
The Large Binocular Telescope (LBT) is an optical telescope for astronomy located on 10,700-foot (3,300 m) Mount Graham, in the Pinaleno Mountains of southeastern Arizona, United States. It is a part of the Mount Graham International Observatory.
The Joint Institute for Very Long Baseline Interferometry European Research Infrastructure Consortium (JIVE) was established by a decision of the European Commission in December 2014, and assumed the activities and responsibilities of the JIVE foundation, which was established in December 1993. JIVE's mandate is to support the operations and users of the European VLBI Network (EVN), in the widest sense.
The Cagliari Observatory is an astronomical observatory owned and operated by Italy's Istituto Nazionale di Astrofisica. It is located 20 km away from Cagliari in Sardinia. It was founded in 1899 to study the Earth's rotation.

The Astronomical Observatory of Capodimonte is the Neapolitan department of Istituto Nazionale di Astrofisica, the most important Italian institution promoting, developing and conducting scientific research in the fields of astronomy, astrophysics, and space science.

The Observatory of Turin is an astronomical observatory owned and operated by Italy's National Institute for Astrophysics. It is located on the top of a hill in the town of Pino Torinese near Turin, in the north Italian Piedmont region. The observatory was founded in 1759. At Pino Torinese, several asteroid discoveries were made by Italian astronomer Luigi Volta in the late 1920s and early 1930s. The asteroid 2694 Pino Torinese was named after the observatory's location.

Astronomical Observatory of Trieste is an astronomical center of studies located in the city of Trieste in northern Italy.

Medicina is an Italian comune with c. 16,000 inhabitants in the Metropolitan City of Bologna, part of the region of Emilia-Romagna.

The Astronomical Observatory of Rome is one of twelve Astronomical Observatories in Italy. The main site of the Observatory is Monte Porzio Catone. Part of the Istituto Nazionale di Astrofisica since 2002.

The Medicina Radio Observatory is an astronomical observatory located 30 km from Bologna, Italy. It is operated by the Institute for Radio Astronomy of the National Institute for Astrophysics (INAF) of the government of Italy.
The Noto VLBI Station is a radio observatory located on Sicily, southern Italy, outside the city of Noto. The facility is operated by the Istituto di Radioastronomia di Bologna.
The Shapley Supercluster or Shapley Concentration is the largest concentration of galaxies in our nearby universe that forms a gravitationally interacting unit, thereby pulling itself together instead of expanding with the universe. It appears as a striking overdensity in the distribution of galaxies in the constellation of Centaurus. It is 650 million light-years away (z=0.046).

The National Institute for Astrophysics is an Italian research institute in astronomy and astrophysics, founded in 1999. INAF funds and operates twenty separate research facilities, which in turn employ scientists, engineers and technical staff. The research they perform covers most areas of astronomy, ranging from planetary science to cosmology.

The Sardinia Radio Telescope (SRT) is 64-metre fully steerable radio telescope near San Basilio, Province of Cagliari, Sardinia, Italy. Completed in 2011, it is a collaboration between the Istituto di Radioastronomia di Bologna, the Cagliari Observatory (Cagliari) and the Arcetri Astrophysical Observatory (Florence).

The European Solar Telescope (EST) is a pan-European project to build a next-generation 4-metre class solar telescope, to be located at the Roque de los Muchachos Observatory in the Canary Islands, Spain. It will use state-of-the-art instruments with high spatial and temporal resolution that can efficiently produce two-dimensional spectral information in order to study the Sun's magnetic coupling between its deep photosphere and upper chromosphere. This will require diagnostics of the thermal, dynamic and magnetic properties of the plasma over many scale heights, by using multiple wavelength imaging, spectroscopy and spectropolarimetry.
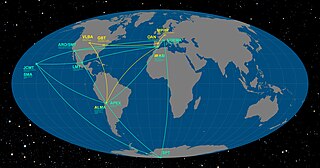
The Event Horizon Telescope (EHT) is a large telescope array consisting of a global network of radio telescopes. The EHT project combines data from several very-long-baseline interferometry (VLBI) stations around Earth, which form a combined array with an angular resolution sufficient to observe objects the size of a supermassive black hole's event horizon. The project's observational targets include the two black holes with the largest angular diameter as observed from Earth: the black hole at the center of the supergiant elliptical galaxy Messier 87, and Sagittarius A* at the center of the Milky Way.
Giampaolo Vettolani is an Italian astrophysicist, scientific director of the National Institute for Astrophysics in Rome (INAF) since 2012.

Guido Horn d'Arturo was an Italian astronomer born in Trieste, then part of the Austrian Empire. He obtained Italian citizenship after serving as a volunteer in the Italian army during the First World War. To avoid being persecuted as an irredentist by the Austrian authorities, he officially added to his surname Horn that of "d'Arturo" which he used in the war.

Nicolò D'Amico (1953-2020), also known as Nichi D’Amico, was an astronomer and President of Istituto Nazionale di Astrofisica.

Alessandro De Angelis is an Italian and Argentine physicist and astrophysicist. A Professor of Experimental Physics at the University of Padova and Professor Catedratico of Astroparticle Physics at IST Lisboa, he is mostly known for his role in the proposal, construction and data analysis of new telescopes for gamma-ray astrophysics. He is a member of Istituto nazionale di fisica nucleare (INFN), Istituto nazionale di astrofisica (INAF), Italian Physical Society (SIF), International Astronomical Union (IAU), Gruppo2003.













