
A radio telescope is a specialized antenna and radio receiver used to detect radio waves from astronomical radio sources in the sky. Radio telescopes are the main observing instrument used in radio astronomy, which studies the radio frequency portion of the electromagnetic spectrum emitted by astronomical objects, just as optical telescopes are the main observing instrument used in traditional optical astronomy which studies the light wave portion of the spectrum coming from astronomical objects. Unlike optical telescopes, radio telescopes can be used in the daytime as well as at night.

Radio astronomy is a subfield of astronomy that studies celestial objects at radio frequencies. The first detection of radio waves from an astronomical object was in 1932, when Karl Jansky at Bell Telephone Laboratories observed radiation coming from the Milky Way. Subsequent observations have identified a number of different sources of radio emission. These include stars and galaxies, as well as entirely new classes of objects, such as radio galaxies, quasars, pulsars, and masers. The discovery of the cosmic microwave background radiation, regarded as evidence for the Big Bang theory, was made through radio astronomy.

Noto is a city and comune in the Province of Syracuse, Sicily, Italy. It is 32 kilometres (20 mi) southwest of the city of Syracuse at the foot of the Iblean Mountains. It lends its name to the surrounding area Val di Noto. In 2002 Noto and its church were declared a UNESCO World Heritage Site.

Very-long-baseline interferometry (VLBI) is a type of astronomical interferometry used in radio astronomy. In VLBI a signal from an astronomical radio source, such as a quasar, is collected at multiple radio telescopes on Earth or in space. The distance between the radio telescopes is then calculated using the time difference between the arrivals of the radio signal at different telescopes. This allows observations of an object that are made simultaneously by many radio telescopes to be combined, emulating a telescope with a size equal to the maximum separation between the telescopes.

The Karl G. Jansky Very Large Array (VLA) is a centimeter-wavelength radio astronomy observatory located in central New Mexico on the Plains of San Agustin, between the towns of Magdalena and Datil, ~50 miles (80 km) west of Socorro. The VLA comprises twenty-eight 25-meter radio telescopes deployed in a Y-shaped array and all the equipment, instrumentation, and computing power to function as an interferometer. Each of the massive telescopes is mounted on double parallel railroad tracks, so the radius and density of the array can be transformed to adjust the balance between its angular resolution and its surface brightness sensitivity. Astronomers using the VLA have made key observations of black holes and protoplanetary disks around young stars, discovered magnetic filaments and traced complex gas motions at the Milky Way's center, probed the Universe's cosmological parameters, and provided new knowledge about the physical mechanisms that produce radio emission.

The National Astronomical Observatory of Japan (NAOJ) is an astronomical research organisation comprising several facilities in Japan, as well as an observatory in Hawaii and Chile. It was established in 1988 as an amalgamation of three existing research organizations - the Tokyo Astronomical Observatory of the University of Tokyo, International Latitude Observatory of Mizusawa, and a part of Research Institute of Atmospherics of Nagoya University.

HALCA, also known for its project name VSOP, the code name MUSES-B, or just Haruka (はるか) was a Japanese 8 meter diameter radio telescope satellite which was used for Very Long Baseline Interferometry (VLBI). It was the first such space-borne dedicated VLBI mission.

The Northeastern Space Radio Observatory is a 14.2 m (47 ft) radio dish antenna located in the municipality of Eusébio in the state of Ceará, Brazil, approximately 20 kilometres (12 mi) south of Fortaleza. The facility is owned by the National Institute for Space Research (INPE) and managed by the Center of Radio Astronomy and Astrophysics at Universidade Presbiteriana Mackenzie (CRAAM). It was initially funded by several by Brazilian institutions and the United States National Oceanic Atmospheric Administration (NOAA). It has been operating since 1993 and is used primarily for geodetic very long baseline interferometry (VLBI).

The Mount Pleasant Radio Observatory is a radio astronomy based observatory owned and operated by University of Tasmania, located 20 km east of Hobart in Cambridge, Tasmania. It is home to three radio astronomy antennas and the Grote Reber Museum.

Haystack Observatory is a multidisciplinary radio science center, ionospheric observatory, and astronomical microwave observatory owned by Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT). It is located in Westford, Massachusetts (US), approximately 45 kilometers (28 mi) northwest of Boston. Haystack was initially built by MIT's Lincoln Laboratory for the United States Air Force and was known as Haystack Microwave Research Facility. Construction began in 1960, and the antenna began operating in 1964. In 1970 the facility was transferred to MIT, which then formed the Northeast Radio Observatory Corporation (NEROC) with a number of other universities to operate the site as the Haystack Observatory. As of January 2012, a total of nine institutions participated in NEROC.

Medicina is an Italian comune with c. 16,000 inhabitants in the Metropolitan City of Bologna, part of the region of Emilia-Romagna.
The Istituto di Radioastronomia di Bologna is one of research facilities of the Italian Istituto Nazionale di Astrofisica. Staff conduct research in astronomy, physics, engineering and information science. It was previously part of the Consiglio Nazionale delle Ricerche.

The Algonquin Radio Observatory (ARO) is a radio observatory located in Algonquin Provincial Park in Ontario, Canada. It opened in 1959 in order to host a number of the National Research Council of Canada's (NRC) ongoing experiments in a more radio-quiet location than Ottawa.

The Medicina Radio Observatory is an astronomical observatory located 30 km from Bologna, Italy. It is operated by the Institute for Radio Astronomy of the National Institute for Astrophysics (INAF) of the government of Italy.

The National Institute for Astrophysics is an Italian research institute in astronomy and astrophysics, founded in 1999. INAF funds and operates twenty separate research facilities, which in turn employ scientists, engineers and technical staff. The research they perform covers most areas of astronomy, ranging from planetary science to cosmology.

The Sardinia Radio Telescope (SRT) is 64-metre fully steerable radio telescope near San Basilio, Province of Cagliari, Sardinia, Italy. Completed in 2011, it is a collaboration between the Istituto di Radioastronomia di Bologna, the Cagliari Observatory (Cagliari) and the Arcetri Astrophysical Observatory (Florence).
The Soviet Deep Space Network was a network of large antennas and communication facilities that supports interplanetary spacecraft missions, and radio and radar astronomy observations for the exploration of the solar system and the universe during Soviet times. It was built to support the space missions of the Soviet Union. Similar networks are run by the USA, China, Europe, Japan, and India.
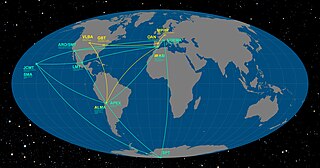
The Event Horizon Telescope (EHT) is a large telescope array consisting of a global network of radio telescopes. The EHT project combines data from several very-long-baseline interferometry (VLBI) stations around Earth, which form a combined array with an angular resolution sufficient to observe objects the size of a supermassive black hole's event horizon. The project's observational targets include the two black holes with the largest angular diameter as observed from Earth: the black hole at the center of the supergiant elliptical galaxy Messier 87 (M87), and Sagittarius A* at the center of the Milky Way.

The Korean VLBI Network (KVN) is a radio astronomy observatory located in South Korea. It comprises three 21-meter radio telescopes that function as an interferometer, using the technique of very-long-baseline interferometry (VLBI).
Giampaolo Vettolani is an Italian astrophysicist, scientific director of the National Institute for Astrophysics in Rome (INAF) since 2012.
















