Related Research Articles
Arabic language names have historically been based on a long naming system. Many people from the Arabic-speaking and also non-Arab Muslim countries have not had given/middle/family names but rather a chain of names. This system remains in use throughout the Arabic and Muslim worlds.
Abd Allah, also spelled Abdallah, Abdellah, Abdollah, Abdullah, Abdulla, Abdalla and many others, is an Arabic name meaning "Servant of God". It is built from the Arabic words ʻabd (عبد) and Allāh (الله). Although the first letter "a" in Allāh, as the first letter of the article al-, is usually unstressed in Arabic, it is usually stressed in the pronunciation of this name. The variants Abdollah and Abdullah represent the elision of this "a" following the "u" of the Classical Arabic nominative case. Abd Allah is one of many Arabic theophoric names, meaning servant of God. God's Follower is also a meaning of this name.
This is an alphabetical list of topics related to Islam, the history of Islam, Islamic culture, and the present-day Muslim world, intended to provide inspiration for the creation of new articles and categories. This list is not complete; please add to it as needed. This list may contain multiple transliterations of the same word: please do not delete the multiple alternative spellings—instead, please make redirects to the appropriate pre-existing Wikipedia article if one is present.
Shams ad-Dīn adh-Dhahabī, also known as Shams ad-Dīn Abū ʿAbdillāh Muḥammad ibn Aḥmad ibn ʿUthmān ibn Qāymāẓ ibn ʿAbdillāh at-Turkumānī al-Fāriqī ad-Dimashqī was an Athari theologian, Islamic historian and Hadith scholar.

The Muwaṭṭaʾ or Muwatta Imam Malik of Imam Malik (711–795) written in the 8th-century, is one of the earliest collections of hadith texts comprising the subjects of Islamic law, compiled by the Imam, Malik ibn Anas. Malik's best-known work, Al-Muwatta was the first legal work to incorporate and combine hadith and fiqh.
Muhammad ibn Thalib ibn Abd Allah ibn Ni`mat Allah ibn Sadr ad-Din ibn Shaykh Baha' ad-Din ash-Shirazi was a 15th-century Persian physician from Shiraz, Iran.
Jābir ibn ʿAbd Allāh ibn ʿAmr ibn Ḥarām al-Anṣārī, Abu Muhammad and Abu Abd al-Rahman also wrote his nickname was a prominent companion of the Islamic prophet Muhammad. Imami sources say Jabir was one of Ali's special and chosen companions and one of Hassan, Hussein, Zain al-Abidin and Muhammad Baqir's companions. Jaber narrated hadiths from Abu Bakr, Umar, Ammar ibn Yasir and Muadh ibn Jabal, and he narrated hadiths from young companions including Saʽid al-Khudri and Abu Hurayra. Jabir bin Abdullah also had a scientific reputation among the companions. According to Hisham ibn Urwah, he had a circle for teaching in the Prophet's Mosque, which brought followers around him in connection with the Quran.
Ibn al‐Bannāʾ al‐Marrākushī, full name: Abu'l-Abbas Ahmad ibn Muhammad ibn Uthman al-Azdi al-Marrakushi, was a Maghrebi Muslim polymath who was active as a mathematician, astronomer, Islamic scholar, Sufi and astrologer.

Mishkat al-Masabih by Walī ad-Dīn Abū ʿAbd Allāh Muḥammad ibn ʿAbd Allāh al-Khaṭīb at-Tibrīzī (d.1248) is an expanded and revised version of al-Baghawī's Maṣābīḥ as-Sunnah. Khaṭīb at-Tibrīzī rendered this version of the original text more accessible to those not having an advanced knowledge of the science of hadith.
Abu Ja'far Muhammad ibn 'Ali ibn Babawayh al-Qummi, commonly referred to as Ibn Babawayh or al-Shaykh al-Saduq was a Persian Shia Islamic scholar whose work, entitled Man La Yahduruhu al-Faqih, forms part of The Four Books of the Shia Hadith collection.
Abū Aḥmad ʿAbd Allāh ibn Muḥammad ibn Ismāʿīl, was a descendant of the Islamic prophet Muhammad and the eight of the Isma'ili Imams, succeeding his father, Muhammad ibn Isma'il. Abd Allah traveled throughout Persia and the Middle East. At an unknown date, in the first half of the 3rd/9th century, he found refuge in Syria, where he eventually re-established contact with some of his da'is, and settled in Salamiyah, continuing to pose as a Hashimite merchant. Abd Allah did not reveal his true identity publicly and only a few high ranking Isma'ili hujjats and da'is were aware of his whereabouts. He is known by the epithets al-Wāfī and al-Raḍī. Abd Allah designated his son Ahmad as his successor and died around 828.
ʿAbd Allāh ibn ʿUmar ibn al-Khaṭṭāb, commonly known as Ibn Umar, was a companion of the Islamic prophet Muhammad and a son of the second Caliph Umar. He was a prominent authority in hadith and law. He remained neutral during the events of the first Fitna (656–661).
Abd Allah ibn Amr ibn al-As was the son of Amr ibn al-As of Banu Sahm and was a companion of the Islamic prophet Muhammad. He was the author of "Al-Sahifah al-Sadiqah", the first known hadith compilation document. The document contained about one thousand of Muhammad's narrations.

The doctrine of the Imamate in Isma'ilism differs from that of the Twelvers because the Isma'ilis had living Imams for centuries after the last Twelver Imam went into concealment. They followed Isma'il ibn Ja'far, elder brother of Musa al-Kadhim, as the rightful Imam after his father, Ja'far al-Sadiq. The Ismailis believe that whether Imam Ismail did or did not die before Imam Ja'far, he had passed on the mantle of the imamate to his son Muhammad ibn Isma'il as the next imam.

Sahifah of al-Ridha, also known as Sahifat of al-Reza and Sahifatal-Imam al-Ridha, is a collection of 240 hadiths attributed to Ali ibn Musa al-Ridha, the eighth Shia Imam.
‘Abd Allāh ibn ‘Abbās ibn Ṣiddīq al-Ḥanafī al-Makkī was the penultimate Hanafi Mufti of Mecca.
Al-Kūfah began as a military base ca. 670 near Ḥīrah on the western branch of the Euphrates river and grew, as had its counterpart at Al-Basrah thirty years earlier also grown, from an encampment into a town that attracted the great intellectual elites from across the region. The first grammarian of al-Kūfah was Al-Ru'asi who lived in the eighth century, whereas the earliest scholars of the School at Baṣrah, lived during the seventh century. The great intellectual project that developed out of both schools of philology, created the sciences of Arabic grammar and lexicography. What emerged from an impetus to interpret the sacred texts of the Qu’rān and Ḥadīth, by humanists of al-Baṣrah and al-Kūfah, led to a communal quest for the purest, least corrupt, Arabic source material, for which they turned to the Pre-Islamic oral poetry as recited by the rāwī. The compositions of famous poets were collected, arranged, and committed to writing. The grammarians of al-Baṣrah and al-Kūfah collected the ancient Arabian poetry and arranged the material into “Dīwān” according to certain principles; either by classes of individuals, tribal groupings, selected qaṣīdas, or by themes of fragments, and edited into anthologies. Examples of their works are the Mu’allaqāt, and the Mufaḍḍaliyāt by al-Mufaḍḍal al-Ḍabbī.
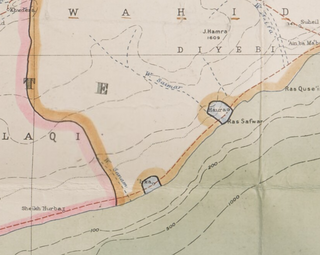
The Sheikhdom of al-ʽIrqa was a city-state which was part of the Protectorate of South Arabia, and existed from the 19th century to 1951.
References
- ↑ Savage-Smith, Emilie. "Asfarā'nī, 'Abd Allāh ibn Aḥmad ibn Muḥammad". Islamic Medical Manuscripts at the National Library of Medicine. National Library of Medicine. Retrieved 8 December 2022.