Related Research Articles

The Rutland Railroad was a railroad in the northeastern United States, located primarily in the state of Vermont but extending into the state of New York at both its northernmost and southernmost ends. After its closure in 1961, parts of the railroad were taken over by the State of Vermont in early 1963 and are now operated by the Vermont Railway.

The Delaware, Lackawanna and Western Railroad, also known as the DL&W or Lackawanna Railroad, was a U.S. Class 1 railroad that connected Buffalo, New York, and Hoboken, New Jersey, and by ferry with New York City, a distance of 395 miles (636 km). The railroad was incorporated in Pennsylvania in 1853, and created primarily to provide a means of transport of anthracite coal from the Coal Region in Northeast Pennsylvania to large coal markets in New York City. The railroad gradually expanded both east and west, and eventually linked Buffalo with New York City.

The Erie Lackawanna Railway, known as the Erie Lackawanna Railroad until 1968, was formed from the 1960 merger of the Erie Railroad and the Delaware, Lackawanna & Western Railroad. The official motto of the line was "The Friendly Service Route".

The Florida East Coast Railway is a Class II railroad operating in the U.S. state of Florida, currently owned by Grupo México.

The Rome, Watertown and Ogdensburg Railroad was a railroad that grew, in stages, from Rome, New York to Watertown and then to Ogdensburg, New York and Massena, New York. The original Rome and Watertown Railroad terminated in Cape Vincent, NY on the St. Lawrence River. A branch of the Rome, Watertown and Ogdensburg Railroad, commonly known as "The Hojack Line", operated along the south shore of Lake Ontario, from Oswego, New York to Niagara Falls, New York.

The St. Lawrence and Atlantic Railroad, known as St-Laurent et Atlantique Quebec in Canada, is a short-line railway operating between Portland, Maine, on the Atlantic Ocean, and Montreal, Quebec, on the St. Lawrence River. It crosses the Canada–US border at Norton, Vermont, and Stanhope, Quebec, and is owned by short-line operator Genesee & Wyoming.

The Bangor and Aroostook Railroad was a United States railroad company that brought rail service to Aroostook County in northern Maine. Brightly-painted BAR boxcars attracted national attention in the 1950s. First-generation diesel locomotives operated on BAR until they were museum pieces. The economic downturn of the 1980s, coupled with the departure of heavy industry from northern Maine, forced the railroad to seek a buyer and end operations in 2003. It was succeeded by the Montreal, Maine and Atlantic Railway.
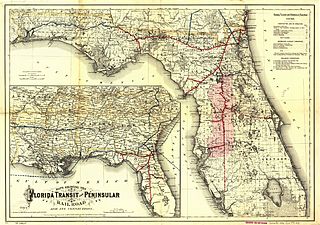
The Florida Central and Peninsular Railroad was the final name of a system of railroads throughout Florida, becoming part of the Seaboard Air Line Railway in 1900. The system, including some of the first railroads in Florida, stretched from Jacksonville west through Tallahassee and south to Tampa. Much of the FC&P network is still in service under the ownership of CSX Transportation.

The Plant System, named after its owner, Henry B. Plant, was a system of railroads and steamboats in the U.S. South, taken over by the Atlantic Coast Line Railroad in 1902. The original line of the system was the Savannah, Florida and Western Railway, running across southern Georgia. The Plant Investment Company was formed in 1882 to lease and buy other railroads and expand the system. Other major lines incorporated into the system include the Savannah and Charleston Railroad and the Brunswick and Western Railroad.
The New York and Ottawa Railway was a railway connecting Tupper Lake in northeastern New York to Ottawa, Ontario, via Ramsayville, Russell, Embrun, Finch and Cornwall. It became part of the New York Central Railroad system in 1913, although it was under the larger company's possession since the end of 1904. It had started out as the Northern Adirondack Railroad and evolved into the Northern New York Railroad, the New York and Ottawa Railroad, and was last known as the New York and Ottawa Railway before being merged into the New York Central and Hudson River Railroad. Other lines that were a part of this route are described below.

The Adirondack Railroad is a heritage railway serving the Adirondack Park that operates over former New York Central Railroad trackage between Utica and Tupper Lake. The railroad is operated by the not-for-profit Adirondack Railroad Preservation Society, with train crews composed largely of volunteers.

The Wiregrass Central Railroad is a shortline railroad operating 19.5 miles (31.4 km) of track from a CSX Transportation connection at Waterford, near Newton, to Enterprise, Alabama via the south side of Fort Novosel. The company was initially a subsidiary of Gulf and Ohio Railways and began operations in 1987 following the purchase of the Enterprise Subdivision branch line of CSX Transportation.

The Boehlert Transportation Center at Union Station is a train station served by Amtrak and the Adirondack Railroad in Utica, New York. It is owned by Oneida County, and named for retired U.S. Rep. Sherwood Boehlert.

The Montreal Subdivision is a railroad line owned by the St. Lawrence and Adirondack Railway and Canadian National. Operations are currently by Canadian National. The line originally ran from Massena, New York, northeast to Kahnawake, Quebec, along a former New York Central Railroad line. At its south end, the St. Lawrence Subdivision continues south; its north end was at Adirondack Junction, a junction with the Canadian Pacific Railway's Adirondack Subdivision, along which it had trackage rights north over the Saint-Laurent Railway Bridge into Montreal.

The railroad history of Portland, Maine, began in 1842 with the arrival of the Portland, Saco & Portsmouth Railroad (PS&P). Most of the rail activity in Portland concerned agricultural goods bound for export and European import freight. But Maine's largest city also enjoyed 125 years of continuous passenger rail service from 1842 until 1967, and has been served by Amtrak since 2001. For most of Portland's history, passenger train schedules were designed with intercity travel—to Boston, Montreal, Nova Scotia, and points west—rather than daily commuting.

The Mohawk and Malone Railway was a railroad that ran from the New York Central Railroad's main line at Herkimer north to Malone, crossing the northern Adirondacks at Tupper Lake Junction, just north of Tupper Lake. The road's founder, Dr. William Seward Webb, was president of the Wagner Palace Car Company and a Vanderbilt in-law. He began by purchasing the 3 ft narrow gauge Herkimer, Newport and Poland Railway, which ran 16 miles (26 km) from Herkimer to Poland, converting its trackage to 4 ft 8+1⁄2 instandard gauge, and straightening it to avoid multiple crossings of the West Canada Creek. He then had track built from Tupper Lake to Moira and thence to Malone. A separate company, the St. Lawrence and Adirondack Railway, completed the line to Montreal, Quebec.
The Erie and Central New York Railroad was first graded in 1870 and was abandoned and the bridges rotted. Reconstruction was started in 1895, opened May 1, 1898, and sold to the Delaware, Lackawanna and Western Railroad in 1903. The railroad ran from Cortland Junction to Cincinnatus, and an extension to Hancock or Deposit was planned.
The Atlantic Coast Line Railroad's DuPont—Lakeland Line was a historic rail line in southern Georgia and the northern west coast of Florida. On employee timetables, the line was actually divided into the DuPont—High Springs Line and the High Springs—Lakeland Line. The line was primarily used for freight, though some passenger services ran on parts of it in Florida. While parts of the line were built as early as 1863, the full line was not complete until 1913. Parts of the line in Florida are still active today.
The Rouses Point Subdivision is a railway line in southwestern Quebec. It runs north–south from the northern end of Canadian Subdivision, on the border with New York, to the St-Hyacinthe Subdivision, in the vicinity of Montreal. The oldest part of the line was the original main line of the Champlain and St. Lawrence Railroad, completed in 1836. Today, the Canadian National Railway owns the line. Amtrak's Adirondack operates over the full length, providing daily service between New York City and Montreal.