Related Research Articles

Amplitude modulation (AM) is a modulation technique used in electronic communication, most commonly for transmitting messages with a radio wave. In amplitude modulation, the amplitude of the wave is varied in proportion to that of the message signal, such as an audio signal. This technique contrasts with angle modulation, in which either the frequency of the carrier wave is varied, as in frequency modulation, or its phase, as in phase modulation.
The amplitude of a periodic variable is a measure of its change in a single period. The amplitude of a non-periodic signal is its magnitude compared with a reference value. There are various definitions of amplitude, which are all functions of the magnitude of the differences between the variable's extreme values. In older texts, the phase of a periodic function is sometimes called the amplitude.
In signal processing, distortion is the alteration of the original shape of a signal. In communications and electronics it means the alteration of the waveform of an information-bearing signal, such as an audio signal representing sound or a video signal representing images, in an electronic device or communication channel.
In signal processing, group delay and phase delay are two related ways of describing how a signal's frequency components are delayed in time when passing through a linear time-invariant (LTI) system. Phase delay describes the time shift of a sinusoidal component. Group delay describes the time shift of the envelope of a wave packet, a "pack" or "group" of oscillations centered around one frequency that travel together, formed for instance by multiplying a sine wave by an envelope.

A loudspeaker is an electroacoustic transducer that converts an electrical audio signal into a corresponding sound. A speaker system, also often simply referred to as a speaker or loudspeaker, comprises one or more such speaker drivers, an enclosure, and electrical connections possibly including a crossover network. The speaker driver can be viewed as a linear motor attached to a diaphragm which couples that motor's movement to motion of air, that is, sound. An audio signal, typically from a microphone, recording, or radio broadcast, is amplified electronically to a power level capable of driving that motor in order to reproduce the sound corresponding to the original unamplified electronic signal. This is thus the opposite function to the microphone; indeed the dynamic speaker driver, by far the most common type, is a linear motor in the same basic configuration as the dynamic microphone which uses such a motor in reverse, as a generator.

A microphone, colloquially called a mic, is a transducer that converts sound into an electrical signal. Microphones are used in many applications such as telephones, hearing aids, public address systems for concert halls and public events, motion picture production, live and recorded audio engineering, sound recording, two-way radios, megaphones, and radio and television broadcasting. They are also used in computers for recording voice, speech recognition, VoIP, and for other purposes such as ultrasonic sensors or knock sensors.
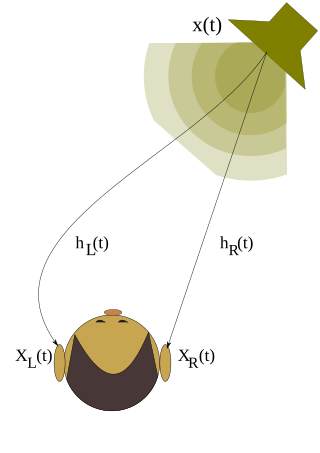
A head-related transfer function (HRTF), also known as anatomical transfer function (ATF), or a head shadow, is a response that characterizes how an ear receives a sound from a point in space. As sound strikes the listener, the size and shape of the head, ears, ear canal, density of the head, size and shape of nasal and oral cavities, all transform the sound and affect how it is perceived, boosting some frequencies and attenuating others. Generally speaking, the HRTF boosts frequencies from 2–5 kHz with a primary resonance of +17 dB at 2,700 Hz. But the response curve is more complex than a single bump, affects a broad frequency spectrum, and varies significantly from person to person.

Headphones are a pair of small loudspeaker drivers worn on or around the head over a user's ears. They are electroacoustic transducers, which convert an electrical signal to a corresponding sound. Headphones let a single user listen to an audio source privately, in contrast to a loudspeaker, which emits sound into the open air for anyone nearby to hear. Headphones are also known as earphones or, colloquially, cans. Circumaural and supra-aural headphones use a band over the top of the head to hold the speakers in place. Another type, known as earbuds or earpieces consist of individual units that plug into the user's ear canal. A third type are bone conduction headphones, which typically wrap around the back of the head and rest in front of the ear canal, leaving the ear canal open. In the context of telecommunication, a headset is a combination of headphone and microphone.

Surround sound is a technique for enriching the fidelity and depth of sound reproduction by using multiple audio channels from speakers that surround the listener. Its first application was in movie theaters. Prior to surround sound, theater sound systems commonly had three screen channels of sound that played from three loudspeakers located in front of the audience. Surround sound adds one or more channels from loudspeakers to the side or behind the listener that are able to create the sensation of sound coming from any horizontal direction around the listener.

Active noise control (ANC), also known as noise cancellation (NC), or active noise reduction (ANR), is a method for reducing unwanted sound by the addition of a second sound specifically designed to cancel the first. The concept was first developed in the late 1930s; later developmental work that began in the 1950s eventually resulted in commercial airline headsets with the technology becoming available in the late 1980s. The technology is also used in road vehicles, mobile telephones, earbuds, and headphones.

A sound reinforcement system is the combination of microphones, signal processors, amplifiers, and loudspeakers in enclosures all controlled by a mixing console that makes live or pre-recorded sounds louder and may also distribute those sounds to a larger or more distant audience. In many situations, a sound reinforcement system is also used to enhance or alter the sound of the sources on the stage, typically by using electronic effects, such as reverb, as opposed to simply amplifying the sources unaltered.
In the field of acoustics, a diaphragm is a transducer intended to inter-convert mechanical vibrations to sounds, or vice versa. It is commonly constructed of a thin membrane or sheet of various materials, suspended at its edges. The varying air pressure of sound waves imparts mechanical vibrations to the diaphragm which can then be converted to some other type of signal; examples of this type of diaphragm are found in microphones and the human eardrum. Conversely a diaphragm vibrated by a source of energy beats against the air, creating sound waves. Examples of this type of diaphragm are loudspeaker cones and earphone diaphragms and are found in air horns.

In electrical engineering, a function generator is usually a piece of electronic test equipment or software used to generate different types of electrical waveforms over a wide range of frequencies. Some of the most common waveforms produced by the function generator are the sine wave, square wave, triangular wave and sawtooth shapes. These waveforms can be either repetitive or single-shot. Another feature included on many function generators is the ability to add a DC offset. Integrated circuits used to generate waveforms may also be described as function generator ICs.

There are a number of well-developed microphone techniques used for recording musical, film, or voice sources or picking up sounds as part of sound reinforcement systems. The choice of technique depends on a number of factors, including:

A stage monitor system is a set of performer-facing loudspeakers called monitor speakers, stage monitors, floor monitors, wedges, or foldbacks on stage during live music performances in which a sound reinforcement system is used to amplify a performance for the audience. The monitor system allows musicians to hear themselves and fellow band members clearly.
Psychoacoustics is the branch of psychophysics involving the scientific study of sound perception and audiology—how human auditory system perceives various sounds. More specifically, it is the branch of science studying the psychological responses associated with sound. Psychoacoustics is an interdisciplinary field of many areas, including psychology, acoustics, electronic engineering, physics, biology, physiology, and computer science.

An audio analyzer is a test and measurement instrument used to objectively quantify the audio performance of electronic and electro-acoustical devices. Audio quality metrics cover a wide variety of parameters, including level, gain, noise, harmonic and intermodulation distortion, frequency response, relative phase of signals, interchannel crosstalk, and more. In addition, many manufacturers have requirements for behavior and connectivity of audio devices that require specific tests and confirmations.

In a loudspeaker, a phase plug, phasing plug or acoustical transformer is a mechanical interface between a speaker driver and the audience. The phase plug extends high frequency response because it guides waves outward toward the listener rather than allowing them to interact destructively near the driver.
Perceptual-based 3D sound localization is the application of knowledge of the human auditory system to develop 3D sound localization technology.

The United Kingdom patent 394325 'Improvements in and relating to Sound-transmission, Sound-recording and Sound-reproducing Systems' is a fundamental work on stereophonic sound, written by Alan Blumlein in 1931 and published in 1933. The work exists only in the form of a patent and two accompanying memos addressed to Isaac Shoenberg. The text is exceptionally long for a patent of the period, having 70 numbered claims. It contains a brief summary of sound localization theory, a roadmap for introduction of surround sound in sound film and recording industry, and a description of Blumlein's inventions related to stereophony, notably the matrix processing of stereo signals, the Blumlein stereo microphone and the 45/45 mechanical recording system.
References
- 1 2 Self, Douglas (2009). Audio Power Amplifier Design Handbook (5 ed.). Taylor & Francis US. p. 23. ISBN 978-0240521626.
- ↑ Newell, Philip; Holland, Keith (2012). Loudspeakers: For music recording and reproductio. CRC Press. p. 291. ISBN 978-1136124372.
- ↑ Watkinson, John (2012). "Transducer driver mechanisms". In John Borwick (ed.). Loudspeaker and Headphone Handbook (3 ed.). Taylor & Francis US. pp. 88–89. ISBN 978-0240515786.
- ↑ McCarthy, Bob (2007). Sound Systems: Design and Optimization: Modern Techniques and Tools for Sound System Design and Alignment. Taylor & Francis US. p. 378. ISBN 978-0240520209.
- ↑ Absolute Phase: A Prerequisite To Optimum Performance
- ↑ Winer, Ethan (2012). The Audio Expert: Everything You Need to Know About Audio. Taylor & Francis US. pp. 85–86. ISBN 978-0240821009.
- ↑ Arbiter Systems – Absolute Phase
- ↑ Paulus GG, Grasbon F, Walther H, et al. (November 2001). "Absolute-phase phenomena in photoionization with few-cycle laser pulses". Nature. 414 (6860): 182–4. Bibcode:2001Natur.414..182P. doi:10.1038/35102520. PMID 11700551. S2CID 4414801.