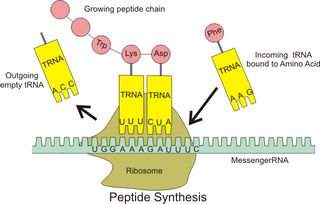
In molecular biology and genetics, translation is the process in which ribosomes in the cytoplasm or ER synthesize proteins after the process of transcription of DNA to RNA in the cell's nucleus. The entire process is called gene expression.

Guanosine-5'-triphosphate (GTP) is a purine nucleoside triphosphate. It is one of the building blocks needed for the synthesis of RNA during the transcription process. Its structure is similar to that of the guanine nucleobase, the only difference being that nucleotides like GTP have a ribose sugar and three phosphates, with the nucleobase attached to the 1' and the triphosphate moiety attached to the 5' carbons of the ribose.
DnaG is a bacterial DNA primase and is encoded by the dnaG gene. The enzyme DnaG, and any other DNA primase, synthesizes short strands of RNA known as oligonucleotides during DNA replication. These oligonucleotides are known as primers because they act as a starting point for DNA synthesis. DnaG catalyzes the synthesis of oligonucleotides that are 10 to 60 nucleotides long, however most of the oligonucleotides synthesized are 11 nucleotides. These RNA oligonucleotides serve as primers, or starting points, for DNA synthesis by bacterial DNA polymerase III. DnaG is important in bacterial DNA replication because DNA polymerase cannot initiate the synthesis of a DNA strand, but can only add nucleotides to a preexisting strand. DnaG synthesizes a single RNA primer at the origin of replication. This primer serves to prime leading strand DNA synthesis. For the other parental strand, the lagging strand, DnaG synthesizes an RNA primer every few kilobases (kb). These primers serve as substrates for the synthesis of Okazaki fragments.
Biosynthesis is a multi-step, enzyme-catalyzed process where substrates are converted into more complex products in living organisms. In biosynthesis, simple compounds are modified, converted into other compounds, or joined together to form macromolecules. This process often consists of metabolic pathways. Some of these biosynthetic pathways are located within a single cellular organelle, while others involve enzymes that are located within multiple cellular organelles. Examples of these biosynthetic pathways include the production of lipid membrane components and nucleotides. Biosynthesis is usually synonymous with anabolism.
The peptidyl transferase is an aminoacyltransferase as well as the primary enzymatic function of the ribosome, which forms peptide bonds between adjacent amino acids using tRNAs during the translation process of protein biosynthesis. The substrates for the peptidyl transferase reaction are two tRNA molecules, one bearing the growing peptide chain and the other bearing the amino acid that will be added to the chain. The peptidyl chain and the amino acids are attached to their respective tRNAs via ester bonds to the O atom at the CCA-3' ends of these tRNAs. Peptidyl transferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the addition of amino acid residue in order to grow polypeptide chain in protein synthesis. It is located in the large ribosomal subunit, where it catalyzes the peptide bond formation. It is composed entirely of RNA. The alignment between the CCA ends of the ribosome-bound peptidyl tRNA and aminoacyl tRNA in the peptidyl transferase center contribute to its ability to catalyze these reactions. This reaction occurs via nucleophilic displacement. The amino group of the aminoacyl tRNA attacks the terminal carboxyl group of the peptidyl tRNA. Peptidyl transferase activity is carried out by the ribosome. Peptidyl transferase activity is not mediated by any ribosomal proteins but by ribosomal RNA (rRNA), a ribozyme. Ribozymes are the only enzymes which are not made up of proteins, but ribonucleotides. All other enzymes are made up of proteins. This RNA relic is the most significant piece of evidence supporting the RNA World hypothesis.
Prokaryotic translation is the process by which messenger RNA is translated into proteins in prokaryotes.
Eukaryotic translation is the biological process by which messenger RNA is translated into proteins in eukaryotes. It consists of four phases: initiation, elongation, termination, and recycling.
Cross-linking immunoprecipitation, or CLIP, is a method used in molecular biology that combines UV cross-linking with immunoprecipitation in order to analyse protein interactions with RNA or to precisely locate RNA modifications. CLIP-based techniques can be used to map RNA binding protein binding sites or RNA modification sites of interest on a genome-wide scale, thereby increasing the understanding of post-transcriptional regulatory networks.

EF-Tu is a prokaryotic elongation factor responsible for catalyzing the binding of an aminoacyl-tRNA (aa-tRNA) to the ribosome. It is a G-protein, and facilitates the selection and binding of an aa-tRNA to the A-site of the ribosome. As a reflection of its crucial role in translation, EF-Tu is one of the most abundant and highly conserved proteins in prokaryotes. It is found in eukaryotic mitochrondria as TUFM.
Protein metabolism denotes the various biochemical processes responsible for the synthesis of proteins and amino acids (anabolism), and the breakdown of proteins by catabolism.

mRNA display is a display technique used for in vitro protein, and/or peptide evolution to create molecules that can bind to a desired target. The process results in translated peptides or proteins that are associated with their mRNA progenitor via a puromycin linkage. The complex then binds to an immobilized target in a selection step. The mRNA-protein fusions that bind well are then reverse transcribed to cDNA and their sequence amplified via a polymerase chain reaction. The result is a nucleotide sequence that encodes a peptide with high affinity for the molecule of interest.
Poly(A)-binding protein is a RNA-binding protein which binds to the poly(A) tail of mRNA. The poly(A) tail is located on the 3' end of mRNA and is 200-250 nucleotides long. The binding protein is also involved in mRNA precursors by helping polyadenylate polymerase add the poly(A) nucleotide tail to the pre-mRNA before translation. The nuclear isoform selectively binds to around 50 nucleotides and stimulates the activity of polyadenylate polymerase by increasing its affinity towards RNA. Poly(A)-binding protein is also present during stages of mRNA metabolism including nonsense-mediated decay and nucleocytoplasmic trafficking. The poly(A)-binding protein may also protect the tail from degradation and regulate mRNA production. Without these two proteins in-tandem, then the poly(A) tail would not be added and the RNA would degrade quickly.

The prokaryotic small ribosomal subunit, or 30S subunit, is the smaller subunit of the 70S ribosome found in prokaryotes. It is a complex of the 16S ribosomal RNA (rRNA) and 19 proteins. This complex is implicated in the binding of transfer RNA to messenger RNA (mRNA). The small subunit is responsible for the binding and the reading of the mRNA during translation. The small subunit, both the rRNA and its proteins, complexes with the large 50S subunit to form the 70S prokaryotic ribosome in prokaryotic cells. This 70S ribosome is then used to translate mRNA into proteins.
Transcription factor II B (TFIIB) is a general transcription factor that is involved in the formation of the RNA polymerase II preinitiation complex (PIC) and aids in stimulating transcription initiation. TFIIB is localised to the nucleus and provides a platform for PIC formation by binding and stabilising the DNA-TBP complex and by recruiting RNA polymerase II and other transcription factors. It is encoded by the TFIIB gene, and is homologous to both archaeal transcription factor B and more distantly to bacterial sigma factors

Insulin-like growth factor-binding protein 7 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the IGFBP7 gene. The major function of the protein is the regulation of availability of insulin-like growth factors (IGFs) in tissue as well as in modulating IGF binding to its receptors. IGFBP7 binds to IGF with high affinity. It also stimulates cell adhesion. The protein is implicated in some cancers.

In molecular biology, Tat is a protein that is encoded for by the tat gene in HIV-1. Tat is a regulatory protein that drastically enhances the efficiency of viral transcription. Tat stands for "Trans-Activator of Transcription". The protein consists of between 86 and 101 amino acids depending on the subtype. Tat vastly increases the level of transcription of the HIV dsDNA. Before Tat is present, a small number of RNA transcripts will be made, which allow the Tat protein to be produced. Tat then binds to cellular factors and mediates their phosphorylation, resulting in increased transcription of all HIV genes, providing a positive feedback cycle. This in turn allows HIV to have an explosive response once a threshold amount of Tat is produced, a useful tool for defeating the body's response.

Kasugamycin (Ksg) is an aminoglycoside antibiotic that was originally isolated in 1965, from Streptomyces kasugaensis, a Streptomyces strain found near the Kasuga shrine in Nara, Japan. Kasugamycin was discovered by Hamao Umezawa, who also discovered kanamycin and bleomycin, as a drug that prevent growth of a fungus causing rice blast disease. It was later found to inhibit bacterial growth also. It exists as a white, crystalline substance with the chemical formula C14H28ClN3O10 (kasugamycin hydrochloride). It is also known as kasumin.
The P-site is the second binding site for tRNA in the ribosome. The other two sites are the A-site (aminoacyl), which is the first binding site in the ribosome, and the E-site (exit), is the third and final binding site in the ribosome. During protein translation, the P-site holds the tRNA which is linked to the growing polypeptide chain. When a stop codon is reached, the peptidyl-tRNA bond of the tRNA located in the P-site is cleaved releasing the newly synthesized protein. During the translocation step of the elongation phase, the mRNA is advanced by one codon, coupled to movement of the tRNAs from the ribosomal A to P and P to E sites, catalyzed by elongation factor EF-G.