Related Research Articles
New Technology File System (NTFS) is a proprietary journaling file system developed by Microsoft. Starting with Windows NT 3.1, it is the default file system of the Windows NT family. It superseded File Allocation Table (FAT) as the preferred filesystem on Windows and is supported in Linux and BSD as well. NTFS reading and writing support is provided using a free and open-source kernel implementation known as NTFS3 in Linux and the NTFS-3G driver in BSD. Windows can convert FAT32/16/12 into NTFS without the need to rewrite all files. NTFS uses several files typically hidden from the user to store metadata about other files stored on the drive which can help improve speed and performance when reading data. Unlike FAT and High Performance File System (HPFS), NTFS supports access control lists (ACLs), filesystem encryption, transparent compression, sparse files and file system journaling. NTFS also supports shadow copy to allow backups of a system while it is running, but the functionality of the shadow copies varies between different versions of Windows.
File Allocation Table (FAT) is a file system developed for personal computers. Originally developed in 1977 for use on floppy disks, it was adapted for use on hard disks and other devices. It is often supported for compatibility reasons by current operating systems for personal computers and many mobile devices and embedded systems, allowing interchange of data between disparate systems. The increase in disk drives capacity required three major variants: FAT12, FAT16 and FAT32. The FAT standard has also been expanded in other ways while generally preserving backward compatibility with existing software.

Disk partitioning or disk slicing is the creation of one or more regions on secondary storage, so that each region can be managed separately. These regions are called partitions. It is typically the first step of preparing a newly installed disk, before any file system is created. The disk stores the information about the partitions' locations and sizes in an area known as the partition table that the operating system reads before any other part of the disk. Each partition then appears to the operating system as a distinct "logical" disk that uses part of the actual disk. System administrators use a program called a partition editor to create, resize, delete, and manipulate the partitions. Partitioning allows the use of different filesystems to be installed for different kinds of files. Separating user data from system data can prevent the system partition from becoming full and rendering the system unusable. Partitioning can also make backing up easier. A disadvantage is that it can be difficult to properly size partitions, resulting in having one partition with too much free space and another nearly totally allocated.
A disk image, in computing, is a computer file containing the contents and structure of a disk volume or of an entire data storage device, such as a hard disk drive, tape drive, floppy disk, optical disc, or USB flash drive. A disk image is usually made by creating a sector-by-sector copy of the source medium, thereby perfectly replicating the structure and contents of a storage device independent of the file system. Depending on the disk image format, a disk image may span one or more computer files.
Disk formatting is the process of preparing a data storage device such as a hard disk drive, solid-state drive, floppy disk or USB flash drive for initial use. In some cases, the formatting operation may also create one or more new file systems. The first part of the formatting process that performs basic medium preparation is often referred to as "low-level formatting". Partitioning is the common term for the second part of the process, dividing the device into several sub-devices and, in some cases, writing information to the device allowing an operating system to be booted from it. The third part of the process, usually termed "high-level formatting" most often refers to the process of generating a new file system. In some operating systems all or parts of these three processes can be combined or repeated at different levels and the term "format" is understood to mean an operation in which a new disk medium is fully prepared to store files. Some formatting utilities allow distinguishing between a quick format, which does not erase all existing data and a long option that does erase all existing data.

SystemRescue is a Linux distribution for x86 64 and x86 computers. The primary purpose of SystemRescue is to repair unbootable or otherwise damaged computer systems after a system crash. SystemRescue is not intended to be used as a permanent operating system. It runs from a Live CD, a USB flash drive or any type of hard drive. It was designed by a team led by François Dupoux, and is based on Arch Linux since version 6.0. Starting with version 6.0, it has systemd as its init system.

Network-attached storage (NAS) is a file-level computer data storage server connected to a computer network providing data access to a heterogeneous group of clients. NAS is specialized for serving files either by its hardware, software, or configuration. It is often manufactured as a computer appliance – a purpose-built specialized computer. NAS systems are networked appliances that contain one or more storage drives, often arranged into logical, redundant storage containers or RAID. Network-attached storage removes the responsibility of file serving from other servers on the network. They typically provide access to files using network file sharing protocols such as NFS, SMB, or AFP. From the mid-1990s, NAS devices began gaining popularity as a convenient method of sharing files among multiple computers. Potential benefits of dedicated network-attached storage, compared to general-purpose servers also serving files, include faster data access, easier administration, and simple configuration.
In information technology, a backup, or data backup is a copy of computer data taken and stored elsewhere so that it may be used to restore the original after a data loss event. The verb form, referring to the process of doing so, is "back up", whereas the noun and adjective form is "backup". Backups can be used to recover data after its loss from data deletion or corruption, or to recover data from an earlier time. Backups provide a simple form of disaster recovery; however not all backup systems are able to reconstitute a computer system or other complex configuration such as a computer cluster, active directory server, or database server.
Disk cloning is the process of creating a 1-to-1 copy of a hard disk drive (HDD) or solid-state drive (SSD), not just its files. Disk cloning may be used for upgrading a disk or replacing an aging disk with a fresh one. In this case, the clone can replace the original disk in its host computer. Disk cloning may also be used for disaster recovery or forensics. In the context of backup software, disk cloning is very similar to disk imaging; in case of the latter, a 1-to-1 copy of a disk is created inside a disk image file.
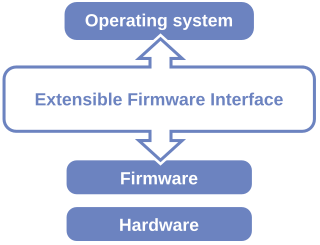
The Unified Extensible Firmware Interface (UEFI) is a publicly available specification that defines a software interface between an operating system and platform firmware. UEFI replaces the legacy Basic Input/Output System (BIOS) firmware interface originally present in all IBM PC-compatible personal computers, with most UEFI firmware implementations providing support for legacy BIOS services. UEFI can support remote diagnostics and repair of computers, even with no operating system installed.

In computing, file system or filesystem is a method and data structure that the operating system uses to control how data is stored and retrieved. Without a file system, data placed in a storage medium would be one large body of data with no way to tell where one piece of data stopped and the next began, or where any piece of data was located when it was time to retrieve it. By separating the data into pieces and giving each piece a name, the data is easily isolated and identified. Taking its name from the way a paper-based data management system is named, each group of data is called a "file." The structure and logic rules used to manage the groups of data and their names is called a "file system."

Acronis International GmbH, simply referred to as Acronis, is a global technology company with its corporate headquarters in Schaffhausen, Switzerland and global headquarters in Singapore. Acronis develops on-premises and cloud software for backup, disaster recovery, and secure file sync and share and data access. Acronis has 18 offices worldwide. Its R&D centers, Acronis Labs, are based in Russia, the United States and Singapore. Acronis has Cloud data centers around the world, including the United States, France, Singapore, Japan, and Germany.
In computing, data recovery is a process of salvaging deleted, inaccessible, lost, corrupted, damaged or formatted data from secondary storage, removable media or files, when the data stored in them cannot be accessed in a usual way. The data is most often salvaged from storage media such as internal or external hard disk drives (HDDs), solid-state drives (SSDs), USB flash drives, magnetic tapes, CDs, DVDs, RAID subsystems, and other electronic devices. Recovery may be required due to physical damage to the storage devices or logical damage to the file system that prevents it from being mounted by the host operating system (OS).

The terms Recovery disc, Rescue Disk/Disc and Emergency Disk all refer to a capability to boot from an external device, possibly a thumb drive, that includes a self-running operating system: the ability to be a boot disk/Disc that runs independent of an internal hard drive that may be failing, or for some other reason is not the operating system to be run.
This article refers to a product of Acronis targeting home users. For the business solution of the same name, please see Acronis Cyber Protect
In computing, label is a command included with some operating systems. It is used to create, change, or delete a volume label on a logical drive, such as a hard disk partition or a floppy disk. Used without parameters, label changes the current volume label or deletes the existing label.
This is a partial comparison list of disk cloning software, computer programs that can copy the contents of one disk into another disk or into a disk image.

Clonezilla is a suite of open source drive cloning, drive imaging and system deployment utilities used to simpify deployment and maintenance of a group of computers. CloneZilla Server Edition uses multicast technologies to deploy a single image file to a group of computers on a local area network. Clonezilla was designed by Steven Shiau and developed by the NCHC Free Software Labs in Taiwan.
A master boot record (MBR) is a special type of boot sector at the very beginning of partitioned computer mass storage devices like fixed disks or removable drives intended for use with IBM PC-compatible systems and beyond. The concept of MBRs was publicly introduced in 1983 with PC DOS 2.0.
A FAT file system is a specific type of computer file system architecture and a family of industry-standard file systems utilizing it.