Sources
| 1941 |
|
|---|---|
| 1942 | |
| 1943 | |
| 1944 | |
| 1945 | |
| Croatia | |
| Macedonia | |
| Serbia | |
| Slovenia | |
| Strategic bombing | |
The 5th Bosnian Corps (Serbo-Croatian Latin : Peti bosanski udarni korpus) was a Yugoslav Partisan corps that fought against the Germans, Independent State of Croatia (NDH) and Chetniks in occupied Democratic Federal Yugoslavia during World War II.
It was first created on 11 May 1943 as the 2nd Bosnian Corps from the 1st Bosnian Corps, together with the 5th Division. Virtually all units of the 1st Bosnian Corps were transferred to the 2nd Bosnian Corps including the 4th, 10th and 11th Krajina divisions for a total of around 7,500 soldiers. Its commander was Slavko Rodić and its Political Commissar Veljo Stojnić.
The 2nd Bosnian Corps was ordered to move to eastern Bosnia. Its adversary, the German 369th, 373rd, 114th and 7th SS divisions, together with NDH forces and local Chetniks had over 160,000 soldiers. This forced the 2nd Bosnian Corps to conduct guerrilla warfare and avoid open battles.
On 5 October 1943 the Corps was renamed the 5th (Bosnian) Corps. It kept fighting in Bosnia, carried out the Banja Luka operation, and in May 1944 helped resist the German Seventh Offensive around Drvar. In the final offensive in 1945, it participated in the final liberation of many places in western and central Bosnia.
In the last phase of the war the 5th Corps participated in the Sarajevo Operation attacking north of the city to cut off the escape routes of the German garrison. The mission was not completely successful as the bulk of the enemy forces managed to fall back to the north-west. But elements of the Corps were able to enter liberated Sarajevo, together with the other partisan formations of the 2nd and 3rd Corps.
The 5th Corps was disbanded on 22 April 1945 and its divisions were added to the 2nd Army.

Case White, also known as the Fourth Enemy Offensive, was a combined Axis strategic offensive launched against the Yugoslav Partisans throughout occupied Yugoslavia during World War II. It was one of the most significant confrontations of World War II in Yugoslavia. The offensive took place in early 1943, between 20 January and mid-to-late March. The Axis operation prompted the Partisan Supreme Command to enact its plans to drive toward eastern Herzegovina, Sandžak and Montenegro.

The Yugoslav Partisans, or the National Liberation Army, officially the National Liberation Army and Partisan Detachments of Yugoslavia, was the communist-led anti-fascist resistance to the Axis powers in occupied Yugoslavia during World War II. Led by Josip Broz Tito, the Partisans are considered to be Europe's most effective anti-Axis resistance movement during World War II.

The 13th Waffen Mountain Division of the SS Handschar was a mountain infantry division of the Waffen-SS, an armed branch of the German Nazi Party that served alongside but was never formally part of the Wehrmacht during World War II. At the post-war Nuremberg trials, the Waffen-SS was declared to be a criminal organisation due to its major involvement in war crimes and crimes against humanity. From March to December 1944, the division fought a counter-insurgency campaign against communist-led Yugoslav Partisan resistance forces in the Independent State of Croatia, a fascist puppet state of Germany that encompassed almost all of modern-day Croatia, all of modern-day Bosnia and Herzegovina and parts of Serbia.

Operation Southeast Croatia was a large-scale German-led counter-insurgency operation conducted in the southeastern parts of the Independent State of Croatia during World War II. It was the first of two German-led operations targeting mainly Yugoslav Partisans in eastern Bosnia between 15 January and 4 February 1942. Several days after the conclusion of Operation Southeast Croatia, a follow-up operation known as Operation Ozren was carried out between the Bosna and Spreča rivers. Both operations also involved Croatian Home Guard and Italian troops and are associated with what is known as the Second Enemy Offensive in post-war Yugoslav historiography. The Second Enemy Offensive forms part of the Seven Enemy Offensives framework in Yugoslav historiography.

Operation Trio was the first large-scale joint German-Italian counter-insurgency operation of World War II conducted in the Independent State of Croatia (NDH), which included modern-day Bosnia and Herzegovina. It was carried out in two phases within eastern Bosnia from 20 April to 13 May 1942, with Ustaše militia and Croatian Home Guard forces taking part on the Axis side. The aim of the operation was to target all insurgents between Sarajevo and the Drina river in eastern Bosnia. These included the communist-led Yugoslav Partisans and Serb nationalist Chetniks. Differentiating between the rank and file of the two insurgent factions was difficult, as even the communist-led insurgent groups consisted mainly of Serb peasants who had little understanding of the political aims of their leaders.
The Russian Protective Corps was an armed force composed of anti-communist White Russian émigrés that was raised in the German occupied territory of Serbia during World War II. Commanded for almost its whole existence by Lieutenant General Boris Shteifon, it served primarily as a guard force for factories and mines between late 1941 and early 1944, initially as the "Separate Russian Corps" then Russian Factory Protective Group. It was incorporated into the Wehrmacht on 1 December 1942 and later clashed with the communist-led Yugoslav Partisans and briefly with the Chetniks. In late 1944, it fought against the Red Army during the Belgrade Offensive, later withdrawing to Bosnia and Slovenia as the German forces retreated from Yugoslavia and Greece. After Shteifon′s death in Zagreb, the Independent State of Croatia, on 30 April 1945, Russian Colonel Anatoly Rogozhin took over and led his troops farther north to surrender to the British in southern Austria. Unlike most other Russian formations that fought for Nazi Germany, Rogozhin and his men, who were not formally treated as Soviet citizens, were exempt from forced repatriation to the Soviet Union and were eventually set free and allowed to resettle in the West.

World War II in the Kingdom of Yugoslavia began on 6 April 1941, when the country was invaded and swiftly conquered by Axis forces and partitioned among Germany, Italy, Hungary, Bulgaria and their client regimes. Shortly after Germany attacked the USSR on 22 June 1941, the communist-led republican Yugoslav Partisans, on orders from Moscow, launched a guerrilla liberation war fighting against the Axis forces and their locally established puppet regimes, including the Axis-allied Independent State of Croatia (NDH) and the Government of National Salvation in the German-occupied territory of Serbia. This was dubbed the National Liberation War and Socialist Revolution in post-war Yugoslav communist historiography. Simultaneously, a multi-side civil war was waged between the Yugoslav communist Partisans, the Serbian royalist Chetniks, the Axis-allied Croatian Ustaše and Home Guard, Serbian Volunteer Corps and State Guard, Slovene Home Guard, as well as Nazi-allied Russian Protective Corps troops.
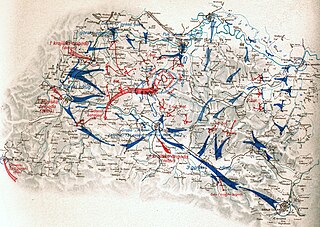
The Kozara Offensive, also known as Operation Ksaver was a large-scale German-led counter-insurgency operation against the Yugoslav Partisans in the Bosnian mountain region of Kozara in the Independent State of Croatia during World War II. It was launched on 10 June 1942, with the goal to encircle and destroy the Partisans who were operating in the Kozara mountain region near Banja Luka, which threatened German access to the Belgrade-Zagreb railway.

The Battle of Lijevče Field was fought between 30 March and 8 April 1945 between the Croatian Armed Forces and Chetnik forces on the Lijevče field near Banja Luka in what was then the Independent State of Croatia (NDH).

Dobroslav Jevđević was a Bosnian Serb politician and self-appointed Chetnik commander in the Herzegovina region of the Axis-occupied Kingdom of Yugoslavia during World War II. He was a member of the interwar Chetnik Association and the Organisation of Yugoslav Nationalists, a Yugoslav National Party member of the National Assembly, and a leader of the opposition to King Alexander between 1929 and 1934. The following year, he became the propaganda chief for the Yugoslav government.

Operation Alfa was an offensive carried out in early October 1942 by the military forces of Italy and the Axis puppet state, the Independent State of Croatia (NDH), supported by Chetnik forces under the control of vojvoda Ilija Trifunović-Birčanin. The offensive was directed against the communist-led Partisans in the Prozor region, then a part of the NDH. The operation was militarily inconclusive, and in the aftermath, Chetnik forces conducted mass killings of civilians in the area.

Pavle Đurišić was a Montenegrin Serb regular officer of the Royal Yugoslav Army who became a Chetnik commander (vojvoda) and led a significant proportion of the Chetniks in Montenegro during World War II. He distinguished himself and became one of the main commanders during the popular uprising against the Italians in Montenegro in July 1941, but later collaborated with the Italians in actions against the Communist-led Yugoslav Partisans. In 1943, his troops carried out several massacres against the Muslim population of Bosnia, Herzegovina, and the Sandžak in which an estimated 10,000 people were killed between January and March, including thousands of women, children, and the elderly. He then led his troops during their participation in the anti-Partisan Case White offensive alongside Italian forces. Đurišić was captured by the Germans in May 1943, escaped, and was recaptured.

The 369th (Croatian) Infantry Division was a legionary division of the German Army (Wehrmacht) during World War II.

The 373rd (Croatian) Infantry Division was a division of the German Army during World War II. It was formed in June 1943 using a brigade from the Home Guard of the Independent State of Croatia with the addition of a German cadre. The division was commanded by Germans down to battalion and even company level in nearly all cases, and was commonly referred to as a "legionnaire division". Originally formed with the intention of service on the Eastern Front, it was used instead for anti-Partisan operations in the territory of the NDH until the end of the war. It fought mainly in the western areas of the NDH, and was involved in the attempt to kill or capture the leader of the Partisans, Josip Broz Tito, in May 1944. Severely depleted by desertion, the division withdrew towards the Reich border in the early months of 1945, eventually surrendering to the Partisans on 10 May 1945 near Brežice in modern-day Slovenia.

Petar Baćović was a Bosnian Serb Chetnik commander within occupied Yugoslavia during World War II. From the summer of 1941 until April 1942, he headed the cabinet of the Ministry of Internal Affairs for Milan Nedić's puppet Government of National Salvation in the German-occupied territory of Serbia. In May and June 1942, Baćović participated in the joint Italian-Chetnik offensive against the Yugoslav Partisans in Montenegro. In July 1942, Baćović was appointed by the Chetnik leader Draža Mihailović and his Supreme Command as the commander of the Chetnik units in the regions of eastern Bosnia and Herzegovina within the Axis puppet state, the Independent State of Croatia. In this role, Baćović continued collaborating with the Italians against the Yugoslav Partisans, with his Chetniks formally recognised as Italian auxiliaries from mid-1942.

The battle of Knin was a major Yugoslav Partisan operation during World War II in Yugoslavia launched by the 8th Dalmatian Corps from 7 November to 9 December 1944 with the purpose of destroying German, Ustaše and Chetnik formations in North Dalmatia and the city of Knin, then part of the Independent State of Croatia. It was the final part of the 8th Corps offensive for the liberation of Dalmatia which began on 12 September 1944. The Knin operation had three phases: Initial battles on approaches to Knin from 7 November to 25 November, main battle and liberation of Knin from 26 November to 4 December, and final battles and pursuit of retreating Axis forces to Otrić in Lika from 5 December to 9 December.

The Partisan Long March was the redeployment of Josip Broz Tito's Partisan Supreme Headquarters and the major fighting elements of the Yugoslav Partisans across the Independent State of Croatia, from south-eastern to north-western Bosnia that commenced in late June 1942. The march followed the first large-scale joint German-Italian counter-insurgency operation in the NDH, Operation Trio, and the combined Italian-Montenegrin Chetnik offensive in Montenegro and eastern Herzegovina.
The Battle of Višegrad was the battle between Chetnik forces and Axis, and part of an Chetnik offensive in Eastern Bosnia in autumn of 1943, in Axis occupied Yugoslavia during World War II. The Chetnik forces of 2,500 captured Višegrad, destroyed big railway bridge across river Drina and continued their advances toward Rogatica and Sokolac. The German and Ustaše garrison in Višegrad and garrison that protected the bridge of total 1,100 soldiers had 350 dead and 400 wounded. The Chetniks had 21 dead and 30 wounded. In subsequent battle for Rogatica waged ten days later, the Chetniks captured Rogatica and killed more than 200 Axis soldiers.

The Sarajevo Operation was an operation by the Yugoslav Partisan Army which led to the liberation of Sarajevo and Central Bosnia in March-April 1945.

The 5th Krajina Division was a Yugoslav Partisan division formed in Glamočko polje on 9 November 1942.