
The ASEAN Free Trade Area (AFTA) is a trade bloc agreement by the Association of Southeast Asian Nations supporting local trade and manufacturing in all ASEAN countries, and facilitating economic integration with regional and international allies. It stands as one of the largest and most important free trade areas (FTA) in the world, and together with its network of dialogue partners, drove some of the world's largest multilateral forums and blocs, including Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation, East Asia Summit and Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership.

The Australia–New Zealand Closer Economic Relations Trade Agreement, commonly known as Closer Economic Relations (CER), is a free trade agreement between Australia and New Zealand. It came into force on 1 January 1983, but the actual treaty was not signed until 28 March 1983 by the Deputy Prime Minister of Australia and Minister for Trade, Lionel Bowen and the New Zealand High Commissioner to Australia, Laurie Francis in Canberra, Australia. This was because Malcolm Fraser and Robert Muldoon hated each other personally to such an extent that they refused to ratify the agreement if the other was there.

New Zealand is party to several free trade agreements (FTAs) worldwide.

India-Singapore relations, also known as Indian-Singaporean relations or Indo-Singaporeanrelations, are the bilateral relations between India and Singapore. Relations between the two countries have traditionally been strong and friendly, with the two nations enjoying extensive cultural and commercial relations. India and Singapore have signed the Comprehensive Economic Cooperation Agreement (CECA) and strategic-relationship agreement in order to increase trade, investments and economic cooperation, and expanded bilateral cooperation on maritime security, training forces, joint naval exercises, developing military technology and fighting terrorism.
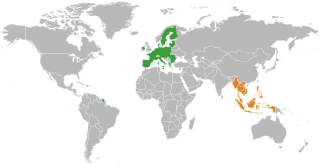
The ASEAN–European Union relations are the bilateral foreign relations between the two organisations; the European Union (EU), and the Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN). EU and ASEAN have been interacting with each other on the economic, trade, and political levels for more than four decades. The partnership between the EU and ASEAN dates back to 1972, when the EU established ties with ASEAN. The EU became an ASEAN Dialogue Partner in 1977.

Malaysia–New Zealand relations refers to foreign relations between Malaysia and New Zealand. Malaysia has a High Commission in Wellington, and New Zealand has a High Commission in Kuala Lumpur. Both countries are full members of the Commonwealth of Nations and Malaysia is important to New Zealand for strategic, political and economic reasons, with both countries' leaders were engaged in frequent visits to boost their relations.

The Trans-Pacific Strategic Economic Partnership Agreement (TPSEP), also known as P4, is a trade agreement between four Pacific Rim countries concerning a variety of matters of economic policy. The agreement was signed by Brunei, Chile, Singapore and New Zealand in 2005 and entered into force in 2006. It is a comprehensive trade agreement, affecting trade in goods, rules of origin, trade remedies, sanitary and phytosanitary measures, technical barriers to trade, trade in services, intellectual property, government procurement and competition policy. Among other things, it called for reduction by 90 percent of all tariffs between member countries by 1 January 2006, and reduction of all trade tariffs to zero by the year 2015.

Australia and Singapore share longstanding and multifaceted relations, elevated by the establishment of the Comprehensive Strategic Partnership (CSP) in 2015. Australia was the first country to establish diplomatic relations with Singapore upon its independence in 1965. Both countries also work closely in multilateral fora and enjoy warm people-to-people relations.
The Comprehensive Economic Partnership for East Asia (CEPEA) is a Japanese led proposal for trade co-operation, free trade agreement, among the 16 present member countries of the East Asia Summit. All those movements and efforts were taken over by the following Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership.
The ASEAN–India Free Trade Area (AIFTA) is a free trade area among the ten member states of the Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN) and the Republic of India. The initial framework agreement was signed on 8 October 2003 in Bali, Indonesia. and the final agreement was on 13 August 2009. The free trade area came into effect on 1 January 2010. India hosted the latest ASEAN-India Commemorative Summit in New Delhi on 26 January 2018. In the financial year 2017–18, Indo-ASEAN bilateral trade grew by almost 14% to reach US$81.3 billion. India's imports from ASEAN were valued at US$47.13 billion while its exports to ASEAN stood at US$34.2 billion.

Singapore–United Kingdom relations, also referred to as British–Singaporean relations, are the relations between the states of Singapore and the United Kingdom. Both countries are full members of the Commonwealth of Nations and are marked by historical, cultural, institutional and language ties, extensive people-to-people links, aligned security interests, sporting tournaments, and significant trade and investment co-operation.

The European Union has concluded free trade agreements (FTAs) and other agreements with a trade component with many countries worldwide and is negotiating with many others. The European Union negotiates free trade deals on behalf of all of its member states, as the member states have granted the EU has an "exclusive competence" to conclude trade agreements. Even so, member states' governments control every step of the process :

Vangelis (Evangelos) Vitalis is a New Zealand diplomat and trade negotiator currently working as the Deputy Secretary for the country's Ministry of Foreign Affairs and Trade.

Relations between the European Union (EU) and Japan date back to 1959. They have a strong trade relationship, particularly in investment flows.

The Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership is a free trade agreement among the Asia-Pacific countries of Australia, Brunei, Cambodia, China, Indonesia, Japan, South Korea, Laos, Malaysia, Myanmar, New Zealand, the Philippines, Singapore, Thailand, and Vietnam. The 15 member countries account for about 30% of the world's population and 30% of global GDP, making it the largest trade bloc in history. Signed in November 2020, RCEP is the first free trade agreement among the largest economies in Asia, including China, Indonesia, Japan, and South Korea.
The Hong Kong – New Zealand Closer Economic Partnership Agreement is a bilateral free trade agreement signed between the Hong Kong Special Administrative Region of China and New Zealand in March 2010. It is the first bilateral free trade agreement on goods and services that Hong Kong SAR has signed with a foreign country. Hong Kong-New Zealand CEPA complements New Zealand's Free Trade Agreement (FTA) with China two years before, and enhances the potential for Hong Kong to be used as a platform for trade into the Mainland China. Hong Kong is a Special Administrative Region of China but has autonomy in matters of trade.

The most significant initiative made by the Narendra Modi government is the focus on neighbouring countries and major Asian powers coupled with emphasizing on the two decades old Look East policy. Asia being the major focus area of his foreign policy, Modi and his foreign minister chose several Asian countries for their initial bilateral visits. He has made state visits to Bhutan and Nepal and Japan within the first 100 days of his government and also hosted Asian leaders like former Prime Minister Tony Abbott of Australia, President Xi Jinping of China and Prime Minister Nguyễn Tấn Dũng of Vietnam, apart from inviting SAARC leaders in his inauguration ceremony. External Affairs Minister Sushma Swaraj has also made official visits to several Asian capitals like Dhaka, Bangladesh, Kathmandu, Nepal, Naypidaw, Myanmar, Singapore, Hanoi, Vietnam, Manama, Bahrain, Kabul, Afghanistan, Dushanbe, Tajikistan, Malé, Maldives, Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates, Seoul, South Korea and Beijing China.
The negotiations for the Trans-Pacific Partnership Agreement were held between 12 countries between 2008 and 2015. The negotiations were aimed at obtaining an agreement between the Trans-Pacific Strategic Economic Partnership Agreement parties Brunei, Chile, Singapore and New Zealand, as well as the Australia and the United States.
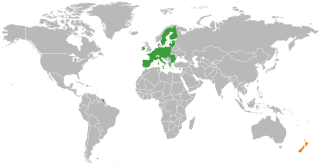
New Zealand and the European Union (EU) have solid relations and increasingly see eye-to-eye on international issues. The EU-New Zealand relations are founded on a Joint Declaration on Relations and Cooperation, first agreed in 2007. It covers not just economic relations, but broader political issues and cooperation.















