Other uses
- Act of Union, a poem by Seamus Heaney, written in 1975
- Bull of Union with the Greeks (Laetentur Caeli), a 1439 papal bull sometimes referred to as the Act of Union
Act of Union may refer to:
The Acts of Union were two Acts of Parliament: the Union with Scotland Act 1706 passed by the Parliament of England, and the Union with England Act passed in 1707 by the Parliament of Scotland. They put into effect the terms of the Treaty of Union that had been agreed on 22 July 1706, following negotiation between commissioners representing the parliaments of the two countries. By the two Acts, the Kingdom of England and the Kingdom of Scotland—which at the time were separate states with separate legislatures, but with the same monarch—were, in the words of the Treaty, "United into One Kingdom by the Name of Great Britain".

The Parliament of the United Kingdom is the supreme legislative body of the United Kingdom, the Crown dependencies and the British overseas territories. It alone possesses legislative supremacy and thereby ultimate power over all other political bodies in the UK and the overseas territories. Parliament is bicameral but has three parts, consisting of the sovereign (Crown-in-Parliament), the House of Lords, and the House of Commons. Both houses of Parliament meet in separate chambers at the Palace of Westminster in the City of Westminster, one of the inner boroughs of the capital city, London.

The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a sovereign country in north-western Europe, off the north-western coast of the European mainland. The United Kingdom includes the island of Great Britain, the north-eastern part of the island of Ireland, and many smaller islands within the British Isles. Northern Ireland shares a land border with the Republic of Ireland. Otherwise, the United Kingdom is surrounded by the Atlantic Ocean, with the North Sea to the east, the English Channel to the south and the Celtic Sea to the south-west, giving it the 12th-longest coastline in the world. The Irish Sea separates Great Britain and Ireland. The total area of the United Kingdom is 93,628 square miles (242,500 km2), with an estimated population in 2020 of over 67 million.

The legislatures of the United Kingdom are derived from a number of different sources. The parliament of the United Kingdom is the supreme legislative body for the United Kingdom and the British overseas territories with Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland each having their own devolved legislatures. Each of the three major jurisdictions of the United Kingdom has its own laws and legal system.

The Union Jack, or Union Flag, is the de facto national flag of the United Kingdom. Although no law has been passed making the Union Jack the official national flag of the United Kingdom, it has effectively become such through precedent. It is sometimes asserted that the term Union Jack properly refers only to naval usage, which assertion has been dismissed by the Flag Institute in 2013, following historical investigations. The flag has official status in Canada, by parliamentary resolution, where it is known as the Royal Union Flag. It is the national flag of all British overseas territories, being localities within the British state, or realm, although local flags have also been authorised for most, usually comprising the blue or red ensign with the Union Flag in the canton and defaced with the distinguishing arms of the territory. These may be flown in place of, or along with the national flag. Governors of British Overseas Territories have their own personal flags, which are the Union Flag with the distinguishing arms of the colony at the centre. The Union Flag also appears in the canton of the flags of several nations and territories that are former British possessions or dominions, as well as in the flag of the US State of Hawaii, which has no such connection.

The United Kingdom has four legal systems, each of which derives from a particular geographical area for a variety of historical reasons: English law, Scots law, Northern Ireland law, and, since 2007, purely Welsh law. Overarching these systems is the law of the United Kingdom, also known as United Kingdom law. UK law arises from laws applying to the United Kingdom and/or its citizens as a whole, most obviously constitutional law, but also other areas, for instance tax law.

The Acts of Union 1800 were parallel acts of the Parliament of Great Britain and the Parliament of Ireland which united the Kingdom of Great Britain and the Kingdom of Ireland to create the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland. The acts came into force on 1 January 1801, and the merged Parliament of the United Kingdom had its first meeting on 22 January 1801.

The administrative geography of the United Kingdom is complex, multi-layered and non-uniform. The United Kingdom, a sovereign state to the northwest of continental Europe, consists of England, Northern Ireland, Scotland and Wales. For local government in the United Kingdom, England, Northern Ireland, Scotland and Wales each have their own system of administrative and geographic demarcation. Consequently, there is "no common stratum of administrative unit encompassing the United Kingdom".
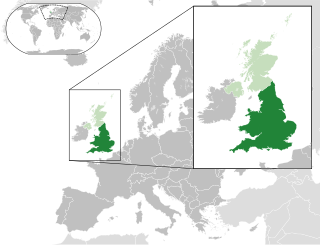
England and Wales is a legal jurisdiction covering England and Wales, two of the four countries of the United Kingdom. England and Wales forms the constitutional successor to the former Kingdom of England and follows a single legal system, known as English law.

The Kingdom of England was a sovereign state on the island of Great Britain from 12 July 927, when it emerged from various Anglo-Saxon kingdoms, until 1 May 1707, when it united with Scotland to form the Kingdom of Great Britain. The Kingdom of England was among the most powerful states in Europe during the medieval period.

Politics of England forms the major part of the wider politics of the United Kingdom, with England being more populous than all the other countries of the United Kingdom put together. As England is also by far the largest in terms of area and GDP, its relationship to the UK is somewhat different from that of Scotland, Wales or Northern Ireland. The English capital London is also the capital of the UK, and English is the dominant language of the UK. Dicey and Morris (p26) list the separate states in the British Islands. "England, Scotland, Northern Ireland, the Isle of Man, Jersey, Guernsey, Alderney, and Sark.... is a separate country in the sense of the conflict of laws, though not one of them is a State known to public international law." But this may be varied by statute.

In the United Kingdom (UK), each of the electoral areas or divisions called constituencies elects one member to the House of Commons.
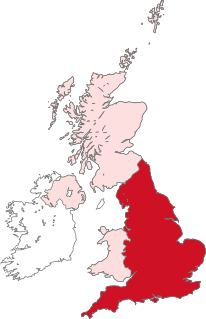
English independence is a political stance advocating secession of England from the United Kingdom. Support for secession of England has been influenced by the increasing devolution of political powers to Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland, where independence from the United Kingdom is a prominent subject of political debate.
Citation of United Kingdom legislation includes the systems used for legislation passed by devolved parliaments and assemblies, for secondary legislation, and for prerogative instruments. It is relatively complex both due to the different sources of legislation in the United Kingdom, and because of the different histories of the constituent countries of the United Kingdom.

Unionism in the United Kingdom, also referred to as British unionism, is a political ideology favouring the continued unity of England, Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland as one sovereign state, the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland. Those who support the union are referred to as "Unionists". British unionism can be associated with British nationalism, which asserts that the British are a nation and promotes the cultural unity of the Britons, which may include people of English, Scottish, Welsh, Irish, Cornish and Manx descent.

The formation of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland has involved personal and political union across Great Britain and the wider British Isles. The United Kingdom is the most recent of a number of sovereign states that have been established in Great Britain at different periods in history, in different combinations and under a variety of polities. Historian Norman Davies has counted sixteen different states over the past 2,000 years.

The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland (UK), since 1922, comprises three constituent countries: England, Scotland, and Wales, and the province of Northern Ireland,. The UK Prime Minister's website has used the phrase "countries within a country" to describe the United Kingdom. Some statistical summaries, such as those for the twelve NUTS 1 regions of the United Kingdom, refer to Scotland, Wales, and Northern Ireland as "regions". With regard to Northern Ireland, Scotland and Wales particularly, the descriptive name one uses "can be controversial, with the choice often revealing one's political preferences".

The British people or Britons, also known colloquially as Brits, are the citizens of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, the British Overseas Territories, and the Crown dependencies. British nationality law governs modern British citizenship and nationality, which can be acquired, for instance, by descent from British nationals. When used in a historical context, "British" or "Britons" can refer to the Ancient Britons, the indigenous inhabitants of Great Britain and Brittany, whose surviving members are the modern Welsh people, Cornish people, and Bretons. It also refers to citizens of the former British Empire, who settled in the country prior to 1973, and hold neither UK citizenship nor nationality.

In England, Unionism is a political ideology which favours the continuation of some form of political union between England and the other countries of the United Kingdom. It is part of the wider British unionist movement and is closely linked to the notion of Britishness. Unionism in England is characterised by both opposition to England's independence as a separate state and the belief that Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland should continue to be constituent countries of the Union.
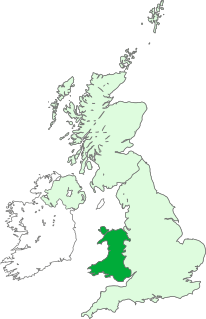
Unionism in Wales favours the continuation of some form of political union between Wales and the other countries of the United Kingdom, and hence is opposed to Welsh independence.