
Vernouillet is a commune in the Eure-et-Loir department in northern France.

Mariposa-Yosemite Airport is a public airport located four miles (6 km) west of the central business district of Mariposa, in Mariposa County, California, United States. It is owned by the County of Mariposa.

Needles Airport is a county-owned public airport in San Bernardino County, California, five miles (9 km) south of Needles.

During World War II, the United States Army Air Forces (AAF) established numerous airfields in Oklahoma for training pilots and aircrews of AAF fighters and bombers or as major maintenance and supply centers.

Perry–Foley Airport is a public-use airport located 3 miles (4.8 km) south of the central business district of the city of Perry in Taylor County, Florida, United States. The airport is publicly owned.
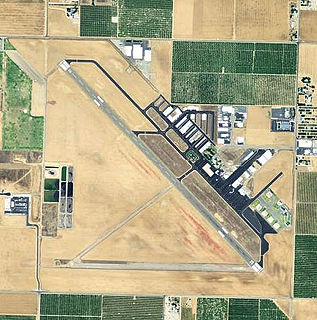
Porterville Municipal Airport is a city-owned public-use airport located three nautical miles southwest of the central business district of Porterville, a city in Tulare County, California, United States. According to the FAA's National Plan of Integrated Airport Systems for 2009–2013, it is categorized as a general aviation facility.
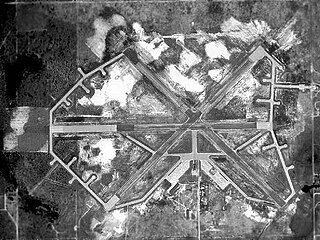
Hillsborough Army Airfield is a former World War II United States Army Air Forces airfield which was located about 7 miles north of Tampa, Florida, near Temple Terrace, Florida. After World War II it served as a civilian airport called Henderson Hillsborough International Airport for several years until it closed.

Imeson Field, also known as Jacksonville Imeson Airport, was the airport serving Jacksonville, Florida, from 1927 until its closing in 1968. It was known as Jacksonville Municipal Airport prior to World War II, Jacksonville Army Airfield when the United States Army Air Forces controlled the facility during World War II, and at its closing the airport was Jacksonville - Thomas Cole Imeson Municipal Airport.

Corcoran Airport was a public use airport located two nautical miles (3.7 km) west of the central business district of Corcoran, a town in Kings County, California, United States. It is privately owned by Lakeland Dusters, Inc. The airport has been permanently closed.

Casablanca–Anfa Airport was an airport in Morocco (IATA: CAS, ICAO: GMMC), located about 6 kilometres (4 mi) southwest of Casablanca. Anfa Airport was one of three airports serving the Casablanca area, the others being the newer and larger Mohammed V International Airport and the Casablanca Tit Mellil Airport.

Grand Island Army Airfield was a United States Army Air Forces airfield which operated from 1942 to 1946. After its closure, the base was reopened as Central Nebraska Regional Airport.

Hancock Field is a former airport and military airfield about 2 miles (3.2 km) south-southeast of Santa Maria, California. Also known as Santa Maria Municipal Airport, the airport was closed about 1959 and today is the site of Allan Hancock College.
Lancaster Airport was an airport about 1.5 miles (2.4 km) northwest of Lancaster, California. It was closed in the late 1940s and is now a housing development.

Amedee Army Airfield is a military use airport located nine nautical miles (17 km) north of the central business district of Herlong, in Lassen County, California, United States. It is owned by the United States Army and located at the Sierra Army Depot in the Honey Lake Valley, east of the Sierra Nevada mountain range.

Coalinga Municipal Airport (Old) is a closed airport located 1 mile north of Coalinga, California. The airport was closed approximately 2000, all aviation use was moved to the New Coalinga Municipal Airport.

Kingdon Airpark is a general aviation airport located 4 miles southwest of Lodi, California.

Inyo County Airport is a closed airport located east of Fresno, California.

Henderson Airport is a closed airport located two miles (3.2 km) north-northeast of Millers Ferry, Alabama. During World War II, it operated as Henderson Auxiliary Field.

Tallassee Airport is closed airport located 4 miles south of Tallassee, Alabama.
Dothan Municipal Airport is a closed airport located 3 miles (5 km) west-northwest of Dothan, Alabama, United States.

























