
The Ubaid period is a prehistoric period of Mesopotamia. The name derives from Tell al-'Ubaid where the earliest large excavation of Ubaid period material was conducted initially in 1919 by Henry Hall and later by Leonard Woolley.
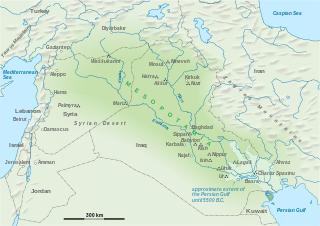
The history of Mesopotamia ranges from the earliest human occupation in the Paleolithic period up to Late antiquity. This history is pieced together from evidence retrieved from archaeological excavations and, after the introduction of writing in the late 4th millennium BC, an increasing amount of historical sources. While in the Paleolithic and early Neolithic periods only parts of Upper Mesopotamia were occupied, the southern alluvium was settled during the late Neolithic period. Mesopotamia has been home to many of the oldest major civilizations, entering history from the Early Bronze Age, for which reason it is often called a cradle of civilization.

Al Markh is one of the oldest and smallest villages of Bahrain. It neighbors Budaiya highway and the village of Duraz to the north, Saar and Magaba highway to the east, the villages of Bani Jamra and Al Garya to the west, and the village of Saar to the south.

Jōn al Kuwayt, also known as Kuwait Bay, is a bay in Kuwait. It is the head of the Persian Gulf. Kuwait City lies on a tip of the bay.
Umm Al Nar is a Bronze Age culture that existed around 2600-2000 BCE in the area of the modern-day United Arab Emirates and Northern Oman. The etymology derives from the island of the same name which lies adjacent to the city of Abu Dhabi, the capital of the UAE, which provided early evidence and finds that came to define the period.

The Halaf culture is a prehistoric period which lasted between about 6100 BC and 5100 BC. The period is a continuous development out of the earlier Pottery Neolithic and is located primarily in the fertile valley of the Khabur River, of south-eastern Turkey, Syria, and northern Iraq, although Halaf-influenced material is found throughout Greater Mesopotamia.

Jebel Faya is an archaeological site and limestone hill or escarpment near Al Madam in the Emirate of Sharjah, the UAE, located about 50 km (31 mi) east of the city of Sharjah, and between the shoreline of the Gulf and Al Hajar Mountains. It contains tool assemblages from the Paleolithic, Neolithic, Iron Age, and Bronze Age. Because its deepest assemblage has been dated to 125,000 years ago, it was thought to be the world's most ancient settlement yet discovered of anatomically modern humans outside of Africa at the time of its discovery in 2011. Finds of a yet earlier date have since been found at Misliya cave in the Levant.

Dosariyah is an archeological site in the Eastern Province, Saudi Arabia, dating to the late 6th and early 5th millennium BCE. The spectrum of archaeological remains relate the site to the Arabian Neolithic. The earliest samples of Ubaid style pottery in Saudi Arabia were found at Dosariyah.

Tell al-'Ubaid is a low, relatively small tell west of nearby Ur in southern Iraq's Dhi Qar Governorate. Most of the remains are from the Chalcolithic Ubaid period, for which Tell al-'Ubaid is the type site, with an Early Dynastic temple and cemetery at the highest point. It was a cult center for the goddess Ninhursag.
Al Da'asa is an archaeological site located on the western coast of Qatar. It is the most extensive Ubaid site in the country. It was excavated by a Danish team in 1961.

Archaeology of Qatar as a field study began in 1956. Three major expeditions were carried out in Qatar throughout the mid-20th century, with the first being launched by a Danish team who began work in the 1950s. This was followed by British and French expeditions in 1970s and 1980s, respectively. Approximately 200 archaeological sites were discovered during these expeditions, with the most extensive being the coastal areas of Al Da'asa, Ras Abrouq and Al Khor Island. Artifacts such as flint tools, Ubaid and Barbar pottery and encampments were found in situ.

Meliha Archaeological Centre is a visitor centre and exhibition based around the history and archaeology of the areas surrounding the village of Mleiha in Sharjah, the United Arab Emirates. Built around a preserved Umm Al Nar era tomb, the centre details the excavations and discoveries made over the past 40 years at Mleiha and surrounding areas, particularly the important Faya North East find, which provides evidence that 'anatomically modern humans' were in the Mleiha area between 130,000 and 120,000 years ago. These finds point to the spread of humanity from Africa across the Red Sea to the Persian Gulf region, and onward to populate the world through Iran, India, Europe and Asia.

Ed Dur, also known as Al Dour and Ad Dour is an Ancient Near Eastern City, today located in Umm Al Quwain, in the United Arab Emirates (UAE). One of the largest archaeological sites in the emirates, comprising an area of some 5 km2 (1.9 sq mi), the coastal settlement overlooks Al Beidha Lake. One of the most important archaeological finds in the UAE, and closely associated with the inland trading centre of Mleiha, Ed Dur has been dubbed 'one of the most significant lost cities of Arabia'.

The Wadi Suq culture defines human settlement in the United Arab Emirates and Oman in the period from 2,000 to 1,300 BCE. It takes its name from a wadi, or seasonal watercourse, west of Sohar in Oman and follows on from the Umm Al Nar culture. Although archaeologists have traditionally tended to view the differences in human settlements and burials between the Umm Al Nar and Wadi Suq periods as the result of major external disruption, contemporary opinion has moved towards a gradual change in human society which is centred around more sophisticated approaches to animal husbandry as well as changes in the surrounding trade and social environments.
Bidaa Bint Saud is an archaeological site in Eastern Region of the Emirate of Abu Dhabi, the U.A.E., notable for its Hafit Period tombs, Iron Age irrigation systems and rare remains of an Iron Age building thought to have been a distribution centre for water from two aflaj. It is a listed UN World Heritage Site. Finds from the site are displayed at Al Ain National Museum.
The area currently known as the United Arab Emirates (UAE) was formerly populated by inhabitants of a number of coastal and inland settlements, with human remains pointing to a pattern of transmigration and settlement as far back as 125,000 years. Prehistoric settlement in the UAE spanned the Neolithic, with a number of distinctive eras of ancient settlement including the Stone Age Arabian Bifacial and Ubaid cultures from 5,000 to 3,100 BCE; the Hafit period with its distinctive beehive shaped tombs and Jemdet Nasr pottery, from 3,200 to 2,600 BCE; the Umm Al Nar period from 2,600 to 2,000 BCE; the Wadi Suq culture from 2,000 to 1,300 BCE and the three Iron Ages of the UAE.
The territory currently known as the United Arab Emirates was home to three distinct Iron Age periods. Iron Age I spanned 1,200–1,000 BCE, Iron Age II from 1,000 to 600 BCE, and Iron Age III from 600 to 300 BCE. This period of human development in the region was followed by the Mleiha or Late Pre-Islamic era, from 300 BCE onwards through to the Islamic era which commenced with the culmination of the 7th-century Ridda Wars.
Sharma or Sharmah was a medieval trading port in Ḥaḍramawt on the Gulf of Aden. It was deeply involved in the Indian Ocean trade and was "one of the busiest harbours of the Indian Ocean" until its abrupt abandonment around 1180. Although known from texts, the location of the settlement was only discovered in 1996. Archaeological excavations began in 2001. They have revealed a large, heavily fortified port founded around 980 by merchants from Siraf on the Persian Gulf.
Bahra 1 is an archaeological site in the Subiya region on the coast of Kuwait Bay (Kuwait) associated with the Ubaid culture. It is one of the earliest Ubaid culture settlements in the Persian Gulf region, about 5500–4900 BC.
H3 is an archaeological site in the Subiya Region (Kuwait) that was occupied during the second half of the sixth millennium BC. It was the Mesopotamian frontier of the Arabian Neolithic. Among the finds at the site were a boat model and pieces of bitumen covered with reed impressions that may have come from an actual boat, making this among the earliest evidence of a sea-going vessel in the world.












