Related Research Articles

A genetic disorder is a health problem caused by one or more abnormalities in the genome. It can be caused by a mutation in a single gene (monogenic) or multiple genes (polygenic) or by a chromosomal abnormality. Although polygenic disorders are the most common, the term is mostly used when discussing disorders with a single genetic cause, either in a gene or chromosome. The mutation responsible can occur spontaneously before embryonic development, or it can be inherited from two parents who are carriers of a faulty gene or from a parent with the disorder. When the genetic disorder is inherited from one or both parents, it is also classified as a hereditary disease. Some disorders are caused by a mutation on the X chromosome and have X-linked inheritance. Very few disorders are inherited on the Y chromosome or mitochondrial DNA.

Microcephaly is a medical condition involving a smaller-than-normal head. Microcephaly may be present at birth or it may develop in the first few years of life. Brain development is often affected; people with this disorder often have an intellectual disability, poor motor function, poor speech, abnormal facial features, seizures and dwarfism.

Ribonuclease H is a family of non-sequence-specific endonuclease enzymes that catalyze the cleavage of RNA in an RNA/DNA substrate via a hydrolytic mechanism. Members of the RNase H family can be found in nearly all organisms, from bacteria to archaea to eukaryotes.
Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM) is a continuously updated catalog of human genes and genetic disorders and traits, with a particular focus on the gene-phenotype relationship. As of 28 June 2019, approximately 9,000 of the over 25,000 entries in OMIM represented phenotypes; the rest represented genes, many of which were related to known phenotypes.
Aicardi syndrome is a rare genetic malformation syndrome characterized by the partial or complete absence of a key structure in the brain called the corpus callosum, the presence of retinal lacunes, and epileptic seizures in the form of infantile spasms. Other malformations of the brain and skeleton may also occur. The syndrome includes intellectual disability that is usually severe or moderate. So far, the syndrome has only been diagnosed in girls and in boys with two X chromosomes.
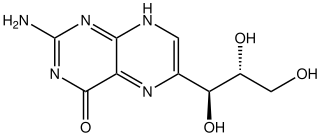
Neopterin is an organic compound belonging to the pteridine class of heterocyclic compounds.

T-box transcription factor TBX1 also known as T-box protein 1 and testis-specific T-box protein is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TBX1 gene. Genes in the T-box family are transcription factors that play important roles in the formation of tissues and organs during embryonic development. To carry out these roles, proteins made by this gene family bind to specific areas of DNA called T-box binding element (TBE) to control the expression of target genes.
Chromosome instability syndromes are a group of inherited conditions associated with chromosomal instability and breakage. They often lead to an increased tendency to develop certain types of malignancies.

X-linked dominant inheritance, sometimes referred to as X-linked dominance, is a mode of genetic inheritance by which a dominant gene is carried on the X chromosome. As an inheritance pattern, it is less common than the X-linked recessive type. In medicine, X-linked dominant inheritance indicates that a gene responsible for a genetic disorder is located on the X chromosome, and only one copy of the allele is sufficient to cause the disorder when inherited from a parent who has the disorder. In this case, someone who expresses an X-linked dominant allele will exhibit the disorder and be considered affected.

Zinc finger transcription factor Trps1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TRPS1 gene.

Three prime repair exonuclease 1 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the TREX1 gene.

Voltage-dependent calcium channel gamma-3 subunit is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CACNG3 gene.

SAM domain and HD domain-containing protein 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SAMHD1 gene. SAMHD1 is a cellular enzyme, responsible for blocking replication of HIV in dendritic cells, macrophages, monocytes and resting CD4+ T lymphocytes. It is an enzyme that exhibits phosphohydrolase activity, converting deoxynucleoside triphosphates (dNTPs) to inorganic phosphate (iPPP) and a 2'-deoxynucleoside (i.e. deoxynucleosides without a phosphate group). In doing so, SAMHD1 depletes the pool of dNTPs available to a reverse transcriptase for viral cDNA synthesis and thus prevents viral replication. SAMHD1 has also shown nuclease activity. Although a ribonuclease activity was described to be required for HIV-1 restriction, recent data confirmed that SAMHD1-mediated HIV-1 restriction in cells does not involve ribonuclease activity.

Acrocallosal syndrome is an extremely rare autosomal recessive syndrome characterized by corpus callosum agenesis, polydactyly, multiple dysmorphic features, motor and intellectual disabilities, and other symptoms. The syndrome was first described by Albert Schinzel in 1979. Mutations in KIF7 are causative for ACLS, and mutations in GLI3 are associated with a similar syndrome.
Oculocerebrocutaneous syndrome is a condition characterized by orbital cysts, microphthalmia, porencephaly, agenesis of the corpus callosum, and facial skin tags.

Ribonuclease H2 subunit A, also known as RNase H2 subunit A, is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the RNASEH2A gene.
Ribonuclease H2, subunit B is a protein that in humans is encoded by the RNASEH2B gene. RNase H2 is composed of a single catalytic subunit (A) and two non-catalytic subunits, and degrades the RNA of RNA:DNA hybrids. The non-catalytic B subunit of RNase H2 is thought to play a role in DNA replication.
Benign familial infantile epilepsy (BFIE) is an epilepsy syndrome. Affected children, who have no other health or developmental problems, develop seizures during infancy. These seizures have focal origin within the brain but may then spread to become generalised seizures. The seizures may occur several times a day, often grouped in clusters over one to three days followed by a gap of one to three months. Treatment with anticonvulsant drugs is not necessary but they are often prescribed and are effective at controlling the seizures. This form of epilepsy resolves after one or two years, and appears to be completely benign. The EEG of these children, between seizures, is normal. The brain appears normal on MRI scan.

Aicardi–Goutières syndrome (AGS), which is completely distinct from the similarly named Aicardi syndrome, is a rare, usually early onset childhood, inflammatory disorder most typically affecting the brain and the skin. The majority of affected individuals experience significant intellectual and physical problems, although this is not always the case. The clinical features of AGS can mimic those of in utero acquired infection, and some characteristics of the condition also overlap with the autoimmune disease systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). Following an original description of eight cases in 1984, the condition was first referred to as 'Aicardi–Goutières syndrome' (AGS) in 1992, and the first international meeting on AGS was held in Pavia, Italy, in 2001.

Ribonuclease H2 subunit C is a protein that in humans is encoded by the RNASEH2C gene. RNase H2 is composed of a single catalytic subunit (A) and two non-catalytic subunits, and degrades the RNA of RNA:DNA hybrids.
References
- ↑ "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ↑ "Entrez Gene: Aicardi syndrome" . Retrieved 2018-03-04.