
Mare Marginis ; MAR-jin-iss) is a lunar mare that lies on the very edge of the lunar nearside. The selenographic coordinates of this feature are 13.3° N, 86.1° E, and the diameter is 358 km.

Abu Rayhan Muhammad ibn Ahmad al-Biruni, known as al-Biruni, was a Khwarazmian Iranian scholar and polymath during the Islamic Golden Age. He has been called variously "Father of Comparative Religion", "Father of modern geodesy", Founder of Indology and the first anthropologist.

Khwarazm or Chorasmia is a large oasis region on the Amu Darya river delta in western Central Asia, bordered on the north by the (former) Aral Sea, on the east by the Kyzylkum Desert, on the south by the Karakum Desert, and on the west by the Ustyurt Plateau. It was the center of the Iranian Khwarezmian civilization, and a series of kingdoms such as the Afrighid dynasty and the Anushtegin dynasty, whose capitals were Kath, Gurganj and—from the 16th century on—Khiva. Today Khwarazm belongs partly to Uzbekistan and partly to Turkmenistan.
Khwārezmian is an extinct Eastern Iranian language closely related to Sogdian. The language was spoken in the area of Khwarezm (Chorasmia), centered in the lower Amu Darya south of the Aral Sea.
In Sanskrit texts, Rāja yoga was both the goal of yoga and a method to attain it. The term also became a modern name for the practice of yoga in the 19th-century when Swami Vivekananda gave his interpretation of the Yoga Sutras of Patanjali in his book Raja Yoga. Since then, Rāja yoga has variously been called aṣṭāṅga yoga, royal yoga, royal union, sahaja marg, and classical yoga.

Over the centuries of Islamic history, Muslim rulers, Islamic scholars, and ordinary Muslims have held many different attitudes towards other religions. Attitudes have varied according to time, place and circumstance.

Al-Biruni is an impact crater that lies on the far side of the Moon, just beyond the eastern limb. This portion of the surface is sometimes brought into sight due to librations of the Moon, but due to its location the crater is viewed from the side. Al-Biruni lies to the south of the crater Joliot, and to the northeast of Goddard. It is named after the great Persian scientist Al-Biruni.

Goddard is a lunar impact crater that is located along the eastern limb of the Moon, and so is visible from the edge from Earth. It is best viewed during favorable librations when the orientation of the Moon brings it further into sight. The crater is located in the Mare Marginis, to the northeast of the prominent crater Neper. Ibn Yunus, a crater remnant, is attached to the southeastern rim and is partly overlaid by Goddard. To the northeast is Al-Biruni.

Abū al-Wafāʾ Muḥammad ibn Muḥammad ibn Yaḥyā ibn Ismāʿīl ibn al-ʿAbbās al-Būzjānī or Abū al-Wafā Būzhjānī was a Persian mathematician and astronomer who worked in Baghdad. He made important innovations in spherical trigonometry, and his work on arithmetic for businessmen contains the first instance of using negative numbers in a medieval Islamic text.
Indica is classical Greek and Latin for "of India".

Abu Sa'id Ahmed ibn Mohammed ibn Abd al-Jalil al-Sijzi was an Iranian Muslim astronomer, mathematician, and astrologer. He is notable for his correspondence with al-Biruni and for proposing that the Earth rotates around its axis in the 10th century.
Islamic cosmology is the cosmology of Islamic societies. Islamic cosmology is not a single unitary system, but is inclusive of a number of cosmological systems, including Quranic cosmology, the cosmology of the Hadith collections, as well as those of Islamic astronomy and astrology. Broadly, cosmological conceptions themselves can be divided into thought concerning the physical structure of the cosmos (cosmography) and the origins of the cosmos (cosmogony).
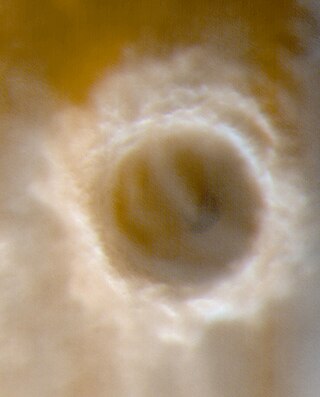
Lomonosov is a crater on Mars, with a diameter close to 150 km. It is located in the Martian northern plains. Since it is large and found close to the boundary between the Mare Acidalium quadrangle and the Mare Boreum quadrangle, it is found on both maps. The topography is smooth and young in this area, hence Lomonosov is easy to spot on large maps of Mars.

9936 Al-Biruni, provisional designation 1986 PN4, is a carbonaceous asteroid from the outer region of the asteroid belt, approximately 24 kilometers in diameter. It was discovered on 8 August 1986, by Belgian and Bulgarian astronomers Eric Elst and Violeta Ivanova at the Rozhen Observatory, located in Bulgaria's Smolyan province near the border to Greece. It was named for Persian medieval scholar Al-Biruni.

The Remaining Signs of Past CenturiesKitāb al-āthār al-bāqiyah `an al-qurūn al-khāliyah, also known as Chronology of Ancient Nations or Vestiges of the Past, after the translation published by Eduard Sachau in 1879) by Abū Rayhān al-Bīrūnī is a comparative study of the calendrical timekeeping of different cultures and civilizations, supported by mathematical, astronomical, and historical research. The text establishes a universal timeline and charts significant historical events, relating the customs and religions of different peoples in time.
Abu al-Abbas Iranshahri was a 9th-century Persian philosopher, mathematician, natural scientist, historian of religion, astronomer and author. According to traditional sources, he is the first figure in the wider Muslim world to be associated with philosophy after the advent of Islam.

The Afrighids were a native Khwarezmian Iranian dynasty who ruled over the ancient kingdom of Khwarazm. Over time, they were under the suzerainty of the Sasanian Empire, the Hephthalite Empire, the Göktürk Khaganate, the Umayyad Caliphate, Abbasid Caliphate and the Samanid Empire.

The flat peach, also known as the doughnut/donut peach or Saturn peach, is a variety of peach with pale yellow fruit that is oblate in shape.
Arabic and Islamic names of Moon craters












