
A valve is a device or natural object that regulates, directs or controls the flow of a fluid by opening, closing, or partially obstructing various passageways. Valves are technically fittings, but are usually discussed as a separate category. In an open valve, fluid flows in a direction from higher pressure to lower pressure. The word is derived from the Latin valva, the moving part of a door, in turn from volvere, to turn, roll.
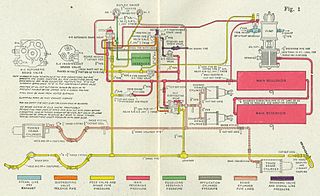
A railway air brake is a railway brake power braking system with compressed air as the operating medium. Modern trains rely upon a fail-safe air brake system that is based upon a design patented by George Westinghouse on April 13, 1869. The Westinghouse Air Brake Company was subsequently organized to manufacture and sell Westinghouse's invention. In various forms, it has been nearly universally adopted.

Pneumatics is a branch of engineering that makes use of gas or pressurized air.
An actuator is a component of a machine that is responsible for moving and controlling a mechanism or system, for example by opening a valve. In simple terms, it is a "mover".

Fluid power is the use of fluids under pressure to generate, control, and transmit power. Fluid power is subdivided into hydraulics using a liquid such as mineral oil or water, and pneumatics using a gas such as air or other gases. Compressed-air and water-pressure systems were once used to transmit power from a central source to industrial users over extended geographic areas; fluid power systems today are usually within a single building or mobile machine.

Hydraulic machines use liquid fluid power to perform work. Heavy construction vehicles are a common example. In this type of machine, hydraulic fluid is pumped to various hydraulic motors and hydraulic cylinders throughout the machine and becomes pressurized according to the resistance present. The fluid is controlled directly or automatically by control valves and distributed through hoses, tubes, or pipes.
A wastegate is a valve that controls the flow of exhaust gases to the turbine wheel in a turbocharged engine system.
Manifold vacuum, or engine vacuum in an internal combustion engine is the difference in air pressure between the engine's intake manifold and Earth's atmosphere.

A damper is a valve or plate that stops or regulates the flow of air inside a duct, chimney, VAV box, air handler, or other air-handling equipment. A damper may be used to cut off central air conditioning to an unused room, or to regulate it for room-by-room temperature and climate control -- for example in the case of Volume Control Dampers. Its operation can be manual or automatic. Manual dampers are turned by a handle on the outside of a duct. Automatic dampers are used to regulate airflow constantly and are operated by electric or pneumatic motors, in turn controlled by a thermostat or building automation system. Automatic or motorized dampers may also be controlled by a solenoid, and the degree of air-flow calibrated, perhaps according to signals from the thermostat going to the actuator of the damper in order to modulate the flow of air-conditioned air in order to effect climate control.

A solenoid valve is an electromechanically operated valve.

Lego pneumatics is a variety of Lego bricks which use air pressure and specialised components to perform various actions using the principles of pneumatics.
A pneumatic circuit is an interconnected set of components that convert compressed gas into mechanical work. In the normal sense of the term, the circuit must include a compressor or compressor-fed tank.
A control valve is a valve used to control fluid flow by varying the size of the flow passage as directed by a signal from a controller. This enables the direct control of flow rate and the consequential control of process quantities such as pressure, temperature, and liquid level.
A shutdown valve is an actuated valve designed to stop the flow of a hazardous fluid upon the detection of a dangerous event. This provides protection against possible harm to people, equipment or the environment. Shutdown valves form part of a safety instrumented system. The process of providing automated safety protection upon the detection of a hazardous event is called functional safety.

An angle seat piston valve is a pneumatically-controlled valve with a piston actuator providing linear actuation to lift a seal off its seat. The seat is set at an angle to provide the maximum possible flow when unseated. Angle seat piston valves are particularly suited to applications where high temperatures and large flow rates are required, such as steam or water. When used in reverse some models of angle seat piston valve will eliminate water hammer when operated.
Directional control valves (DCVs) are one of the most fundamental parts of hydraulic and pneumatic systems. DCVs allow fluid flow into different paths from one or more sources. DCVs will usually consist of a spool inside a cylinder which is mechanically or electrically actuated. The position of the spool restricts or permits flow, thus it controls the fluid flow.,

A shuttle valve is a type of valve which allows fluid to flow through it from one of two sources. Generally a shuttle valve is used in pneumatic systems, although sometimes it will be found in hydraulic systems.

A booster pump is a machine which will increase the pressure of a fluid. They may be used with liquids or gases, but the construction details will vary depending on the fluid. A gas booster is similar to a gas compressor, but generally a simpler mechanism which often has only a single stage of compression, and is used to increase pressure of a gas already above ambient pressure. Two-stage boosters are also made. Boosters may be used for increasing gas pressure, transferring high pressure gas, charging gas cylinders and scavenging.

A gas cabinet is a metallic enclosure which is used to provide local exhaust ventilation system for virtually all of the gases used or generated in the semiconductor, solar, MEMS, NANO, solar PV, manufacturing and other advanced technologies.












