Related Research Articles

Evolution is the change in the heritable characteristics of biological populations over successive generations. It occurs when evolutionary processes such as natural selection and genetic drift act on genetic variation, resulting in certain characteristics becoming more or less common within a population over successive generations. The process of evolution has given rise to biodiversity at every level of biological organisation.

A skeleton is the structural frame that supports the body of most animals. There are several types of skeletons, including the exoskeleton, which is a rigid outer shell that holds up an organism's shape; the endoskeleton, a rigid internal frame to which the organs and soft tissues attach; and the hydroskeleton, a flexible internal structure supported by the hydrostatic pressure of body fluids.

A cephalopod is any member of the molluscan class Cephalopoda such as a squid, octopus, cuttlefish, or nautilus. These exclusively marine animals are characterized by bilateral body symmetry, a prominent head, and a set of arms or tentacles modified from the primitive molluscan foot. Fishers sometimes call cephalopods "inkfish", referring to their common ability to squirt ink. The study of cephalopods is a branch of malacology known as teuthology.
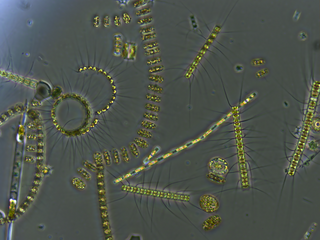
Zooplankton are the heterotrophic component of the planktonic community, having to consume other organisms to thrive. Plankton are aquatic organisms that are unable to swim effectively against currents. Consequently, they drift or are carried along by currents in the ocean, or by currents in seas, lakes or rivers.

Evolutionary developmental biology is a field of biological research that compares the developmental processes of different organisms to infer how developmental processes evolved.

An exoskeleton is a skeleton that is on the exterior of an animal in the form of hardened integument, which both supports the body's shape and protects the internal organs, in contrast to an internal endoskeleton which is enclosed underneath other soft tissues. Some large, hard and non-flexible protective exoskeletons are known as shell or armour.

An eye is a sensory organ that allows an organism to perceive visual information. It detects light and converts it into electro-chemical impulses in neurons (neurones). It is part of an organism's visual system.
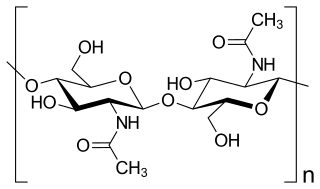
Chitin (C8H13O5N)n ( KY-tin) is a long-chain polymer of N-acetylglucosamine, an amide derivative of glucose. Chitin is the second most abundant polysaccharide in nature (behind only cellulose); an estimated 1 billion tons of chitin are produced each year in the biosphere. It is a primary component of cell walls in fungi (especially filamentous and mushroom-forming fungi), the exoskeletons of arthropods such as crustaceans and insects, the radulae, cephalopod beaks and gladii of molluscs and in some nematodes and diatoms. It is also synthesised by at least some fish and lissamphibians. Commercially, chitin is extracted from the shells of crabs, shrimps, shellfish and lobsters, which are major by-products of the seafood industry. The structure of chitin is comparable to cellulose, forming crystalline nanofibrils or whiskers. It is functionally comparable to the protein keratin. Chitin has proved useful for several medicinal, industrial and biotechnological purposes.

Chitons are marine molluscs of varying size in the class Polyplacophora, formerly known as Amphineura. About 940 extant and 430 fossil species are recognized.

Biomineralization, also written biomineralisation, is the process by which living organisms produce minerals, often resulting in hardened or stiffened mineralized tissues. It is an extremely widespread phenomenon: all six taxonomic kingdoms contain members that are able to form minerals, and over 60 different minerals have been identified in organisms. Examples include silicates in algae and diatoms, carbonates in invertebrates, and calcium phosphates and carbonates in vertebrates. These minerals often form structural features such as sea shells and the bone in mammals and birds.
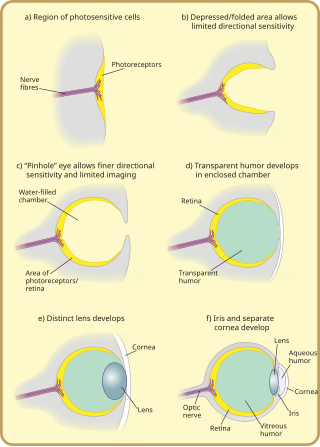
Many scientists have found the evolution of the eye attractive to study because the eye distinctively exemplifies an analogous organ found in many animal forms. Simple light detection is found in bacteria, single-celled organisms, plants and animals. Complex, image-forming eyes have evolved independently several times.

Acanthochitona zelandica is a species of chiton in the family Acanthochitonidae, also sometimes known as the hairy, or "tufted", chiton. It probably developed during the mid to late Pleistocene, and is endemic to New Zealand.

engrailed is a homeodomain transcription factor involved in many aspects of multicellular development. First known for its role in arthropod embryological development, working in consort with the Hox genes, engrailed has been found to be important in other areas of development. It has been identified in many bilaterians, including the arthropods, vertebrates, echinoderms, molluscs, nematodes, brachiopods, and polychaetes. It acts as a "selector" gene, conferring a specific identity to defined areas of the body, and co-ordinating the expression of downstream genes.

The molluscshell is typically a calcareous exoskeleton which encloses, supports and protects the soft parts of an animal in the phylum Mollusca, which includes snails, clams, tusk shells, and several other classes. Not all shelled molluscs live in the sea; many live on the land and in freshwater.

Apposition eyes are the most common form of eye, and are presumably the ancestral form of compound eye. They are found in all arthropod groups, although they may have evolved more than once within this phylum. Some annelids and bivalves also have apposition eyes. They are also possessed by Limulus, the horseshoe crab, and there are suggestions that other chelicerates developed their simple eyes by reduction from a compound starting point. Some caterpillars appear to have evolved compound eyes from simple eyes in the opposite fashion.

Mollusca is a phylum of protostomic invertebrate animals, whose members are known as molluscs or mollusks. Around 76,000 extant species of molluscs are recognized, making it the second-largest animal phylum after Arthropoda. The number of additional fossil species is estimated between 60,000 and 100,000, and the proportion of undescribed species is very high. Many taxa remain poorly studied.

The molluscs have the widest variety of eye morphologies of any phylum, and a large degree of variation in their function. Cephalopods such as octopus, squid, and cuttlefish have eyes as complex as those of vertebrates, while scallops have up to 100 simple eyes.

Plaxiphora albida, the white Plaxiphora chiton, is a species of chiton in the family Mopaliidae.
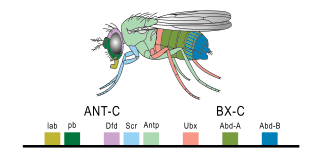
The evo-devo gene toolkit is the small subset of genes in an organism's genome whose products control the organism's embryonic development. Toolkit genes are central to the synthesis of molecular genetics, palaeontology, evolution and developmental biology in the science of evolutionary developmental biology (evo-devo). Many of them are ancient and highly conserved among animal phyla.

Many protists have protective shells or tests, usually made from silica (glass) or calcium carbonate (chalk). Protists are a diverse group of eukaryote organisms that are not plants, animals, or fungi. They are typically microscopic unicellular organisms that live in water or moist environments.
References
- ↑ Boyle, P. R. (1976). "The aesthetes of chitons". Cell and Tissue Research . 172 (3): 379–388. doi:10.1007/BF00399520. PMID 991219. S2CID 29541729.
- 1 2 Serb, J. M.; Eernisse, D. J. (2008). "Charting Evolution's Trajectory: Using Molluscan Eye Diversity to Understand Parallel and Convergent Evolution". Evolution: Education and Outreach. 1 (4): 439–447. doi: 10.1007/s12052-008-0084-1 .
- ↑ Plass, Maya (July 18, 2013). Bailey, Julie (ed.). RSBP Handbook of the Seashore. London: A&C Black. p. 110. ISBN 978-1408178362 . Retrieved 23 November 2015.
- ↑ Li, Ling; Connors, Matthew; Kolle, Mathias; England, Grant; Speiser, Daniel; Xiao, Xianghui; Aizenberg, Joanna; Ortiz, Christine (20 November 2015). "Multifunctionality of chiton biomineralized armor with an integratred visual system". Science. 350 (6263): 952–6. doi: 10.1126/science.aad1246 . hdl: 1721.1/100035 . PMID 26586760.