Sustainable development is an approach to growth and human development that aims to meet the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs. The aim is to have a society where living conditions and resources meet human needs without undermining planetary integrity. Sustainable development aims to balance the needs of the economy, environment, and social well-being. The Brundtland Report in 1987 helped to make the concept of sustainable development better known.

Natural capital is the world's stock of natural resources, which includes geology, soils, air, water and all living organisms. Some natural capital assets provide people with free goods and services, often called ecosystem services. All of these underpin our economy and society, and thus make human life possible.
Green anarchism, also known as ecological anarchism or eco-anarchism, is an anarchist school of thought that focuses on ecology and environmental issues. It is an anti-capitalist and anti-authoritarian form of radical environmentalism, which emphasises social organization, freedom and self-fulfillment.

Bioregionalism is a philosophy that suggests that political, cultural, and economic systems are more sustainable and just if they are organized around naturally defined areas called bioregions, similar to ecoregions. Bioregions are defined through physical and environmental features, including watershed boundaries and soil and terrain characteristics. Bioregionalism stresses that the determination of a bioregion is also a cultural phenomenon, and emphasizes local populations, knowledge, and solutions.

Simple living refers to practices that promote simplicity in one's lifestyle. Common practices of simple living include reducing the number of possessions one owns, depending less on technology and services, and spending less money. In addition to such external changes, simple living also reflects a person's mindset and values. Simple living practices can be seen in history, religion, art, and economics.
Cultural ecology is the study of human adaptations to social and physical environments. Human adaptation refers to both biological and cultural processes that enable a population to survive and reproduce within a given or changing environment. This may be carried out diachronically, or synchronically. The central argument is that the natural environment, in small scale or subsistence societies dependent in part upon it, is a major contributor to social organization and other human institutions. In the academic realm, when combined with study of political economy, the study of economies as polities, it becomes political ecology, another academic subfield. It also helps interrogate historical events like the Easter Island Syndrome.

The Green Party, also known as the Green Party UK, was a Green political party in the United Kingdom.

Edward René David Goldsmith, widely known as Teddy Goldsmith, was an Anglo-French environmentalist, writer and philosopher.
Ecology is a new science and considered as an important branch of biological science, having only become prominent during the second half of the 20th century. Ecological thought is derivative of established currents in philosophy, particularly from ethics and politics.

Ecological restoration, or ecosystem restoration, is the process of assisting the recovery of an ecosystem that has been degraded, damaged, or destroyed. It is distinct from conservation in that it attempts to retroactively repair already damaged ecosystems rather than take preventative measures. Ecological restoration can reverse biodiversity loss, combat climate change, and support local economies.

Environmentalism or environmental rights is a broad philosophy, ideology, and social movement about supporting life, habitats, and surroundings. While environmentalism focuses more on the environmental and nature-related aspects of green ideology and politics, ecologism combines the ideology of social ecology and environmentalism. Ecologism is more commonly used in continental European languages, while environmentalism is more commonly used in English but the words have slightly different connotations.

Garrett James Hardin was an American ecologist and microbiologist. He focused his career on the issue of human overpopulation, and is best known for his exposition of the tragedy of the commons in a 1968 paper of the same title in Science, which called attention to "the damage that innocent actions by individuals can inflict on the environment". He is also known for Hardin's First Law of Human Ecology: "We can never do merely one thing. Any intrusion into nature has numerous effects, many of which are unpredictable."

The Ecologist was a British environmental journal/magazine, published from 1970 to 2009. Founded by Edward Goldsmith, it addressed a wide range of environmental subjects and promoted an ecological systems thinking approach through its news stories, investigations and opinion articles. The Ecologist encouraged its readers to tackle global issues on a local scale. After cessation of its print edition in July 2009, The Ecologist continued as an online magazine. In mid-2012, it merged with Resurgence magazine, edited by Satish Kumar, with the first issue of the new Resurgence & Ecologist appearing in print in September 2012. The Ecologist was based in London.
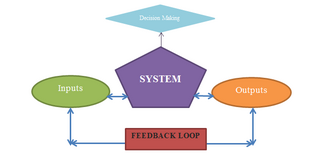
Regenerative design is an approach to designing systems or solutions that aims to work with or mimic natural ecosystem processes for returning energy from less usable to more usable forms. Regenerative design uses whole systems thinking to create resilient and equitable systems that integrate the needs of society with the integrity of nature. Regenerative design is an active topic of discussion in engineering, landscape design, food systems, and community development.
Degrowth is an academic and social movement critical of the concept of growth in gross domestic product as a measure of human and economic development. The idea of degrowth is based on ideas and research from economic anthropology, ecological economics, environmental sciences, and development studies. It argues that modern capitalism's unitary focus on growth causes widespread ecological damage and is unnecessary for the further increase of human living standards. Degrowth theory has been met with both academic acclaim and considerable criticism.
Deep ecology is an environmental philosophy that promotes the inherent worth of all living beings regardless of their instrumental utility to human needs, and argues that modern human societies should be restructured in accordance with such ideas.
Bron Raymond Taylor is an American scholar and conservationist. He is professor of religion and nature at the University of Florida and has also been an affiliated scholar with the Center for Environment and Development at the University of Oslo. Taylor works principally in the areas of religion and ecology, environmental ethics and environmental philosophy. He is also a prominent historian and ethnographer of environmentalism and especially radical environmentalist movements, surfing culture and nature-based spiritualities. Taylor is also editor-in-chief of the Encyclopedia of Religion and Nature and subsequently founded the International Society for the Study of Religion, Nature and Culture, serving as its president from 2006 to 2009. He also founded the society's affiliated Journal for the Study of Religion, Nature and Culture, serving as its editor since 2007.
Environmental theology pertains to "the God-environment relationship and divine expectations of human behavior in relation to the environment".

This Fissured Land: An Ecological History of India is a book by Madhav Gadgil and Ramachandra Guha on the ecological history of India. It examines 'prudent' (sustainable) and 'profligate' (unsustainable) use of natural resources, and their effects. It describes the ecological history of India, from the first humans, through the ages of hunter-gatherers, farmers, empires and the British Raj.

Philosophy of ecology is a concept under the philosophy of science, which is a subfield of philosophy. Its main concerns centre on the practice and application of ecology, its moral issues, and the intersectionality between the position of humans and other entities. This topic also overlaps with metaphysics, ontology, and epistemology, for example, as it attempts to answer metaphysical, epistemic and moral issues surrounding environmental ethics and public policy.












