
Albedo is the measure of the diffuse reflection of solar radiation out of the total solar radiation and measured on a scale from 0, corresponding to a black body that absorbs all incident radiation, to 1, corresponding to a body that reflects all incident radiation.

In physics, a redshift is an increase in the wavelength, and corresponding decrease in the frequency and photon energy, of electromagnetic radiation. The opposite change, a decrease in wavelength and simultaneous increase in frequency and energy, is known as a negative redshift, or blueshift. The terms derive from the colours red and blue which form the extremes of the visible light spectrum.

Evapotranspiration (ET) is the sum of water evaporation and transpiration from a surface area to the atmosphere. Evaporation accounts for the movement of water to the air from sources such as the soil, canopy interception, and water bodies. Transpiration accounts for the movement of water within a plant and the subsequent exit of water as vapor through stomata in its leaves in vascular plants and phyllids in non-vascular plants. A plant that contributes to evapotranspiration is called an evapotranspirator. Evapotranspiration is an important part of the water cycle.
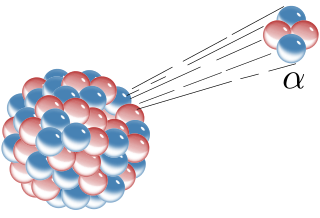
Radioactive decay is the process by which an unstable atomic nucleus loses energy by radiation. A material containing unstable nuclei is considered radioactive. Three of the most common types of decay are alpha decay, beta decay, and gamma decay, all of which involve emitting one or more particles. The weak force is the mechanism that is responsible for beta decay, while the other two are governed by the electromagnetic and strong forces.
Potential evaporation (PE) or potential evapotranspiration (PET) is defined as the amount of evaporation that would occur if a sufficient water source were available. If the actual evapotranspiration is considered the net result of atmospheric demand for moisture from a surface and the ability of the surface to supply moisture, then PET is a measure of the demand side. Surface and air temperatures, insolation, and wind all affect this. A dryland is a place where annual potential evaporation exceeds annual precipitation.

In heat transfer, Kirchhoff's law of thermal radiation refers to wavelength-specific radiative emission and absorption by a material body in thermodynamic equilibrium, including radiative exchange equilibrium.

In physical cosmology, the age of the universe is the time elapsed since the Big Bang. Today, astronomers have derived two different measurements of the age of the universe: a measurement based on direct observations of an early state of the universe, which indicate an age of 13.787±0.020 billion years as interpreted with the Lambda-CDM concordance model as of 2018; and a measurement based on the observations of the local, modern universe, which suggest a younger age. The uncertainty of the first kind of measurement has been narrowed down to 20 million years, based on a number of studies which all gave extremely similar figures for the age. These include studies of the microwave background radiation by the Planck spacecraft, the Wilkinson Microwave Anisotropy Probe and other space probes. Measurements of the cosmic background radiation give the cooling time of the universe since the Big Bang, and measurements of the expansion rate of the universe can be used to calculate its approximate age by extrapolating backwards in time. The range of the estimate is also within the range of the estimate for the oldest observed star in the universe.

The ΛCDM or Lambda-CDM model is a parameterization of the Big Bang cosmological model in which the universe contains three major components: first, a cosmological constant denoted by Lambda associated with dark energy; second, the postulated cold dark matter ; and third, ordinary matter. It is frequently referred to as the standard model of Big Bang cosmology because it is the simplest model that provides a reasonably good account of the following properties of the cosmos:
The Penman equation describes evaporation (E) from an open water surface, and was developed by Howard Penman in 1948. Penman's equation requires daily mean temperature, wind speed, air pressure, and solar radiation to predict E. Simpler Hydrometeorological equations continue to be used where obtaining such data is impractical, to give comparable results within specific contexts, e.g. humid vs arid climates.

According to modern models of physical cosmology, a dark matter halo is a basic unit of cosmological structure. It is a hypothetical region that has decoupled from cosmic expansion and contains gravitationally bound matter. A single dark matter halo may contain multiple virialized clumps of dark matter bound together by gravity, known as subhalos. Modern cosmological models, such as ΛCDM, propose that dark matter halos and subhalos may contain galaxies. The dark matter halo of a galaxy envelops the galactic disc and extends well beyond the edge of the visible galaxy. Thought to consist of dark matter, halos have not been observed directly. Their existence is inferred through observations of their effects on the motions of stars and gas in galaxies and gravitational lensing. Dark matter halos play a key role in current models of galaxy formation and evolution. Theories that attempt to explain the nature of dark matter halos with varying degrees of success include cold dark matter (CDM), warm dark matter, and massive compact halo objects (MACHOs).

The bidirectional reflectance distribution function is a function of four real variables that defines how light is reflected at an opaque surface. It is employed in the optics of real-world light, in computer graphics algorithms, and in computer vision algorithms. The function takes an incoming light direction, , and outgoing direction, , and returns the ratio of reflected radiance exiting along to the irradiance incident on the surface from direction . Each direction is itself parameterized by azimuth angle and zenith angle , therefore the BRDF as a whole is a function of 4 variables. The BRDF has units sr−1, with steradians (sr) being a unit of solid angle.
Compressed sensing is a signal processing technique for efficiently acquiring and reconstructing a signal, by finding solutions to underdetermined linear systems. This is based on the principle that, through optimization, the sparsity of a signal can be exploited to recover it from far fewer samples than required by the Nyquist–Shannon sampling theorem. There are two conditions under which recovery is possible. The first one is sparsity, which requires the signal to be sparse in some domain. The second one is incoherence, which is applied through the isometric property, which is sufficient for sparse signals.
Like the Penman equation, the Penman–Monteith equation approximates net evapotranspiration (ET), requiring as input daily mean temperature, wind speed, relative humidity and solar radiation. Other than radiation, these parameter are implicit in the derivation of , , and , if not conductances below.
The psychrometric constant relates the partial pressure of water in air to the air temperature. This lets one interpolate actual vapor pressure from paired dry and wet thermometer bulb temperature readings.

Multi-junction (MJ) solar cells are solar cells with multiple p–n junctions made of different semiconductor materials. Each material's p-n junction will produce electric current in response to different wavelengths of light. The use of multiple semiconducting materials allows the absorbance of a broader range of wavelengths, improving the cell's sunlight to electrical energy conversion efficiency.
The Minnaert function is a photometric function used to interpret astronomical observations and remote sensing data for the Earth. It was named after the astronomer Marcel Minnaert. This function expresses the radiance factor (RADF) as a function the phase angle, the photometric latitude and the photometric longitude.
The Sakuma–Hattori equation is a mathematical model for predicting the amount of thermal radiation, radiometric flux or radiometric power emitted from a perfect blackbody or received by a thermal radiation detector.
Bimetric gravity or bigravity refers to two different classes of theories. The first class of theories relies on modified mathematical theories of gravity in which two metric tensors are used instead of one. The second metric may be introduced at high energies, with the implication that the speed of light could be energy-dependent, enabling models with a variable speed of light.

The moment distance index (MDI) is a shape-based metric or shape index that can be used to analyze spectral reflectance curves and waveform LiDAR, proposed by Salas and Henebry in 2014. In the case of spectral data, the shape of the reflectance curve should unmask fine points of the spectra usually not considered by existing band-specific indices. It has been used to identify spectral regions for chlorophyll and carotenoids, detect greenhouses using WorldView-2 and Landsat satellite data, identify greenhouse crops, compute canopy heights, estimate green vegetation fraction, and optimize Fourier-transform infrared (FTIR) scans for soil spectroscopy.
BAITSSS is biophysical Evapotranspiration (ET) computer model that determines water use, primarily in agriculture landscape, using remote sensing-based information. It was developed and refined by Ramesh Dhungel and the water resources group at University of Idaho's Kimberly Research and Extension Center since 2010. It has been used in different areas in the United States including Southern Idaho, Northern California, northwest Kansas, and Texas.















