Related Research Articles

Microwave is a form of electromagnetic radiation with wavelengths shorter than other radio waves but longer than infrared waves. Its wavelength ranges from about one meter to one millimeter, corresponding to frequencies between 300 MHz and 300 GHz, broadly construed. A more common definition in radio-frequency engineering is the range between 1 and 100 GHz, or between 1 and 3000 GHz . The prefix micro- in microwave is not meant to suggest a wavelength in the micrometer range; rather, it indicates that microwaves are small, compared to the radio waves used in prior radio technology.

A radio telescope is a specialized antenna and radio receiver used to detect radio waves from astronomical radio sources in the sky. Radio telescopes are the main observing instrument used in radio astronomy, which studies the radio frequency portion of the electromagnetic spectrum emitted by astronomical objects, just as optical telescopes are the main observing instrument used in traditional optical astronomy which studies the light wave portion of the spectrum coming from astronomical objects. Unlike optical telescopes, radio telescopes can be used in the daytime as well as at night.

In radio engineering, an antenna or aerial is the interface between radio waves propagating through space and electric currents moving in metal conductors, used with a transmitter or receiver. In transmission, a radio transmitter supplies an electric current to the antenna's terminals, and the antenna radiates the energy from the current as electromagnetic waves. In reception, an antenna intercepts some of the power of a radio wave in order to produce an electric current at its terminals, that is applied to a receiver to be amplified. Antennas are essential components of all radio equipment.

A parabolic antenna is an antenna that uses a parabolic reflector, a curved surface with the cross-sectional shape of a parabola, to direct the radio waves. The most common form is shaped like a dish and is popularly called a dish antenna or parabolic dish. The main advantage of a parabolic antenna is that it has high directivity. It functions similarly to a searchlight or flashlight reflector to direct radio waves in a narrow beam, or receive radio waves from one particular direction only. Parabolic antennas have some of the highest gains, meaning that they can produce the narrowest beamwidths, of any antenna type. In order to achieve narrow beamwidths, the parabolic reflector must be much larger than the wavelength of the radio waves used, so parabolic antennas are used in the high frequency part of the radio spectrum, at UHF and microwave (SHF) frequencies, at which the wavelengths are small enough that conveniently sized reflectors can be used.
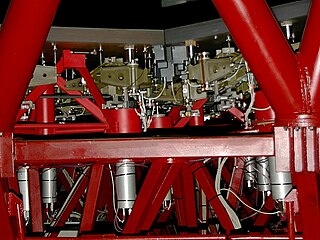
Active optics is a technology used with reflecting telescopes developed in the 1980s, which actively shapes a telescope's mirrors to prevent deformation due to external influences such as wind, temperature, and mechanical stress. Without active optics, the construction of 8 metre class telescopes is not possible, nor would telescopes with segmented mirrors be feasible.

Very-long-baseline interferometry (VLBI) is a type of astronomical interferometry used in radio astronomy. In VLBI a signal from an astronomical radio source, such as a quasar, is collected at multiple radio telescopes on Earth or in space. The distance between the radio telescopes is then calculated using the time difference between the arrivals of the radio signal at different telescopes. This allows observations of an object that are made simultaneously by many radio telescopes to be combined, emulating a telescope with a size equal to the maximum separation between the telescopes.
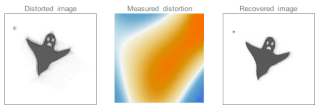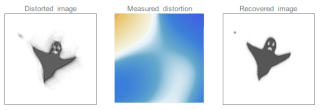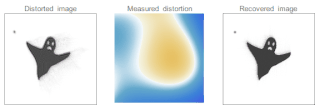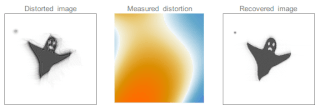
Adaptive optics (AO) is a technique of precisely deforming a mirror in order to compensate for light distortion. It is used in astronomical telescopes and laser communication systems to remove the effects of atmospheric distortion, in microscopy, optical fabrication and in retinal imaging systems to reduce optical aberrations. Adaptive optics works by measuring the distortions in a wavefront and compensating for them with a device that corrects those errors such as a deformable mirror or a liquid crystal array.
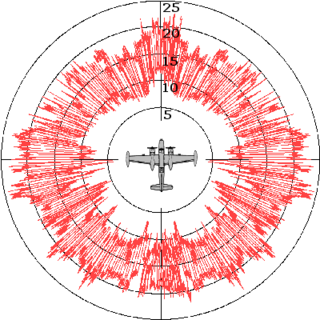
Radar cross-section (RCS), denoted σ, also called radar signature, is a measure of how detectable an object is by radar. A larger RCS indicates that an object is more easily detected.

A horn antenna or microwave horn is an antenna that consists of a flaring metal waveguide shaped like a horn to direct radio waves in a beam. Horns are widely used as antennas at UHF and microwave frequencies, above 300 MHz. They are used as feed antennas for larger antenna structures such as parabolic antennas, as standard calibration antennas to measure the gain of other antennas, and as directive antennas for such devices as radar guns, automatic door openers, and microwave radiometers. Their advantages are moderate directivity, broad bandwidth, low losses, and simple construction and adjustment.

The Submillimeter Array (SMA) consists of eight 6-meter (20 ft) diameter radio telescopes arranged as an interferometer for submillimeter wavelength observations. It is the first purpose-built submillimeter interferometer, constructed after successful interferometry experiments using the pre-existing 15-meter (49 ft) James Clerk Maxwell Telescope and 10.4-meter (34.1 ft) Caltech Submillimeter Observatory as an interferometer. All three of these observatories are located at Mauna Kea Observatory on Mauna Kea, Hawaii, and have been operated together as a ten element interferometer in the 230 and 345 GHz bands. The baseline lengths presently in use range from 16 to 508 meters. The radio frequencies accessible to this telescope range from 194–408 gigahertz (1.545–0.735 mm) which includes rotational transitions of dozens of molecular species as well as continuum emission from interstellar dust grains. Although the array is capable of operating both day and night, most of the observations take place at nighttime when the atmospheric phase stability is best.

A slot antenna consists of a metal surface, usually a flat plate, with one or more holes or slots cut out. When the plate is driven as an antenna by an applied radio frequency current, the slot radiates electromagnetic waves in a way similar to a dipole antenna. The shape and size of the slot, as well as the driving frequency, determine the radiation pattern. Slot antennas are usually used at UHF and microwave frequencies at which wavelengths are small enough that the plate and slot are conveniently small. At these frequencies, the radio waves are often conducted by a waveguide, and the antenna consists of slots in the waveguide; this is called a slotted waveguide antenna. Multiple slots act as a directive array antenna and can emit a narrow fan-shaped beam of microwaves. They are used in standard laboratory microwave sources used for research, UHF television transmitting antennas, antennas on missiles and aircraft, sector antennas for cellular base stations, and particularly marine radar antennas. A slot antenna's main advantages are its size, design simplicity, and convenient adaptation to mass production using either waveguide or PC board technology.

The Allen Telescope Array (ATA), formerly known as the One Hectare Telescope (1hT), is a radio telescope array dedicated to astronomical observations and a simultaneous search for extraterrestrial intelligence (SETI). The array is situated at the Hat Creek Radio Observatory in Shasta County, 290 miles (470 km) northeast of San Francisco, California.

A loop antenna is a radio antenna consisting of a loop or coil of wire, tubing, or other electrical conductor, that for transmitting is usually fed by a balanced power source or for receiving feeds a balanced load. Within this physical description there are two distinct types:

Haystack Observatory is a multidisciplinary radio science center, ionospheric observatory, and astronomical microwave observatory owned by Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT). It is in Westford, Massachusetts, in the United States, about 45 kilometers (28 mi) northwest of Boston. The observatory was built by MIT's Lincoln Laboratory for the United States Air Force and was called the Haystack Microwave Research Facility. Construction began in 1960, and the antenna began operating in 1964. In 1970 the facility was transferred to MIT, which then formed the Northeast Radio Observatory Corporation (NEROC) with other universities to operate the site as the Haystack Observatory. As of January 2012, a total of nine institutions participated in NEROC.
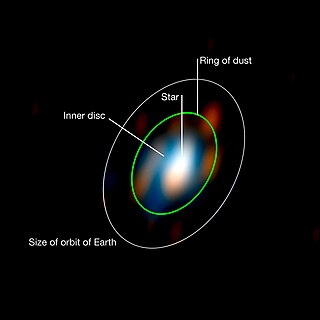
An astronomical interferometer or telescope array is a set of separate telescopes, mirror segments, or radio telescope antennas that work together as a single telescope to provide higher resolution images of astronomical objects such as stars, nebulas and galaxies by means of interferometry. The advantage of this technique is that it can theoretically produce images with the angular resolution of a huge telescope with an aperture equal to the separation, called baseline, between the component telescopes. The main drawback is that it does not collect as much light as the complete instrument's mirror. Thus it is mainly useful for fine resolution of more luminous astronomical objects, such as close binary stars. Another drawback is that the maximum angular size of a detectable emission source is limited by the minimum gap between detectors in the collector array.

A telescope is a device used to observe distant objects by their emission, absorption, or reflection of electromagnetic radiation. Originally it was an optical instrument using lenses, curved mirrors, or a combination of both to observe distant objects – an optical telescope. Nowadays, the word "telescope" is defined as a wide range of instruments capable of detecting different regions of the electromagnetic spectrum, and in some cases other types of detectors.

The Five-hundred-meter Aperture Spherical Telescope, nicknamed Tianyan, is a radio telescope located in the Dawodang depression (大窝凼洼地), a natural basin in Pingtang County, Guizhou, southwest China. FAST has a 500 m (1,600 ft) diameter dish constructed in a natural depression in the landscape. It is the world's largest filled-aperture radio telescope and the second-largest single-dish aperture, after the sparsely-filled RATAN-600 in Russia.

In radio communication, a ground dipole, also referred to as an earth dipole antenna, transmission line antenna, and in technical literature as a horizontal electric dipole (HED), is a huge, specialized type of radio antenna that radiates extremely low frequency (ELF) electromagnetic waves. It is the only type of transmitting antenna that can radiate practical amounts of power in the frequency range of 3 Hz to 3 kHz, commonly called ELF waves. A ground dipole consists of two ground electrodes buried in the earth, separated by tens to hundreds of kilometers, linked by overhead transmission lines to a power plant transmitter located between them. Alternating current electricity flows in a giant loop between the electrodes through the ground, radiating ELF waves, so the ground is part of the antenna. To be most effective, ground dipoles must be located over certain types of underground rock formations. The idea was proposed by U.S. Dept. of Defense physicist Nicholas Christofilos in 1959.

The Large Latin American Millimeter Array (LLAMA) is a single-dish 12 m Nasmyth optics antenna which is under construction in the Puna de Atacama desert in the Province of Salta, Argentina, next to the Qubic experiment. The primary mirror accuracy will allow observation from 40 GHz up to 900 GHz. After installation it will be able to join other similar instruments to perform Very Large Base Line Interferometry or to work in standalone mode. Financial support is provided by the Argentinian and Brazilian governments. The total cost of construction, around US$20 million, and operation as well as the telescope time use will be shared equally by the two countries. Construction planning started in July 2014 after the formal signature of an agreement between the main institutions involved.

The Nançay Radio Observatory, opened in 1956, is part of Paris Observatory, and also associated with the University of Orléans. It is located in the department of Cher in the Sologne region of France. The station consists of several instruments. Most iconic of these is the large decimetric radio telescope, which is one of the largest radio telescopes in the world. Long established are also the radio heliograph, a T-shaped array, and the decametric array operating at wavelengths between 3 m and 30 m.
References
- Parker, D.H. & Payne, J.M. (2002). "Active Surface Architectures of Large Radio Telescopes" (PDF). International Union of Radio Science (URSI) XXVII General Assembly, Maastricht, The Netherlands. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2011-05-22. Retrieved 2008-10-24.
- Orfel, A.; Morsiani, M.; Zacchiroli, G.; Maccaferri, G.; Roda, J. & Fiocchi, F. (2004). "An active surface for large reflector antennas". IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation. 46 (4): 11–19. Bibcode:2004IAPM...46...11O. doi:10.1109/MAP.2004.1373995. S2CID 42428849.. Discusses many practical details of an active surface.
- Normile, Dennis (26 September 2016). "World's largest radio telescope will search for dark matter, listen for aliens". Science News. doi:10.1126/science.aah7346.