Related Research Articles

A cruise missile is a guided missile used against terrestrial or naval targets, that remains in the atmosphere and flies the major portion of its flight path at an approximately constant speed. Cruise missiles are designed to deliver a large warhead over long distances with high precision. Modern cruise missiles are capable of traveling at high subsonic, supersonic, or hypersonic speeds, are self-navigating, and are able to fly on a non-ballistic, extremely low-altitude trajectory.

The Kh-55 is a Soviet/Russian subsonic air-launched cruise missile, designed by MKB Raduga in the 1970s. It has a range of up to 2,500 km (1,350 nmi) and can carry nuclear warheads. Kh-55 is launched exclusively from bomber aircraft and has spawned a number of conventionally armed variants mainly for tactical use, such as the Kh-65SE and Kh-SD, but only the Kh-101 and Kh-555 appear to have been put into service. Contrary to popular belief, the Kh-55 was not the basis of the submarine and ground-launched S-10 Granat or RK-55 Relief designed by NPO Novator. The RK-55 is very similar to the air-launched Kh-55 but the Kh-55 has a drop-down turbofan engine and was designed by MKB Raduga.

The S-125 Neva/Pechora is a Soviet surface-to-air missile system that was designed by Aleksei Isaev to complement the S-25 and S-75. It has a shorter effective range and lower engagement altitude than either of its predecessors and also flies slower, but due to its two-stage design it is more effective against more maneuverable targets. It is also able to engage lower flying targets than the previous systems, and being more modern it is much more resistant to ECM than the S-75. The 5V24 (V-600) missiles reach around Mach 3 to 3.5 in flight, both stages powered by solid fuel rocket motors. The S-125, like the S-75, uses radio command guidance. The naval version of this system has the NATO reporting name SA-N-1 Goa and original designation M-1 Volna.

The S-400 Triumf, previously known as the S-300 PMU-3, is a mobile surface-to-air missile (SAM) system developed in the 1990s by Russia's NPO Almaz as an upgrade to the S-300 family of missiles. The S-400 was approved for service on 28 April 2007 and the first battalion of the systems assumed combat duty on 6 August 2007.

The Babur, is an all-weather, subsonic cruise missile developed and designed by the National Defence Complex (NDC) of Pakistan.

The P-800 Oniks, marketed in export as the Yakhont, is a Soviet / Russian supersonic anti-ship cruise missile developed by NPO Mashinostroyeniya as a ramjet version of P-80 Zubr. Its GRAU designation is 3M55, the air launched Kh-61 variant also exists. The missile has the NATO codename SS-N-26 "Strobile". Development commenced in 1983, and in the 1990s the anti-ship missile was tested on the Project 1234.7 ship. In 2002 the missile passed the whole range of trials and was commissioned. It is reportedly a replacement for the P-270 Moskit, and possibly also of the P-700 Granit.

The 9K720 Iskander is a mobile short-range ballistic missile system produced and deployed by the Russian military. They travel at a terminal hypersonic speed of 2100–2600 m/s and can reach an altitude of 50 km as they range up to 500 km. The missile systems (Искандер-М) were intended to replace by 2020 the supposedly-obsolete OTR-21 Tochka systems in the Russian military.

The Russian Naval Aviation is the air arm of the Russian Navy, a successor of Soviet Naval Aviation. The Russian Navy is divided into four fleets and one flotilla: Northern Fleet, Pacific Fleet, Baltic Fleet, Black Sea Fleet, and Caspian Flotilla.

The Novator Kalibr, also referred to as 3M54-1 Kalibr, 3M14 Biryuza, is a family of Russian cruise missiles developed by NPO Novator (OKB-8). It first saw service in 1994. There are ship-launched, submarine-launched and air-launched versions of the missile, and variants for anti-ship, anti-submarine and land attack use. Some versions have a second propulsion stage that initiates a supersonic sprint in the terminal approach to the target, reducing the time that air defense systems have to react, while subsonic versions have greater range than the supersonic variants. The missile can carry a warhead weighing up to 500 kilograms (1,100 lb) of explosive or a thermonuclear warhead.

The RS-24 Yars - modification 24) also known as RT-24 Yars or Topol'-MR is a Russian MIRV-equipped, thermonuclear armed intercontinental ballistic missile first tested on May 29, 2007, after a secret military R&D project.

Hermes is a family of modularly designed guided missiles developed in Russia by the KBP Instrument Design Bureau.

The Tornado is a family of related multiple rocket launchers developed by NPO Splav for the Russian Ground Forces. Variants of the system, which include the Tornado-G and Tornado-S models, have different capabilities and different battlefield roles. The Tornado is designed primarily to fire cluster munitions but also can be used to fire thermobaric warheads.

The Ra'ad, is a subsonic, standoff, and an air-launched cruise missile (ALCM) designed and jointly developed by the National Engineering & Scientific Commission (NESCOM) and Pakistan Air Force's Air Weapons Complex.
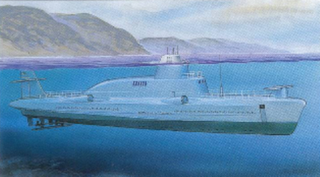
Project 1231 was a hybrid surface combatant and submarine developed in the Soviet Union in the 1960s. It was known as "Dolphin" and "diving missile boat", and represented a fundamentally new type of ship. It was a missile boat, with a considerable surface speed, yet able to dive and move underwater.

The 2S35 Koalitsiya-SV is a Russian self-propelled gun first seen in public in 2015 during rehearsals for the Moscow Victory Day Parade. The 2S35 is expected to supplement and eventually replace the 2S19 Msta in the Russian Ground Forces.

The Avangard is a Russian hypersonic glide vehicle (HGV) that can be carried as a MIRV payload by the UR-100UTTKh, R-36M2 and RS-28 Sarmat heavy ICBMs. It can deliver both nuclear and conventional payloads.

The Nebo-SVU is a very high frequency multi-functional radar and first radar with an active electronically scanned array antenna operating in the metric wavelength. The radar was introduced in 2001 as a replacement for Nebo-SV. It can locate aircraft or other flying object with 0.1 m2 radar cross-section at 100 km (62 mi).
References
- ↑ "Государственный военно-промышленный комитет Республики Беларусь". www.vpk.gov.by. Archived from the original on 2015-12-08. Retrieved 2015-12-03.
- ↑ Gromovsergey3wrote, 2015-11-20 14:37:00 Gromovsergey3 Gromovsergey3 2015-11-20 14:37:00. "Как Украина меняет ракеты на трактора или ОПК поборется за белорусский рынок ракетных технологий". Archived from the original on 2015-12-01. Retrieved 2015-12-03.
- ↑ "У Белоруссии будут ракеты с Россией или без нее | БОРТОВОЙ ЖУРНАЛ". flanker.su. Retrieved 2015-12-03.
- ↑ "НЕВСКИЙ БАСТИОН, ВОЕННО-ТЕХНИЧЕСКИЙ СБОРНИК, ВООРУЖЕНИЯ, ВОЕННАЯ ТЕХНИКА, ВОЕННО-ТЕХНИЧЕСКИЙ СБОРНИК, СОВРЕМЕННОЕ СОСТОЯНИЕ, ИСТОРИЯ РАЗВИТИЯ ОПК, БАСТИОН ВТС, НЕВСКИЙ БАСТИОН, ЖУРНАЛ, СБОРНИК, ВПК, АРМИИ, ВЫСТАВКИ, САЛОНЫ, ВОЕННО-ТЕХНИЧЕСКИЕ, НОВОСТИ, ПОСЛЕДНИЕ НОВОСТИ, ВОЕННЫЕ НОВОСТИ, СОБЫТИЯ ФАКТЫ ВПК, НОВОСТИ ОПК, ОБОРОННАЯ ПРОМЫШЛЕННОСТЬ, МИНИСТРЕСТВО ОБОРОНЫ, СИЛОВЫХ СТРУКТУР, КРАСНАЯ АРМИЯ, СОВЕТСКАЯ АРМИЯ, РУССКАЯ АРМИЯ, ЗАРУБЕЖНЫЕ ВОЕННЫЕ НОВОСТИ, ВиВТ, ПВН". nevskii-bastion.ru. Retrieved 2015-12-03.