Related Research Articles

Von Willebrand factor (VWF) is a blood glycoprotein that promotes primary hemostasis, specifically, platelet adhesion. It is deficient and/or defective in von Willebrand disease and is involved in many other diseases, including thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura, Heyde's syndrome, and possibly hemolytic–uremic syndrome. Increased plasma levels in many cardiovascular, neoplastic, metabolic, and connective tissue diseases are presumed to arise from adverse changes to the endothelium, and may predict an increased risk of thrombosis.
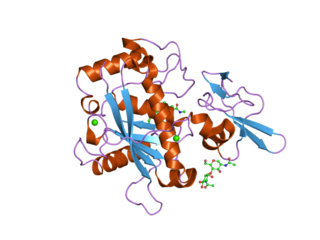
A disintegrin and metalloproteinase with thrombospondin motifs 5 also known as ADAMTS5 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ADAMTS5 gene.
Chromosome 21 is one of the 23 pairs of chromosomes in humans. Chromosome 21 is both the smallest human autosome and chromosome, with 46.7 million base pairs representing about 1.5 percent of the total DNA in cells. Most people have two copies of chromosome 21, while those with three copies of chromosome 21 have Down syndrome.

Chromosome 1 is the designation for the largest human chromosome. Humans have two copies of chromosome 1, as they do with all of the autosomes, which are the non-sex chromosomes. Chromosome 1 spans about 249 million nucleotide base pairs, which are the basic units of information for DNA. It represents about 8% of the total DNA in human cells.
Chromosome 2 is one of the twenty-three pairs of chromosomes in humans. People normally have two copies of this chromosome. Chromosome 2 is the second-largest human chromosome, spanning more than 242 million base pairs and representing almost eight percent of the total DNA in human cells.
Chromosome 3 is one of the 23 pairs of chromosomes in humans. People normally have two copies of this chromosome. Chromosome 3 spans more than 198 million base pairs and represents about 6.5 percent of the total DNA in cells.
Chromosome 4 is one of the 23 pairs of chromosomes in humans. People normally have two copies of this chromosome. Chromosome 4 spans more than 190 million base pairs and represents between 6 and 6.5 percent of the total DNA in cells.
Chromosome 9 is one of the 23 pairs of chromosomes in humans. Humans normally have two copies of this chromosome, as they normally do with all chromosomes. Chromosome 9 spans about 138 million base pairs of nucleic acids and represents between 4.0 and 4.5% of the total DNA in cells.
Chromosome 12 is one of the 23 pairs of chromosomes in humans. People normally have two copies of this chromosome. Chromosome 12 spans about 133 million base pairs and represents between 4 and 4.5 percent of the total DNA in cells.
Chromosome 17 is one of the 23 pairs of chromosomes in humans. People normally have two copies of this chromosome. Chromosome 17 spans more than 84 million base pairs and represents between 2.5 and 3% of the total DNA in cells.
A disintegrin and metalloproteinase with thrombospondin motifs 2 (ADAM-TS2) also known as procollagen I N-proteinase is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ADAMTS2 gene.

A disintegrin and metalloproteinase with thrombospondin motifs 4 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ADAMTS4 gene.

A disintegrin and metalloproteinase with thrombospondin motifs 1 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ADAMTS1 gene.
ADAMTS is a family of multidomain extracellular protease enzymes. 19 members of this family have been identified in humans, the first of which, ADAMTS1, was described in 1997. Known functions of the ADAMTS proteases include processing of procollagens and von Willebrand factor as well as cleavage of aggrecan, versican, brevican and neurocan, making them key remodeling enzymes of the extracellular matrix. They have been demonstrated to have important roles in connective tissue organization, coagulation, inflammation, arthritis, angiogenesis and cell migration. Homologous subfamily of ADAMTSL (ADAMTS-like) proteins, which lack enzymatic activity, has also been described. Most cases of thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura arise from autoantibody-mediated inhibition of ADAMTS13.

A disintegrin and metalloproteinase with thrombospondin motifs 8 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ADAMTS8 gene.

A disintegrin and metalloproteinase with thrombospondin motifs 9 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ADAMTS9 gene.

A disintegrin and metalloproteinase with thrombospondin motifs 3 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ADAMTS3 gene. The protein encoded by this gene is the major procollagen II N-propeptidase.

A disintegrin and metalloproteinase with thrombospondin motifs 12 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ADAMTS12 gene.

ADAM metallopeptidase with thrombospondin type 1 motif, 17 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ADAMTS17 gene.

ADAM metallopeptidase with thrombospondin type 1 motif 6 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ADAMTS6 gene.
References
- ↑ "ADAMTS14 ADAM metallopeptidase with thrombospondin type 1 motif 14 [Homo sapiens (human)] - Gene - NCBI". www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov. Retrieved 2022-05-19.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain .
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain . - ↑ "ADAMTS14 Gene - GeneCards | ATS14 Protein | ATS14 Antibody". www.genecards.org. Retrieved 2022-05-19.