
The Extended Industry Standard Architecture is a bus standard for IBM PC compatible computers. It was announced in September 1988 by a consortium of PC clone vendors as an alternative to IBM's proprietary Micro Channel architecture (MCA) in its PS/2 series.

IEEE 802.11 is part of the IEEE 802 set of local area network (LAN) technical standards, and specifies the set of medium access control (MAC) and physical layer (PHY) protocols for implementing wireless local area network (WLAN) computer communication. The standard and amendments provide the basis for wireless network products using the Wi-Fi brand and are the world's most widely used wireless computer networking standards. IEEE 802.11 is used in most home and office networks to allow laptops, printers, smartphones, and other devices to communicate with each other and access the Internet without connecting wires. IEEE 802.11 is also a basis for vehicle-based communication networks with IEEE 802.11p.

Industry Standard Architecture (ISA) is the 16-bit internal bus of IBM PC/AT and similar computers based on the Intel 80286 and its immediate successors during the 1980s. The bus was (largely) backward compatible with the 8-bit bus of the 8088-based IBM PC, including the IBM PC/XT as well as IBM PC compatibles.

The VESA Local Bus is a short-lived expansion bus introduced during the i486 generation of x86 IBM-compatible personal computers. Created by VESA, the VESA Local Bus worked alongside the then-dominant ISA bus to provide a standardized high-speed conduit intended primarily to accelerate video (graphics) operations. VLB provides a standardized fast path that add-in (video) card makers could tap for greatly accelerated memory-mapped I/O and DMA, while still using the familiar ISA bus to handle basic device duties such as interrupts and port-mapped I/O. Some high-end 386DX motherboards also had a VL-Bus slot.

PC Card is a parallel peripheral interface for laptop computers and PDAs.

Wi-Fi is a family of wireless network protocols based on the IEEE 802.11 family of standards, which are commonly used for local area networking of devices and Internet access, allowing nearby digital devices to exchange data by radio waves. These are the most widely used computer networks, used globally in home and small office networks to link devices and to provide Internet access with wireless routers and wireless access points in public places such as coffee shops, hotels, libraries, and airports to provide visitors.

Micro Channel architecture, or the Micro Channel bus, is a proprietary 16- or 32-bit parallel computer bus introduced by IBM in 1987 which was used on PS/2 and other computers until the mid-1990s. Its name is commonly abbreviated as "MCA", although not by IBM. In IBM products, it superseded the ISA bus and was itself subsequently superseded by the PCI bus architecture.

Ultra high frequency (UHF) is the ITU designation for radio frequencies in the range between 300 megahertz (MHz) and 3 gigahertz (GHz), also known as the decimetre band as the wavelengths range from one meter to one tenth of a meter. Radio waves with frequencies above the UHF band fall into the super-high frequency (SHF) or microwave frequency range. Lower frequency signals fall into the VHF or lower bands. UHF radio waves propagate mainly by line of sight; they are blocked by hills and large buildings although the transmission through building walls is strong enough for indoor reception. They are used for television broadcasting, cell phones, satellite communication including GPS, personal radio services including Wi-Fi and Bluetooth, walkie-talkies, cordless phones, satellite phones, and numerous other applications.

The Personal System/2 or PS/2 is IBM's second generation of personal computers. Released in 1987, it officially replaced the IBM PC, XT, AT, and PC Convertible in IBM's lineup. Many of the PS/2's innovations, such as the 16550 UART, 1440 KB 3.5-inch floppy disk format, 72-pin SIMMs, the PS/2 port, and the VGA video standard, went on to become standards in the broader PC market.

A wireless Internet service provider (WISP) is an Internet service provider with a network based on wireless networking. Technology may include commonplace Wi-Fi wireless mesh networking, or proprietary equipment designed to operate over open 900 MHz, 2.4 GHz, 4.9, 5, 24, and 60 GHz bands or licensed frequencies in the UHF band, LMDS, and other bands from 6 GHz to 80 GHz.

High-speed multimedia radio (HSMM) is the implementation of high-speed wireless TCP/IP data networks over amateur radio frequency allocations using commercial off-the-shelf (COTS) hardware such as 802.11 Wi-Fi access points. This is possible because the 802.11 unlicensed frequency bands partially overlap with amateur radio bands and ISM bands in many countries. Only licensed amateur radio operators may legally use amplifiers and high-gain antennas within amateur radio frequencies to increase the power and coverage of an 802.11 signal.
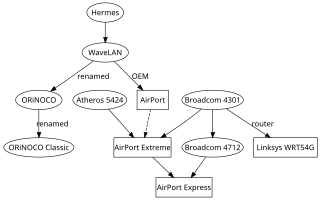
WaveLAN was a brand name for a family of wireless networking technology sold by NCR, AT&T, Lucent Technologies, and Agere Systems as well as being sold by other companies under OEM agreements. The WaveLAN name debuted on the market in 1990 and was in use until 2000, when Agere Systems renamed their products to ORiNOCO. WaveLAN laid the important foundation for the formation of IEEE 802.11 working group and the resultant creation of Wi-Fi.

The HP Compaq TC1100 is a tablet PC sold by Hewlett-Packard that was the follow-up to the Compaq TC1000. The TC1100 had either an Intel Celeron or an Intel Pentium M chip set and could be upgraded up to 2 gigabytes of memory. The switch from Transmeta Crusoe processors to the Pentium M and the ability to add memory was welcomed after numerous complaints about the poor performance of the TC1000. The TC1100 was the last version from HP in this style of tablet. It was replaced by the HP Compaq TC4200, which featured a more traditional one-piece design.
Cisco Aironet is a maker of wireless networking equipment currently operated as a division of Cisco Systems. It was started by ex-Marconi Wireless employees in 1986 as Telesystems SLW in Canada, right after the United States Federal Communications Commission (FCC) opened up the ISM bands for spread spectrum license-free use. Telxon acquired Telesystems SLW in 1992, and Aironet Wireless Communications was spun off from Telxon's RF Division in 1994. Cisco Systems acquired Aironet in 1999.
AMD Turion is the brand name AMD applies to its x86-64 low-power consumption (mobile) processors codenamed K8L. The Turion 64 and Turion 64 X2/Ultra processors compete with Intel's mobile processors, initially the Pentium M and the Intel Core and Intel Core 2 processors.

The ASUS Eee PC was a netbook computer line from Asus, and a part of the ASUS Eee product family. At the time of its introduction in late 2007, it was noted for its combination of a lightweight, Linux-based operating system, solid-state drive (SSD), and relatively low cost. Newer models added the options of Microsoft Windows operating system and rotating media hard disk drives (HDD), and initially retailed for up to 500 euros.
IEEE 802.11g-2003 or 802.11g is an amendment to the IEEE 802.11 specification that operates in the 2.4 GHz microwave band. The standard has extended link rate to up to 54 Mbit/s using the same 20 MHz bandwidth as 802.11b uses to achieve 11 Mbit/s. This specification under the marketing name of Wi-Fi has been implemented all over the world. The 802.11g protocol is now Clause 19 of the published IEEE 802.11-2007 standard, and Clause 19 of the published IEEE 802.11-2012 standard.
The Namco System N2 arcade platform runs on an nForce2-based motherboard that NVIDIA developed. It is based on a NVIDIA GeForce graphics card, using the OpenGL API.
IEEE 802.11ac-2013 or 802.11ac is a wireless networking standard in the IEEE 802.11 set of protocols, providing high-throughput wireless local area networks (WLANs) on the 5 GHz band. The standard has been retroactively labelled as Wi-Fi 5 by Wi-Fi Alliance.