IEEE 802.15 is a working group of the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) IEEE 802 standards committee which specifies Wireless Specialty Networks (WSN) standards. The working group was formerly known as Working Group for Wireless Personal Area Networks.
Digital Imaging and Communications in Medicine (DICOM) is a technical standard for the digital storage and transmission of medical images and related information. It includes a file format definition, which specifies the structure of a DICOM file, as well as a network communication protocol that uses TCP/IP to communicate between systems. The primary purpose of the standard is to facilitate communication between the software and hardware entities involved in medical imaging, especially those that are created by different manufacturers. Entities that utilize DICOM files include components of picture archiving and communication systems (PACS), such as imaging machines (modalities), radiological information systems (RIS), scanners, printers, computing servers, and networking hardware.

IEEE 488, also known as HP-IB and generically as GPIB, is a short-range digital communications 8-bit parallel multi-master interface bus specification developed by Hewlett-Packard. It subsequently became the subject of several standards.
Zigbee is an IEEE 802.15.4-based specification for a suite of high-level communication protocols used to create personal area networks with small, low-power digital radios, such as for home automation, medical device data collection, and other low-power low-bandwidth needs, designed for small scale projects which need wireless connection. Hence, Zigbee is a low-power, low-data-rate, and close proximity wireless ad hoc network.

Power-line communication (PLC) is the carrying of data on a conductor that is also used simultaneously for AC electric power transmission or electric power distribution to consumers. The line that does so is known as a power-line carrier.
IEEE 802.15.4 is a technical standard that defines the operation of a low-rate wireless personal area network (LR-WPAN). It specifies the physical layer and media access control for LR-WPANs, and is maintained by the IEEE 802.15 working group, which defined the standard in 2003. It is the basis for the Zigbee, ISA100.11a, WirelessHART, MiWi, 6LoWPAN, Thread, Matter and SNAP specifications, each of which further extends the standard by developing the upper layers, which are not defined in IEEE 802.15.4. In particular, 6LoWPAN defines a binding for the IPv6 version of the Internet Protocol (IP) over WPANs, and is itself used by upper layers such as Thread.
BACnet is a communication protocol for building automation and control (BAC) networks that use the ASHRAE, ANSI, and ISO 16484-5 standards protocol.
A fieldbus is a member of a family of industrial digital communication networks used for real-time distributed control. Fieldbus profiles are standardized by the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) as IEC 61784/61158.

IEC 62056 is a set of standards for electricity metering data exchange by International Electrotechnical Commission. The IEC 62056 standards are the international standard versions of the DLMS/COSEM specification.
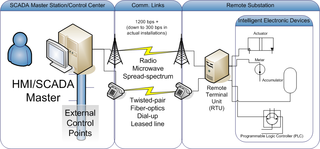
Distributed Network Protocol 3 (DNP3) is a set of communications protocols used between components in process automation systems. Its main use is in utilities such as electric and water companies. Usage in other industries is not common. It was developed for communications between various types of data acquisition and control equipment. It plays a crucial role in SCADA systems, where it is used by SCADA Master Stations, Remote Terminal Units (RTUs), and Intelligent Electronic Devices (IEDs). It is primarily used for communications between a master station and RTUs or IEDs. ICCP, the Inter-Control Center Communications Protocol, is used for inter-master station communications. Competing standards include the older Modbus protocol and the newer IEC 61850 protocol.
CEBus(r), short for Consumer Electronics Bus, also known as EIA-600, is a set of electrical standards and communication protocols for electronic devices to transmit commands and data. It is suitable for devices in households and offices to use, and might be useful for utility interface and light industrial applications.

A smart meter is an electronic device that records information—such as consumption of electric energy, voltage levels, current, and power factor—and communicates the information to the consumer and electricity suppliers. Such an advanced metering infrastructure (AMI) differs from automatic meter reading (AMR) in that it enables two-way communication between the meter and the supplier.
The Link Layer Discovery Protocol (LLDP) is a vendor-neutral link layer protocol used by network devices for advertising their identity, capabilities, and neighbors on a local area network based on IEEE 802 technology, principally wired Ethernet. The protocol is formally referred to by the IEEE as Station and Media Access Control Connectivity Discovery specified in IEEE 802.1AB with additional support in IEEE 802.3 section 6 clause 79.
IEEE 802.1AE is a network security standard that operates at the medium access control layer and defines connectionless data confidentiality and integrity for media access independent protocols. It is standardized by the IEEE 802.1 working group.
The National Transportation Communications for Intelligent Transportation System Protocol (NTCIP) is a family of standards designed to achieve interoperability and interchangeability between computers and electronic traffic control equipment from different manufacturers.
ANSI C12.22 is the American National Standard for Protocol Specification for Interfacing to Data Communication Networks
IEEE 1394 is an interface standard for a serial bus for high-speed communications and isochronous real-time data transfer. It was developed in the late 1980s and early 1990s by Apple in cooperation with a number of companies, primarily Sony and Panasonic. It is most commonly known by the name FireWire (Apple), though other brand names exist such as i.LINK (Sony), and Lynx.
ISO/IEEE 11073 Personal Health Device (PHD) standards are a group of standards addressing the interoperability of personal health devices (PHDs) such as weighing scales, blood pressure monitors, blood glucose monitors and the like. The standards draw upon earlier IEEE11073 standards work, but differ from this earlier work due to an emphasis on devices for personal use and a simpler communications model.
The Open Smart Grid Protocol (OSGP) is a family of specifications published by the European Telecommunications Standards Institute (ETSI) used in conjunction with the ISO/IEC 14908 control networking standard for smart grid applications. OSGP is optimized to provide reliable and efficient delivery of command and control information for smart meters, direct load control modules, solar panels, gateways, and other smart grid devices. With over 5 million OSGP based smart meters and devices deployed worldwide it is one of the most widely used smart meter and smart grid device networking standards.