Related Research Articles
Earned Value Management (EVM), earned value project management, or earned value performance management (EVPM) is a project management technique for measuring project performance and progress in an objective manner.

A web server is computer software and underlying hardware that accepts requests via HTTP or its secure variant HTTPS. A user agent, commonly a web browser or web crawler, initiates communication by making a request for a web page or other resource using HTTP, and the server responds with the content of that resource or an error message. A web server can also accept and store resources sent from the user agent if configured to do so.
Project management software (PMS) has the capacity to help plan, organize, and manage resource tools and develop resource estimates. Depending on the sophistication of the software, it can manage estimation and planning, scheduling, cost control and budget management, resource allocation, collaboration software, communication, decision-making, quality management, time management and documentation or administration systems. Numerous PC and browser-based project management software and contract management software products and services are available.
Value engineering (VE) is a systematic analysis of the functions of various components and materials to lower the cost of goods, products and services with a tolerable loss of performance or functionality. Value, as defined, is the ratio of function to cost. Value can therefore be manipulated by either improving the function or reducing the cost. It is a primary tenet of value engineering that basic functions be preserved and not be reduced as a consequence of pursuing value improvements. The term "value management" is sometimes used as a synonym of "value engineering", and both promote the planning and delivery of projects with improved performance

Justin Kirk is an American actor. He is best known for portraying Prior Walter in Mike Nichols's screen adaptation of Angels in America, for which he was nominated for the Primetime Emmy Award for Outstanding Supporting Actor in a Miniseries or a Movie, losing to costar Jeffrey Wright. Kirk is also known for his portrayal of Andy Botwin on the series Weeds.
APB may refer to:
The World Wide Web has become a major delivery platform for a variety of complex and sophisticated enterprise applications in several domains. In addition to their inherent multifaceted functionality, these Web applications exhibit complex behaviour and place some unique demands on their usability, performance, security, and ability to grow and evolve. However, a vast majority of these applications continue to be developed in an ad hoc way, contributing to problems of usability, maintainability, quality and reliability. While Web development can benefit from established practices from other related disciplines, it has certain distinguishing characteristics that demand special considerations. In recent years, there have been developments towards addressing these considerations.
The ARM Advanced Microcontroller Bus Architecture (AMBA) is an open-standard, on-chip interconnect specification for the connection and management of functional blocks in system-on-a-chip (SoC) designs. It facilitates development of multi-processor designs with large numbers of controllers and components with a bus architecture. Since its inception, the scope of AMBA has, despite its name, gone far beyond microcontroller devices. Today, AMBA is widely used on a range of ASIC and SoC parts including applications processors used in modern portable mobile devices like smartphones. AMBA is a registered trademark of ARM Ltd.
In the United States, the processes of government procurement enable federal, state and local government bodies in the country to acquire goods, services, and interests in real property.

An all-points bulletin (APB) is an electronic information broadcast sent from one sender to a group of recipients, to rapidly communicate an important message. The technology used to send this broadcast has varied throughout time, and includes teletype, radio, computerized bulletin board systems (CBBS), and the Internet.

APB: All Points Bulletin is an open world multiplayer online video game for Microsoft Windows developed by Realtime Worlds and acquired by Reloaded Productions, which is part of the GamersFirst company. Little Orbit acquired GamersFirst in 2018 and is now in charge of the game's development. Based in urban sprawls and featuring two factions, Enforcers and the Criminals, can form sub-groups in either faction and carry out missions. The game design was led by David Jones. It was released in 2010 in North America and Europe.

In computer architecture, multithreading is the ability of a central processing unit (CPU) to provide multiple threads of execution concurrently, supported by the operating system. This approach differs from multiprocessing. In a multithreaded application, the threads share the resources of a single or multiple cores, which include the computing units, the CPU caches, and the translation lookaside buffer (TLB).
Cost engineering is "the engineering practice devoted to the management of project cost, involving such activities as estimating, cost control, cost forecasting, investment appraisal and risk analysis". "Cost Engineers budget, plan and monitor investment projects. They seek the optimum balance between cost, quality and time requirements."

A computer cluster is a set of computers that work together so that they can be viewed as a single system. Unlike grid computers, computer clusters have each node set to perform the same task, controlled and scheduled by software.
The Analysis of Alternatives (AoA) in the United States is a requirement of military acquisition policy, as controlled by the Office of Management and Budget (OMB) and the United States Department of Defense (DoD). It ensures that at least three feasible alternatives are analyzed prior to making costly investment decisions. The AoA establishes and benchmarks metrics for Cost, Schedule, Performance (CSP) and Risk (CSPR) depending on military "needs" derived from the Joint Capabilities Integration Development System process. It moves away from employing a single acquisition source to the exploration of multiple alternatives so agencies have a basis for funding the best possible projects in a rational, defensible manner considering risk and uncertainty.
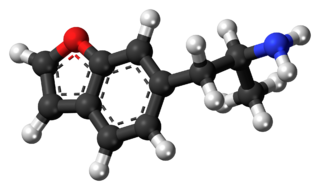
6-APB is an empathogenic psychoactive compound of the substituted benzofuran and substituted phenethylamine classes. 6-APB and other compounds are sometimes informally called "Benzofury" in newspaper reports. It is similar in structure to MDA, but differs in that the 3,4-methylenedioxyphenyl ring system has been replaced with a benzofuran ring. 6-APB is also the unsaturated benzofuran derivative of 6-APDB. It may appear as a tan grainy powder. While the drug never became particularly popular, it briefly entered the rave and underground clubbing scene in the UK before its sale and import were banned. It falls under the category of research chemicals, sometimes called "legal highs." Because 6-APB and other substituted benzofurans have not been explicitly outlawed in some countries, they are often technically legal, contributing to their popularity.

5-APB is an empathogenic psychoactive compound of the substituted benzofuran, substituted amphetamine and substituted phenethylamine classes. 5-APB and other compounds are sometimes informally called "Benzofury".
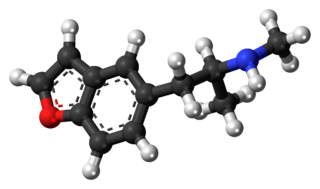
5-MAPB is an entactogenic designer drug similar to MDMA in its structure and effects.

5-EAPB is a potentially entactogenic amphetamine which is structurally related to 5-MAPB and 5-APB. It might be predicted to show similar effects to these drugs in humans, but the pharmacology of 5-EAPB remains unstudied as of 2020.
Key Performance Parameters (KPPs) specify what the critical performance goals are in a United States Department of Defense (DoD) acquisition under the JCIDS process.
References
- ↑ Cochrane, C. B. (July 2004). Joint program management handbook. Fort Belvoir, Washington: DIANE Publishing. p. 20. ISBN 0-16-073130-5.