, straight-walled centerfire pistol cartridge introduced by John Browning in 1905 alongside the Fabrique Nationale M1905 pistol.

The 2mm Kolibri was the smallest commercially available centerfire cartridge, patented in 1910 and introduced in 1914 by Franz Pfannl, an Austrian watchmaker, with financial support from Georg Grabner. It was designed to accompany the Kolibri semi-auto pistol or single-shot pistol, both marketed as self-defense weapons.

The HK4 is a pocket pistol, first introduced by Heckler & Koch in 1967. Government agencies received 12,000 pistols in the .32 ACP caliber with the designation P11 and were serial numbered 40001 to 52400.
The 9mm Winchester Magnum, which is also known as the 9×29mm, is a centerfire handgun cartridge developed by Winchester in the late 1970s. The cartridge was developed to duplicate the performance of the .357 S&W Magnum in an auto-pistol cartridge.

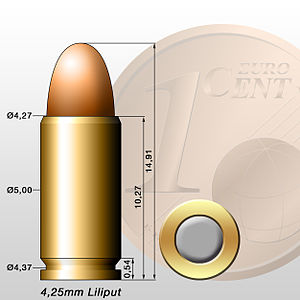
The 4.25 mm Liliput pistol is one of the smallest semiautomatic handguns ever made. Hence its name, derived from the fictional island of Lilliput, inhabited by tiny people.

A handgun is a firearm designed to be usable with only one hand. It is distinguished from a long gun which needs to be held by both hands and braced against the shoulder. The two most common types of handguns are revolvers and semi-automatic pistols, although other types such as derringers and machine pistols also see infrequent usage.
.22 caliber, or 5.6 mm caliber, refers to a common firearms bore diameter of 0.22 inch (5.6 mm).

The 5 mm Remington Rimfire Magnum or 5 mm RFM is a bottlenecked rimfire cartridge introduced by Remington Arms Company in 1969. Remington chambered it in a pair of bolt-action rifles, the Model 591 and Model 592, but this ammunition never became very popular, and the rifles were discontinued in 1974. About 52,000 rifles and 30,000 barrels for the T/C Contender pistol were sold during its brief production run. Remington discontinued the cartridge itself in 1982, leaving owners with no source of ammunition.
The .356 TSW is a centerfire pistol cartridge designed by Smith & Wesson in the early-1990s.
The 9×23mm Steyr, also known as 9mm Steyr, is a centerfire pistol cartridge originally developed for the Steyr M1912 pistol.

The 9mm Browning Long [9 x 20mm SR] is a military centerfire pistol cartridge developed in 1903 for the FN Model 1903 adopted by Belgium, France, Estonia, the Netherlands, and Sweden.

The 8mm Roth–Steyr is a military centerfire pistol cartridge adopted by the Austro-Hungarian cavalry in 1907 for the Repetierpistole M7—the first self-loading pistol adopted by a major military power. The cartridge headspaces on the mouth of the case. Ammunition was typically packaged in a unique ten-round charger. Austrian military production contained greased un-plated steel-jacketed bullets. A few private firms in Austria manufactured ammunition with cupro-nickel-jacketed bullets.
The .35 Smith & Wesson (S&W) is an obsolete centerfire pistol cartridge developed in 1912 for the newly designed Model 1913 self-loading pocket pistol.
The 7.65mm Roth–Sauer is a centerfire cartridge resembling a shortened .32 ACP. Two self-loading pocket pistols were designed for this cartridge. One was manufactured by Roth-Sauer of Germany, and the other by Frommer of Hungary.
The 5mm Clement is a centerfire cartridge produced for early self-loading pocket pistols made by Charola-Anitua and a 1903 design by Clement. The steeply conical, bottle-necked case is semi-rimmed, but headspaces on the shoulder of the case. The long bullet was inadequately stabilized and tended to tumble in flight. The Charola-Anitua pistol was produced in very limited numbers, and Clement pistol production shifted to the .25 ACP cartridge after 1906.

The .350 Legend, also called 350 LGND (9×43mm), is a SAAMI-standardized straight-walled intermediate rifle cartridge developed by Winchester Repeating Arms. The cartridge was designed for use in American states that have specific regulations for deer hunting with straight-walled centerfire cartridges. At the cartridge's introduction, Winchester claimed that the .350 Legend was the fastest production straight-walled hunting cartridge in the world, although some .450 Bushmaster .444 Marlin and .458 Winchester Magnum loads are faster and had lot more energy, and the .350 Legend would be surpassed in 2023 by the .360 Buckhammer. It is designed for deer hunting out to a maximum effective range of 250 yards (230 m).