
Helmand, also known as Hillmand, in ancient times, as Hermand and Hethumand, is one of the 34 provinces of Afghanistan, in the south of the country. It is the largest province by area, covering 58,584 square kilometres (20,000 sq mi) area. The province contains 13 districts, encompassing over 1,000 villages, and roughly 1,446,230 settled people. Lashkargah serves as the provincial capital. Helmand was part of the Greater Kandahar region until made into a separate province by the Afghan government in the 20th century.

Mullah Abdul Salam Zaeef is an Afghan diplomat who was the Afghan ambassador to Pakistan before the US invasion of Afghanistan.

Abdulrab Rasul Sayyaf is an exiled Afghan politician and former mujahideen commander. He took part in the war against the Marxist–Leninist People's Democratic Party of Afghanistan (PDPA) government in the 1980s, leading the Afghan mujahideen faction Ittehad-al-Islami.

Atta Muhammad Nur is an Afghan exiled politician and former militant who served as the Governor of Balkh Province in Afghanistan from 2004 to January 25, 2018. An ethnic Tajik, he worked to educate the Mujahideen after the 1979 Soviet invasion of Afghanistan, gaining the nickname "The Teacher". He then became a mujahideen resistance commander for the Jamiat-e Islami against the Soviets.
The Islamic Revolution Movement is a traditionalist Islamist political party. It was once one of the biggest Afghan mujahideen factions fighting against Soviet forces during the Soviet–Afghan War. Mohammad Nabi Mohammadi was the leader of the group at the time.

Mohammad Nabi Mohammadi was an Afghan politician and mujahideen leader who was the founder and leader of the Harakat-i-Inqilab-i-Islami political party and paramilitary group. He served as President of Afghanistan under the mujahideen from January 1993 to 1996.
Sher Mohammed Akhundzada is a tribal leader who was the Governor of Helmand in Afghanistan from 2001 to 2005.
Mohammad Daoud was the governor of Helmand in Afghanistan until he was removed from his post for his ties to the opium trade. Daoud was appointed in December 2005, and replaced in December 2006 after the insistence of the British ISAF troops. The U.S. used the warlords to help them hunt Al Qaeda and the Taliban and it is rumored this extended to ignoring their involvement in the production and sale of opium.

The 1989–1992 Afghan Civil War took place between the Soviet withdrawal from Afghanistan on 15 February 1989 until 27 April 1992, ending the day after the proclamation of the Peshawar Accords proclaiming a new interim Afghan government which was supposed to start serving on 28 April 1992.

The 1992–1996 Afghan Civil War took place between 28 April 1992—the date a new interim Afghan government was supposed to replace the Republic of Afghanistan of President Mohammad Najibullah—and the Taliban's conquest of Kabul establishing the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan on 27 September 1996.

Nāwa-I-Barakzāyi District is an administrative district in Helmand Province, Afghanistan located south of the provincial capital of Lashkar Gah along the Helmand River. It is bordered by the districts of Lashkar Gah, Nad Ali, Garmsir, and Rig, as well as the provinces of Nimruz and Kandahar. It falls within the area known as Pashtunistan,, an area comprising most of southeast Afghanistan and northwest Pakistan. The dominant language is Pashto and many of the 89,000 residents practice the traditional code of Pashtunwali. Nawa-I-Barakzayi's name reflects the dominant Pashtun tribe in the district, the Barakzai. Prior to the 1970s, it was called Shamalan after a small village at the south end of the district

Garmsir District is located in the southern part of Helmand Province, Afghanistan. The district is large, but all the villages are along the Helmand River. The rest is a desert. The district capital, Garmsir, is located in the northwestern part of the district on the east bank of Helmand River.

The Afghan mujahideen were various armed Islamist rebel groups that fought against the government of the Democratic Republic of Afghanistan and the Soviet Union during the Soviet–Afghan War and the subsequent First Afghan Civil War. The term mujahideen is used in a religious context by Muslims to refer to those engaged in a struggle of any nature for the sake of Islam, commonly referred to as jihad (جهاد). The Afghan mujahideen consisted of numerous groups that differed from each other across ethnic and/or ideological lines, but were united by their anti-communist and pro-Islamic goals. The union was also widely referred to by their Western backers as the Afghan resistance, while Western press often referred to them as Muslim rebels, guerrillas, or "Mountain Men". They were popularly referred to by Soviet troops as dukhi as derivation from Dari word دشمان dushman, which turned into short dukh and also was suitable due to their guerrilla tactics; Afghan civilians often referred to them as the tanzim, while the Afghan government called them dushman, a term also employed by the Soviets.

The Other Side of the Sky: A Memoir is a memoir by Farah Ahmedi with Tamim Ansary. The book profiles the life of Farah Ahmedi from the time she was born until she was seventeen years old.
Mohammad Yousef Pashtun is an Afghan technocrat and politician. He served as Minister of Urban Development and Housing for two terms and as Governor of Kandahar province in 2003, replacing Gul Agha Sherzai under President Hamid Karzai's administration. In 2010, he was appointed as Senior Adviser to President Karzai on Construction, Mines, Water & Energy. In 2014, minister Pashtun continued to serve as Senior Adviser to President Ashraf Ghani. Yِousef Pashtun is also chairing the Kabul New City Development Authority Board.
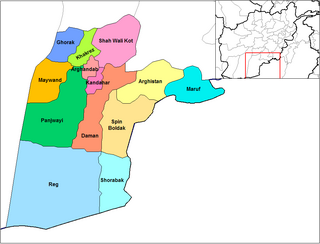
The Battle of Arghandab was an offensive launched by Afghan government forces, supported by Soviet troops, against mujahideen strongholds in the Arghandab District of Kandahar Province, Afghanistan, in 1987. The operation ended in failure, and the government forces withdrew after suffering heavy losses.

Afghanistan–Israel relations refer to the bilateral ties between Afghanistan and the State of Israel. The two countries have never had formal diplomatic relations, and Afghanistan has never recognized Israel since the latter's independence in 1948. Zablon Simintov, who lived in Kabul and managed Afghanistan's only remaining synagogue, was thought to be the last Jew still living in Afghanistan. However, shortly after the 2021 Taliban offensive, it was discovered that his lost relative, Tova Moradi, was actually the last Jew in Afghanistan after Israeli businessman Mordechai Kahana arranged for Simintov's evacuation to Israel on 7 September 2021; Moradi also made aliyah to Israel on 29 October 2021. Simintov's desire to leave Afghanistan stemmed from his concerns over possibly being attacked by more radical Islamist terrorist groups such as the Islamic State – KP rather than the Taliban.

The Afghan conflict, also called the Afghan crisis or Instability in Afghanistan is a series of events and wars that have kept Afghanistan in a near-continuous state of armed conflict since the 1970's. The country's instability began after the collapse of the Kingdom of Afghanistan in the 1973 coup d'état; with the overthrow of Afghan monarch Mohammed Zahir Shah, who reigned for almost forty years, Afghanistan’s relatively peaceful period in modern history came to an end. The triggering event for the first major war in Afghanistan during this period was the Saur Revolution of 1978, which overthrew the Republic of Afghanistan and established the Democratic Republic of Afghanistan. Rampant post-revolution fighting across the country ultimately led to a pro-government military intervention by the Soviet Union, sparking the Soviet–Afghan War in the 1980s.

Peace processes have taken place during several phases of the Afghanistan conflict, which has lasted since the 1978 Saur Revolution.















