Related Research Articles
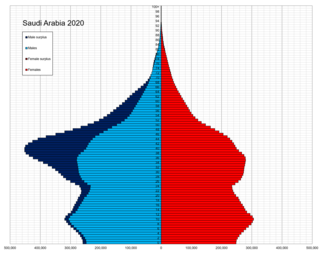
Saudi Arabia is the fourth largest state in the Arab world, with a reported population of 35,013,414 as of 2018. 38.3% of inhabitants are immigrants. Saudi Arabia has experienced a population explosion in the last 40 years, and continues to grow at a rate of 1.62% per year.

The economy of Saudi Arabia is the largest in the Arab States and the eighteenth largest in the world. A permanent and founding member of the OPEC, Saudi Arabia is also a member of the G20 forum as one of the world's largest economies. The country's economy relies heavily on Crude oil and services supported by the national government.

The Saudi Arabian Armed Forces(SAAF) & also known as the Royal Saudi Armed Forces, are the military forces of the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia. It consists of the Saudi Arabian Land Forces, the Royal Saudi Navy, the Royal Saudi Air Force, the Royal Saudi Air Defense, and the Royal Saudi Strategic Missile Force. The King of Saudi Arabia is the commander-in-chief of the armed forces and forms military policy with the Ministry of Defense and the Ministry of Interior. The five Armed Forces are among eight military forces of Saudi Arabia, with the others including the Saudi Arabian National Guard, the Saudi Royal Guard Regiment and Saudi Arabian Border Guards.

Foreign relations of Saudi Arabia refers to diplomatic and trade relations between Saudi Arabia and other countries around the world. The foreign policy of Saudi Arabia is focused on co-operation with the oil-exporting Gulf States, the unity of the Arab world, Islamic solidarity, and support for the United Nations. In practice, the main concerns in recent years have been relations with the US, the Saudi Arabian–led intervention in Yemen, the Israeli–Palestinian conflict, Iraq, the perceived threat from the Islamic Republic of Iran, and the effect of oil pricing. Saudi Arabia contributes large amounts of development aid to Muslim countries. From 1986 to 2006, the country donated £49 billion in aid.

The Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries is an intergovernmental organization of 13 countries. Founded on 14 September 1960 in Baghdad by the first five members, it has, since 1965, been headquartered in Vienna, Austria, although Austria is not an OPEC member state. As of September 2018, the 13 member countries accounted for an estimated 44 percent of global oil production and 81.5 percent of the world's proven oil reserves, giving OPEC a major influence on global oil prices that were previously determined by the so-called "Seven Sisters" grouping of multinational oil companies.

Faisal bin Abdulaziz Al Saud was a Saudi Arabian statesman and diplomat who was King of Saudi Arabia from 2 November 1964 until his assassination in 1975. Prior to his ascension, he served as Crown Prince of Saudi Arabia from 9 November 1953 to 2 November 1964, and he was briefly regent to his half-brother King Saud in 1964. He was the third son of King Abdulaziz, the founder of modern Saudi Arabia, and the second of Abdulaziz's six sons who were kings.

The Cooperation Council for the Arab States of the Gulf, also known as the Gulf Cooperation Council, is a regional, intergovernmental, political, and economic union comprising Bahrain, Kuwait, Oman, Qatar, Saudi Arabia, and the United Arab Emirates. The council's main headquarters is located in Riyadh, Saudi Arabia. The Charter of the GCC was signed on 25 May 1981, formally establishing the institution.

Saudi Arabia, officially the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia (KSA), is a country on the Arabian Peninsula in Western Asia. It has a land area of about 2,150,000 km2 (830,000 sq mi), making it the fifth-largest country in Asia, the second-largest in the Arab world, and the largest in Western Asia. It is bordered by the Red Sea to the west; Jordan, Iraq, and Kuwait to the north; the Persian Gulf, Qatar and the United Arab Emirates to the east; Oman to the southeast; and Yemen to the south. Bahrain is an island country off the east coast. The Gulf of Aqaba in the northwest separates Saudi Arabia from Egypt. Saudi Arabia is the only country with a coastline along both the Red Sea and the Persian Gulf, and most of its terrain consists of arid desert, lowland, steppe, and mountains. Its capital and largest city is Riyadh. The country is home to Mecca and Medina, the two holiest cities in Islam.

The Saudi Arabia national football team represent Saudi Arabia in men's international football. They are known as Al-Suqour Al-Akhdhar in reference to their traditional colours of green and white and represent both FIFA and the Asian Football Confederation (AFC).

Salman bin Abdulaziz Al Saud is King of Saudi Arabia, reigning since 2015, and served as Prime Minister of Saudi Arabia from 2015 to 2022. The 25th son of King Abdulaziz, the founder of Saudi Arabia, he assumed the throne on 23 January 2015. Prior to his accession, he was Crown Prince of Saudi Arabia from 16 June 2012 to 23 January 2015. Salman is the 4th oldest living head of state and the oldest living monarch.

The King Cup, officially known as The Custodian of the Two Holy Mosques' Cup, is the Saudi Arabian football knockout cup competition, run by the Saudi Arabian Football Federation.

Abdullah bin Abdulaziz Al Saud was King and Prime Minister of Saudi Arabia from 1 August 2005 until his death in 2015. Prior to his ascension, he was Crown Prince of Saudi Arabia since 13 June 1982. He was the tenth son of King Abdulaziz, the founder of Saudi Arabia, and the fifth of Abdulaziz's six sons who were kings.

The Hajj is an annual Islamic pilgrimage to Mecca, Saudi Arabia, the holiest city for Muslims. Hajj is a mandatory religious duty for Muslims that must be carried out at least once in their lifetime by all adult Muslims who are physically and financially capable of undertaking the journey, and of supporting their family during their absence from home.

Salman Mohammed Al-Faraj is a Saudi Arabian professional footballer who plays as a midfielder and captains both Al-Hilal and the Saudi Arabia national football team.

The Saudi Council of Ministers is the cabinet of the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia. It is led by the King. The council consists of the king, the Crown Prince, and cabinet ministers. The Crown Prince is also Prime Minister and Chair of the Council of Ministers. Since 2015, there are 23 ministers with portfolio and seven ministers of state, two of whom have special responsibilities. All members of the council are appointed by royal decree.

Mohammed bin Salman Al Saud, colloquially known as MBS or MbS, is Crown Prince and Prime Minister of Saudi Arabia. He also serves as the chairman of the Council of Economic and Development Affairs and chairman of the Council of Political and Security Affairs. Even prior to his appointment as prime minister, he was considered the de facto ruler of Saudi Arabia, and he served as minister of defense from 2015 to 2022. He is the seventh son of King Salman.

The crown prince of Saudi Arabia is the second most important position in Saudi Arabia, second to the King, and is his designated successor. Currently, the Crown Prince assumes power with the approval of the Allegiance Council after he is nominated by the King. This system was introduced to the country during the reign of King Abdullah. In the absence of the King, an order is issued to have the Crown Prince manage the affairs of the state until the King's return.

On 26 March 2015, Saudi Arabia, leading a coalition of nine countries from West Asia and North Africa, launched an intervention in the Yemeni Civil War in response to calls from the president of Yemen Abdrabbuh Mansur Hadi for military support after he was ousted by the Houthi movement. The conflict ignited between the government forces, the Houthi rebels and other armed groups after the draft constitution and power-sharing arrangements collapsed, despite progress in the political transition led by the United Nations at that time, leading to an escalation of violence in mid-2014. The Houthis and allied units of the armed forces seized control of Sana’a and other parts of the country in September 2014 and in the following months. This prompted President Hadi to ask Saudi Arabia to intervene against the Iranian-backed Houthis.
Saudi Arabia's involvement in the Syrian Civil War involved the large-scale supply of weapons and ammunition to various rebel groups in Syria during the Syrian Civil War.

The Iran–Saudi Arabia proxy conflict, sometimes also referred to as the Middle Eastern Cold War, is the ongoing struggle for influence in the Middle East and other Muslim regions between Iran and Saudi Arabia. The two countries have provided varying degrees of support to opposing sides in nearby conflicts, including the civil wars in Syria and Yemen; and disputes in Bahrain, Lebanon, Qatar, and Iraq. It also extends to disputes or broader competition in other regions such as Nigeria, Pakistan, Afghanistan and other parts of North and East Africa, South Asia, Central Asia, Southeast Asia, the Balkans, and the Caucasus.
References
- ↑ "2015 World Championship Roster" (PDF). IHF. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2 February 2015. Retrieved 15 January 2015.
