
Abyei District was a former district of the Sudan, considered part of the state of West Kurdufan. Upon the dissolution of West Kurdufan in 2005, it was included in the state of South Kurdufan. Its administrative centre was the town of Abyei.

Abyei District was a former district of the Sudan, considered part of the state of West Kurdufan. Upon the dissolution of West Kurdufan in 2005, it was included in the state of South Kurdufan. Its administrative centre was the town of Abyei.
| | This section needs expansion. You can help by adding to it. (July 2011) |
The 2004 Protocol on the resolution of the Abyei conflict (Abyei Protocol) in the Comprehensive Peace Agreement (CPA) that ended the Second Sudanese Civil War included provisions to replace the Abyei district with a new jurisdiction to be accorded "special administrative status". [1] The new area was to have different borders, intended to represent "the area of the nine Ngok Dinka chiefdoms transferred to Kordofan in 1905", with demarcation to be determined by a multinational commission. After considerable dispute, a consensus on boundaries enclosing a territory considerably smaller than the existing Abyei district was reached in 2009. A new administration was established for the new Abyei Area, covering the southwestern part of the former district. It is unclear what local government provisions were put in place for the district's remaining territory.

A federated state is a territorial and constitutional community forming part of a federation. Such states differ from fully sovereign states, in that they do not have full sovereign powers, as the sovereign powers have been divided between the federated states and the central or federal government. Importantly, federated states do not have standing as entities of international law. Instead, the federal union as a single entity is the sovereign state for purposes of international law. Depending on the constitutional structure of a particular federation, a federated state can hold various degrees of legislative, judicial, and administrative jurisdiction over a defined geographic territory and is a form of regional government.

Below is a list of the 18 states of the Sudan. Prior to 9 July 2011, the Republic of the Sudan was composed of 25 states. The ten southern states now form part of the independent country of South Sudan. Two additional states were created in 2012 within the Darfur region, and one in 2013 in Kordofan, bringing the total to 18.
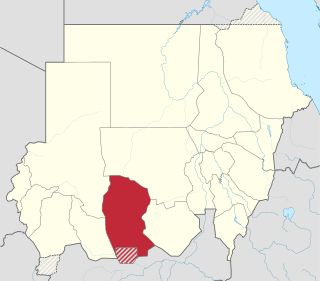
West Kordofan is one of the 18 wilayat or provinces of Sudan. In 2006 it had an area of 111,373 km2 and an estimated population of approximately 1,320,405. Al-Fulah is the capital of the state.
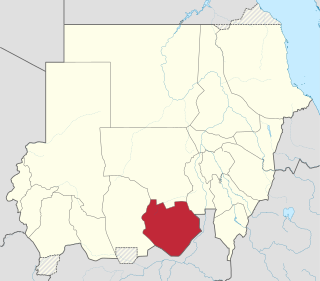
South Kordofan is one of the 18 wilayat or states of Sudan. It has an area of 158,355 km2 and an estimated population of approximately 2,107,623 people. Kaduqli is the capital of the state. It is centered on the Nuba Mountains. At one time it was supposed that South Kordofan was the only state in (North) Sudan suitable for producing oil, but oil has also been discovered in neighboring White Nile State in larger quantities.

North Darfur State is one of the wilayat or states of Sudan. It is one of the five states composing the Darfur region. It has an area of 296,420 km2 and an estimated population of approximately 2,304,950 in 2018. Al-Fashir is the capital of the state. Other significant towns include Ailliet, Kebkabiya, Kutum, Mellit (Malit), Tawilah and Umm Keddada.

The Bahr el Ghazal is a region of northwestern South Sudan. Its name came from the river Bahr el Ghazal. The name translates as "sea of gazelles" from Arabic.
An autonomous administrative division is a subnational administrative division or internal territory of a sovereign state that has a degree of autonomy—self-governance—under the national government. Autonomous areas are distinct from the constituent units of a federation in that they possess unique powers for their given circumstances. Typically, it is either geographically distinct from the rest of the state or populated by a national minority, which may exercise home rule. Decentralization of self-governing powers and functions to such divisions is a way for a national government to try to increase democratic participation or administrative efficiency or to defuse internal conflicts. States that include autonomous areas may be federacies, federations, or confederations. Autonomous areas can be divided into territorial autonomies, subregional territorial autonomies, and local autonomies.

This article covers the period of the history of Sudan between 1985 and 2019 when the Sudanese Defense Minister Abdel Rahman Swar al-Dahab seized power from Sudanese President Gaafar Nimeiry in the 1985 Sudanese coup d'état. Not long after, Lieutenant General Omar al-Bashir, backed by an Islamist political party, the National Islamic Front, overthrew the short lived government in a coup in 1989 where he ruled as President until his fall in April 2019. During Bashir's rule, also referred to as Bashirist Sudan, he was re-elected three times while overseeing the independence of South Sudan in 2011. His regime was criticized for human rights abuses, atrocities and genocide in Darfur and allegations of harboring and supporting terrorist groups in the region while being subjected to United Nations sanctions beginning in 1995, resulting in Sudan's isolation as an international pariah.
Heglig, or Panthou, is a small town at the border between the South Kordofan state of Sudan and the Unity State in South Sudan. The entirety of Heglig is claimed by both Sudan and South Sudan, but administered by Sudan. The area was contested during the Sudanese Civil War. In mid-April 2012, South Sudan's Sudan People's Liberation Army (SPLA) captured the Heglig oil field from Sudan. Sudan took it back at the Second Battle of Heglig ten days later.
The Daju people are a group of seven distinct ethnicities speaking related languages living on both sides of the Chad-Sudan border and in the Nuba Mountains. Separated by distance and speaking different languages, at present, they generally have little cultural affinity to each other.

The Abyei Area is an area of 10,546 km2 or 4,072 sq mi on the border between South Sudan and Sudan that has been accorded "special administrative status" by the 2004 Protocol on the Resolution of the Abyei Conflict in the Comprehensive Peace Agreement (CPA) that ended the Second Sudanese Civil War. The capital of the Abyei Area is Abyei Town. Under the terms of the Abyei Protocol, the Abyei Area is considered, on an interim basis, to be simultaneously part of both the Republic of South Sudan and Republic of Sudan, effectively a condominium.

The Comprehensive Peace Agreement, also known as the Naivasha Agreement, was an accord signed on 9 January 2005, by the Sudan People's Liberation Movement (SPLM) and the Government of Sudan. The CPA was meant to end the Second Sudanese Civil War, develop democratic governance countrywide, and share oil revenues. It also set a timetable for a Southern Sudanese independence referendum.

Southern Sudan was an autonomous region consisting of the ten southern states of Sudan between its formation in July 2005 and independence as the Republic of South Sudan in July 2011. The autonomous government was initially established in Rumbek and later moved to Juba. It was bordered by Ethiopia to the east; Kenya, Uganda, and the Democratic Republic of the Congo to the south; and the Central African Republic to the west. To the north lies the predominantly Arab and Muslim region directly under the control of the central government. The region's autonomous status was a condition of a peace agreement between the Sudan People's Liberation Army/Movement (SPLA/M) and the Government of Sudan represented by the National Congress Party ending the Second Sudanese Civil War. The conflict was Africa's longest running civil war.
United Nations Security Council Resolution 1990, adopted unanimously on June 27, 2011, after recalling all previous resolutions on the situation in Sudan and the Comprehensive Peace Agreement, the Council established the United Nations Interim Security Force for Abyei (UNISFA) in the disputed Abyei region between Sudan and South Sudan.

The geography of South Sudan describes the physical features of South Sudan, a country in East Africa. South Sudan is a landlocked country and borders – clockwise – Sudan from the north, Ethiopia from the east, Kenya, Uganda and the Democratic Republic of the Congo from the south and the Central African Republic from the west.
The history of South Sudan comprises the history of the territory of present-day South Sudan and the peoples inhabiting the region.
United Nations Security Council Resolution 1996, adopted unanimously on July 8, 2011, after welcoming the independence of South Sudan from Sudan, the Council established the United Nations Mission in the Republic of South Sudan (UNMISS) for an initial period of one year.
United Nations Security Council Resolution 2024 was unanimously adopted on 14 December 2011.
The Heglig Crisis was a brief war fought between the countries of Sudan and South Sudan in 2012 over oil-rich regions between South Sudan's Unity and Sudan's South Kordofan states. South Sudan invaded and briefly occupied the small border town of Heglig before being pushed back by the Sudanese army. Small-scale clashes continued until an agreement on borders and natural resources was signed on 26 September, resolving most aspects of the conflict.
Tonj South County is an administrative area in Warrap State, South Sudan.