
The 10th (Irish) Division, was one of the first of Kitchener's New Army K1 Army Group divisions, authorized on 21 August 1914, after the outbreak of the Great War. It included battalions from the various provinces of Ireland. It was led by Irish General Bryan Mahon and fought at Gallipoli, Salonika and Palestine. It was the first of the Irish Divisions to take to the field and was the most travelled of the Irish formations. The division served as a formation of the United Kingdom's British Army during World War I.

The 16th (Irish) Division was an infantry division of the British Army, raised for service during World War I. The division was a voluntary 'Service' formation of Lord Kitchener's New Armies, created in Ireland from the 'National Volunteers', initially in September 1914, after the outbreak of the Great War. In December 1915, the division moved to France, joining the British Expeditionary Force (BEF), under the command of Irish Major General William Hickie, and spent the duration of the war in action on the Western Front. Following enormous losses at the Somme, Passchendaele and Ypres, the 16th (Irish) Division required a substantial refit in England between June and August 1918, which involved the introduction of many non-Irish battalions.

The 19th (Western) Division was an infantry division of the British Army, part of Kitchener's Army, formed in the Great War.

The Italian front was one of the main theatres of war of World War I. It involved a series of military engagements in Northern Italy between the Central Powers and the Entente powers from 1915 to 1918. Following secret promises made by the Allies in the 1915 Treaty of London, the Kingdom of Italy entered the war on the Allied side, aiming to annex the Austrian Littoral, northern Dalmatia and the territories of present-day Trentino and South Tyrol.

The Allies, or the Entente, were an international military coalition of countries led by France, the United Kingdom, Russia, the United States, Italy, and Japan against the Central Powers of Germany, Austria-Hungary, the Ottoman Empire, and Bulgaria in World War I (1914–1918).

The Russian Caucasus Army of World War I was the Russian field army that fought in the Caucasus Campaign and Persian Campaign of World War I. It was renowned for inflicting heavy casualties on the opposing forces of the Ottoman Empire, particularly at the Battle of Sarikamish. It was also known for its extremely diverse ethnic composition, consisting of units from throughout the Russian Empire and both soldiers and officers from the many ethnic communities settled since the 1877-78 Russo-Turkish War in the militarily administered Kars Oblast in the Russian Transcaucasus. These included Georgians, Caucasus Greeks, and Armenians - the latter in particular strongly represented among both the soldiers and senior officers - as well as ethnic Russians and Ukrainians.

V Corps was an army corps of the British Army that saw service in both the First and the Second World Wars. It was first organised in February 1915 and fought through the First World War on the Western front. It was recreated in June 1940, during the Second World War and was substantially reorganised in 1942 for participation in Operation Torch. It fought through the Tunisia Campaign and later the Italian Campaign.

Dmitry Grigoryevich Shcherbachev was a general in the Russian Army during World War I and one of the leaders of the White Movement during the Russian Civil War.
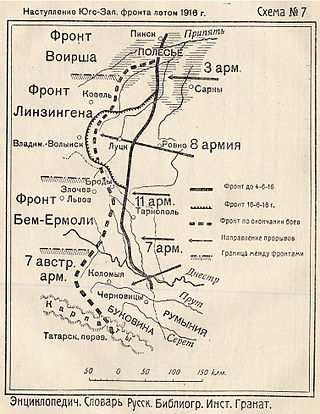
The Russian Third Army was a World War I Russian field army that fought on the Eastern theatre of war.

Vladimir Viktorovich Sakharov was a Russian general of the cavalry who served in the Russian Imperial Army. In an army career lasting from 1869 to 1917, he served in the Russo-Turkish War of 1877-1878, the Russo-Japanese War, and World War I.

The Southwestern Front was an army group of the Imperial Russian Army during World War I as part of the Eastern Front war theater.

Alexander Frantsevich Ragoza, also known as Oleksandr Frantsevych Rohoza, was a Russian general of the infantry during World War I, and Minister of Defense of the Ukrainian State.

The 10th Army was a field army of the Imperial Russian Army during the First World War.
The Russian 11th Army was a World War I Russian field army that fought on the Eastern theatre of war.

The Bavarian Cavalry Division was a unit of the Royal Bavarian Army, part of the German Army, in World War I. The division was formed on the mobilization of the German Army in August 1914. The division was disbanded in 1919, during the demobilization of the German Army after World War I. The division was raised and recruited in Bavaria.
The Russian 9th Army was a World War I Russian field army that fought on the Eastern theatre of war.
The 1st Don Cossack Division was a Don Cossack cavalry division of the Russian Imperial Army. It was part of the 19th Army Corps in the Warsaw Military District.
The 19th Army Corps was an Army corps in the Imperial Russian Army.

Vladimir Vasilyevich Smirnov was an Imperial Russian Army general of the infantry who was a division, corps and field army commander. He fought in the Russian-Turkish War of 1877–1878 and in World War I.

Vasily Egorovich Flug was an Imperial Russian Army General of the Infantry. A career military officer, he served in the Boxer Rebellion, Russo-Japanese War, and World War I, before joining the White movement during the Russian Civil War. Like many other officers, he went into exile after the end of the Russian Civil War, initially moving to Yugoslavia. After World War II, Flug went to the United States, where he died.















