The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) is an agency of the United States Department of Commerce whose mission is to promote American innovation and industrial competitiveness. NIST's activities are organized into physical science laboratory programs that include nanoscale science and technology, engineering, information technology, neutron research, material measurement, and physical measurement. From 1901 to 1988, the agency was named the National Bureau of Standards.

The Malcolm Baldrige National Quality Award recognizes U.S. organizations in the business, health care, education, and nonprofit sectors for performance excellence. The Baldrige Award is the highest formal recognition of the performance excellence of both public and private U.S. organizations given by the President of the United States. It is administered by the Baldrige Performance Excellence Program, which is based at and managed by the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), an agency of the U.S. Department of Commerce.

The U.S. Economic Development Administration (EDA) is an agency in the United States Department of Commerce that provides grants and technical assistance to economically distressed communities in order to generate new employment, help retain existing jobs and stimulate industrial and commercial growth through a variety of investment programs. EDA works with boards and communities across the country on economic development strategies.

The National Telecommunications and Information Administration (NTIA) is an agency of the United States Department of Commerce that serves as the president's principal adviser on telecommunications policies pertaining to the United States' economic and technological advancement and to regulation of the telecommunications industry.

Research and development is the set of innovative activities undertaken by corporations or governments in developing new services or products. R&D constitutes the first stage of development of a potential new service or the production process.

James Sacra Albus was an American engineer, Senior NIST Fellow and founder and former chief of the Intelligent Systems Division of the Manufacturing Engineering Laboratory at the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST).

Semiconductor Research Corporation (SRC), commonly known as SRC, is a high-technology research consortium active in the semiconductor industry. It is a leading semiconductor research consortium. Todd Younkin is the incumbent president and chief executive officer of the company.
The Small Business Innovation Research program is a U.S. government funding program, coordinated by the Small Business Administration, intended to help certain small businesses conduct research and development (R&D). Funding takes the form of contracts or grants. The recipient projects must have the potential for commercialization and must meet specific U.S. government R&D needs.

Lewis McAdory Branscomb was an American physicist, government policy advisor, and corporate research manager. He was best known for being head of the National Bureau of Standards and, later, chief scientist of IBM; and as a prolific writer on science policy issues.

The National Science and Technology Council (NSTC) is a council in the Executive Branch of the United States. It is designed to coordinate science and technology policy across the branches of federal government.
The United States National Academy of Sciences' Board on Science, Technology, and Economic Policy (STEP) is a board of the United States National Academy of Sciences.
The America COMPETES Act was authored by Bart Gordon and signed into law on August 9, 2007, by President George W. Bush. The act aimed to invest in innovation through research and development and improve the competitiveness of the United States.
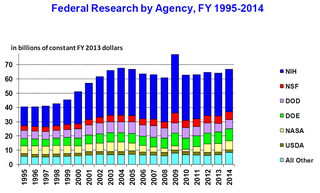
The science policy of the United States is the responsibility of many organizations throughout the federal government. Much of the large-scale policy is made through the legislative budget process of enacting the yearly federal budget, although there are other legislative issues that directly involve science, such as energy policy, climate change, and stem cell research. Further decisions are made by the various federal agencies which spend the funds allocated by Congress, either on in-house research or by granting funds to outside organizations and researchers.
Smart grid policy in the United States refers to legislation and other governmental orders influencing the development of smart grids in the United States.

The Networking and Information Technology Research and Development (NITRD) program consists of a group of U.S. federal agencies to research and develop information technology (IT) capabilities to empower Federal missions; support U.S. science, engineering, and technology leadership; and bolster U.S. economic competitiveness.

Manufacturing USA, previously known as the National Network for Manufacturing Innovation, is a network of research institutes in the United States that focuses on developing manufacturing technologies through public-private partnerships among U.S. industry, universities, and federal government agencies. Modeled similar to Germany's Fraunhofer Institutes, the network currently consists of 16 institutes. The institutes work independently and together on a number of advanced technologies.

The National Windstorm Impact Reduction Act Reauthorization of 2014 is a bill that would reauthorize the National Windstorm Impact Reduction Program (NWIRP), which was created to improve the understanding of windstorms and their impacts and to develop measures to reduce the damage they cause. The bill also would establish new committees to coordinate the activities of federal agencies participating in the program and to assess developments in efforts to mitigate damage from windstorms.

The Revitalize American Manufacturing and Innovation Act of 2013 is a bill that would establish the Network for Manufacturing Innovation Program (NMIP) within the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST). Under the program, NIST would award grants to establish a network of centers of innovation to improve the competitiveness of domestic manufacturers.

The American Innovation and Competitiveness Act (AICA) is a United States federal law enacted in 2017 by President Barack Obama that aims to invest in cybersecurity and cryptography research. The legislation was initially introduced in the Senate by Cory Gardner (R-CO) and Gary Peters (D-MI). The legislation serves as a reauthorization of the 2010 America COMPETES Act that expired in 2013.

The CHIPS and Science Act is a U.S. federal statute enacted by the 117th United States Congress and signed into law by President Joe Biden on August 9, 2022. The act authorizes roughly $280 billion in new funding to boost domestic research and manufacturing of semiconductors in the United States, for which it appropriates $52.7 billion. The act includes $39 billion in subsidies for chip manufacturing on U.S. soil along with 25% investment tax credits for costs of manufacturing equipment, and $13 billion for semiconductor research and workforce training, with the dual aim of strengthening American supply chain resilience and countering China. It also invests $174 billion in the overall ecosystem of public sector research in science and technology, advancing human spaceflight, quantum computing, materials science, biotechnology, experimental physics, research security, social and ethical considerations, workforce development and diversity, equity, and inclusion efforts at NASA, NSF, DOE, EDA, and NIST.











