
A valve is a device or natural object that regulates, directs or controls the flow of a fluid by opening, closing, or partially obstructing various passageways. Valves are technically fittings, but are usually discussed as a separate category. In an open valve, fluid flows in a direction from higher pressure to lower pressure. The word is derived from the Latin valva, the moving part of a door, in turn from volvere, to turn, roll.

An oil well is a drillhole boring in Earth that is designed to bring petroleum oil hydrocarbons to the surface. Usually some natural gas is released as associated petroleum gas along with the oil. A well that is designed to produce only gas may be termed a gas well. Wells are created by drilling down into an oil or gas reserve and if necessary equipped with extraction devices such as pumpjacks. Creating the wells can be an expensive process, costing at least hundreds of thousands of dollars, and costing much more when in difficult-to-access locations, e.g., offshore. The process of modern drilling for wells first started in the 19th century but was made more efficient with advances to oil drilling rigs and technology during the 20th century.
An expense is an item requiring an outflow of money, or any form of fortune in general, to another person or group as payment for an item, service, or other category of costs. For a tenant, rent is an expense. For students or parents, tuition is an expense. Buying food, clothing, furniture, or an automobile is often referred to as an expense. An expense is a cost that is "paid" or "remitted", usually in exchange for something of value. Something that seems to cost a great deal is "expensive". Something that seems to cost little is "inexpensive". "Expenses of the table" are expenses for dining, refreshments, a feast, etc.
A company's earnings before interest, taxes, depreciation, and amortization is a measure of a company's profitability of the operating business only, thus before any effects of indebtedness, state-mandated payments, and costs required to maintain its asset base. It is derived by subtracting from revenues all costs of the operating business but not decline in asset value, cost of borrowing and obligations to governments. Although lease have been capitalised in the balance sheet since IFRS 16, its expenses are often still adjusted back into EBITDA given they are deemed operational in nature.
Well logging, also known as borehole logging is the practice of making a detailed record of the geologic formations penetrated by a borehole. The log may be based either on visual inspection of samples brought to the surface or on physical measurements made by instruments lowered into the hole. Some types of geophysical well logs can be done during any phase of a well's history: drilling, completing, producing, or abandoning. Well logging is performed in boreholes drilled for the oil and gas, groundwater, mineral and geothermal exploration, as well as part of environmental and geotechnical studies.
Steam-assisted gravity drainage is an enhanced oil recovery technology for producing heavy crude oil and bitumen. It is an advanced form of steam stimulation in which a pair of horizontal wells are drilled into the oil reservoir, one a few metres above the other. High pressure steam is continuously injected into the upper wellbore to heat the oil and reduce its viscosity, causing the heated oil to drain into the lower wellbore, where it is pumped out. Dr. Roger Butler, engineer at Imperial Oil from 1955 to 1982, invented the steam assisted gravity drainage (SAGD) process in the 1970s. Butler "developed the concept of using horizontal pairs of wells and injected steam to develop certain deposits of bitumen considered too deep for mining". In 1983 Butler became director of technical programs for the Alberta Oil Sands Technology and Research Authority (AOSTRA), a crown corporation created by Alberta Premier Lougheed to promote new technologies for oil sands and heavy crude oil production. AOSTRA quickly supported SAGD as a promising innovation in oil sands extraction technology.

A blowout is the uncontrolled release of crude oil and/or natural gas from an oil well or gas well after pressure control systems have failed. Modern wells have blowout preventers intended to prevent such an occurrence. An accidental spark during a blowout can lead to a catastrophic oil or gas fire.
Artificial lift is the use of artificial means to increase the flow of liquids, such as crude oil or water, from a production well. Generally this is achieved by the use of a mechanical device inside the well or by decreasing the weight of the hydrostatic column by injecting gas into the liquid some distance down the well. A newer method called Continuous Belt Transportation (CBT) uses an oil absorbing belt to extract from marginal and idle wells. Artificial lift is needed in wells when there is insufficient pressure in the reservoir to lift the produced fluids to the surface, but often used in naturally flowing wells to increase the flow rate above what would flow naturally. The produced fluid can be oil, water or a mix of oil and water, typically mixed with some amount of gas.

In the oil and gas industry, coiled tubing refers to a long metal pipe, normally 1 to 3.25 in in diameter which is supplied spooled on a large reel. It is used for interventions in oil and gas wells and sometimes as production tubing in depleted gas wells. Coiled tubing is often used to carry out operations similar to wirelining. The main benefits over wireline are the ability to pump chemicals through the coil and the ability to push it into the hole rather than relying on gravity. Pumping can be fairly self-contained, almost a closed system, since the tube is continuous instead of jointed pipe. For offshore operations, the 'footprint' for a coiled tubing operation is generally larger than a wireline spread, which can limit the number of installations where coiled tubing can be performed and make the operation more costly. A coiled tubing operation is normally performed through the drilling derrick on the oil platform, which is used to support the surface equipment, although on platforms with no drilling facilities a self-supporting tower can be used instead. For coiled tubing operations on sub-sea wells a mobile offshore drilling unit (MODU) e.g. semi-submersible, drillship etc. has to be utilized to support all the surface equipment and personnel, whereas wireline can be carried out from a smaller and cheaper intervention vessel. Onshore, they can be run using smaller service rigs, and for light operations a mobile self-contained coiled tubing rig can be used.
A production packer is a standard component of the completion hardware of oil or gas wells used to provide a seal between the outside of the production tubing and the inside of the casing, liner, or wellbore wall.
Natural gas is a commodity that can be stored for an indefinite period of time in natural gas storage facilities for later consumption.

Well completion is the process of making a well ready for production after drilling operations. This principally involves preparing the bottom of the hole to the required specifications, running in the production tubing and its associated down hole tools as well as perforating and stimulating as required. Sometimes, the process of running in and cementing the casing is also included. After a well has been drilled, should the drilling fluids be removed, the well would eventually close in upon itself. Casing ensures that this will not happen while also protecting the wellstream from outside incumbents, like water or sand.

Well stimulation is a broad term used to describe the various techniques and well interventions that can be used to restore or enhance the production of hydrocarbons from an oil well.

Offshore oil spill prevention and response is the study and practice of reducing the number of offshore incidents that release oil or hazardous substances into the environment and limiting the amount released during those incidents.
In the petroleum industry, allocation refers to practices of breaking down measures of quantities of extracted hydrocarbons across various contributing sources. Allocation aids the attribution of ownerships of hydrocarbons as each contributing element to a commingled flow or to a storage of petroleum may have a unique ownership. Contributing sources in this context are typically producing petroleum wells delivering flows of petroleum or flows of natural gas to a commingled flow or storage.
An oil water separator (OWS) is a piece of equipment used to separate oil and water mixtures into their separate components. There are many different types of oil-water separator. Each has different oil separation capability and are used in different industries. Oil water separators are designed and selected after consideration of oil separation performance parameters and life cycle cost considerations. "Oil" can be taken to mean mineral, vegetable and animal oils, and the many different hydrocarbons.
Fugitive gas emissions are emissions of gas to atmosphere or groundwater which result from oil and gas or coal mining activity. In 2016, these emissions, when converted to their equivalent impact of carbon dioxide, accounted for 5.8% of all global greenhouse gas emissions.
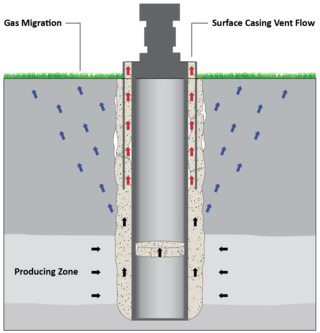
Orphan wells in Alberta, Canada are inactive oil or gas well sites that have no solvent owner that can be held legally or financially accountable for the decommissioning and reclamation obligations to ensure public safety and to address environmental liabilities.

Orphan, orphaned, or abandoned wells are oil or gas wells that have been abandoned by fossil fuel extraction industries. These wells may have been deactivated because had become uneconomic, failure to transfer ownerships, or neglect, and thus no longer have legal owners responsible for their care. Decommissioning wells effectively can be expensive, costing several thousands of dollars for a shallow land well to millions of dollars for an offshore one. Thus the burden may fall on government agencies or surface landowners when a business entity can no longer be held responsible.








