al-Buqa' | |
|---|---|
| Country | |
| Governate | Sa'dah |
| District | Kitaf wa Al Boqe'e District |
| Time zone | UTC+3:00 (MST) |
al-Buqa' is an 'Uzlah in Kitaf wa Al Boqe'e District, Saada Governorate, Yemen.
al-Buqa' | |
|---|---|
| Country | |
| Governate | Sa'dah |
| District | Kitaf wa Al Boqe'e District |
| Time zone | UTC+3:00 (MST) |
al-Buqa' is an 'Uzlah in Kitaf wa Al Boqe'e District, Saada Governorate, Yemen.
The area was allegedly used as Saudi training grounds for child soldiers in the 21st century. [1]
al-Buqa' is one of the northernmost areas in Yemen; a nearby border crossing into Saudi Arabia was a war zone between the two countries in the Second Saudi-Yemeni War. [2]

Maʼrib is the capital city of Maʼrib Governorate, Yemen. It was the capital of the ancient kingdom of Sabaʾ, which some scholars believe to be the ancient Sheba of biblical fame. It is located approximately 120 kilometres east of Yemen's modern capital, Sana'a, and is in the region of the Sarawat Mountains. It has a current population of 16,794.

Human rights in Yemen are seen as problematic in numerous ways. The security forces have been responsible for torture, inhumane treatment and even extrajudicial executions. But according to the Embassy of Yemen, in recent years there has been some improvement, with the government signing several international human rights treaties, and even appointing a woman, Dr. Wahiba Fara’a, to the role of Minister of the State of Human Rights.

The Houthi insurgency in Yemen, also known as the Houthi rebellion, Sa'dah War, or Sa'dah conflict, was a military rebellion pitting Zaidi Shia Houthis against the Yemeni military that began in Northern Yemen and has since escalated into a full-scale civil war. The conflict was sparked in 2004 by the government's attempt to arrest Hussein Badreddin al-Houthi, a Zaidi religious leader of the Houthis and a former parliamentarian on whose head the government had placed a $55,000 bounty. Initially, most of the fighting took place in Sa'dah Governorate in northwestern Yemen, but some of the fighting spread to neighbouring governorates Hajjah, 'Amran, al-Jawf and the Saudi province of Jizan. After the Houthi takeover of the capital city Sana'a in late 2014, the insurgency became a full-blown civil war with a major Saudi-led intervention in Yemen beginning in March 2015.

The Houthi movement, officially called Ansar Allah and colloquially simply Houthis, is an Islamic political and armed movement that emerged from Sa'dah in northern Yemen in the 1990s. The movement was called Houthis because its founder is from the Houthi tribe. They are of the Zaidi school, though the movement also includes Sunnis. Under the leadership of Hussein Badreddin al-Houthi, the group emerged as an opposition to former Yemeni president Ali Abdullah Saleh, whom they charged with massive financial corruption and criticized for being backed by Saudi Arabia and the United States at the expense of the Yemeni people and Yemen's sovereignty. Resisting Saleh's order for his arrest, Hussein was killed in Sa'dah in 2004 along with a number of his guards by the Yemeni army, sparking the Houthi insurgency in Yemen. Since then, except for a short intervening period, the movement has been led by his brother Abdul-Malik al-Houthi.

Operation Scorched Earth was the code-name of a Yemeni military offensive in the northern Saada Governorate that began in August 2009. It marked the fifth wave of violence in an ongoing insurgency by the Houthis against the government. In November 2009, the conflict spread across the border and into neighboring Saudi Arabia. This conflict led to the Saudi military's incursion into Yemen, marking the first military operation conducted by Saudi Arabia since 1991.
The Al-Qaeda insurgency in Yemen was an armed conflict between the Yemeni government, United States, and al-Qaeda-affiliated cells in Yemen. It is a part of the Global War on Terror.
The Yemeni Civil War is an ongoing multi-sided conflict that began in late 2014 mainly between two factions: the Abdrabbuh Mansur Hadi-led Yemeni government and the Houthi armed movement, along with their supporters and allies. Both claim to constitute the official government of Yemen.

The Saudi-led intervention in Yemen is an intervention launched by Saudi Arabia on 26 March 2015, leading a coalition of nine countries from West Asia and North Africa, in response to calls from the pro-Saudi president of Yemen Abdrabbuh Mansur Hadi for military support after he was ousted by the Houthi movement due to economic and political grievances, and fled to Saudi Arabia.

The Taiz campaign (2015–present) is a protracted military confrontation between opposing Yemeni forces in the city of Taiz for control of the city and surrounding area. The battle began one month after the start of the Yemeni Civil War.

The Second Saudi–Yemeni War is an ongoing armed conflict between the Royal Saudi Armed Forces and Yemeni Houthi forces that has been taking place in the Arabian Peninsula, including the southern Saudi regions of Asir, Jizan, and Najran, since the onset of the Saudi Arabian-led intervention in Yemen in 2015.

The Shabwah Governorate offensive (2014–present) is to an insurgent campaign by AQAP forces to take control of Shabwah Governorate during the Yemeni Civil War.

On 4 September 2015, the Houthis launched an OTR-21 Tochka ballistic missile against a military base in Safer, an area in Ma'rib Governorate. The base was being used by military forces of the Saudi-led coalition. The missile hit an ammunition dump, creating a huge explosion which inflicted numerous casualties among coalition troops. 52 Emirati, 10 Saudi, and 5 Bahraini soldiers were killed in the attack. In addition, dozens of pro-Hadi Yemeni troops were also killed in the strike.
There have been many human rights violations committed by various groups after the Yemeni Civil War. There are two main groups involved in the ongoing conflict: forces loyal to the current Yemeni president, Abh Rabbuh Mansur Hadi, and Houthis and other forces supporting Ali Abdullah Saleh, the former Yemeni president. On 29 November 2017, fighting between forces loyal to Ali Abdullah Saleh and the Houthis began in Sana'a. al-Qaeda in the Arabian Peninsula and the Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant have also carried out attacks in Yemen. All sides of the conflict have been accused of human rights violations. Coalition forces led by Saudi Arabia and backed by the United States and other nations have also been accused of violating human rights and in some cases, breaking international law. The coalition forces intervened at Hadi's request, in an attempt to defeat the Houthis and restore Hadi's government. Coalition attacks, especially airstrikes, have been accused of causing large scale civilian deaths, but Saudi Arabia disputes these claims. The use of force by these groups has exacerbated the humanitarian crisis situation in Yemen, as critical infrastructure has been damaged or destroyed in attacks. In addition to the attacks, blockades of critical resources, such as fuel, to Yemen by Saudi Arabia have hindered the transport of food in Yemen, and the ability of civilians to travel to locations where there are adequate medical facilities. The situation in Yemen has been described as "one of the worst crises in the world" by the United Nations Humanitarian Coordinator for Yemen.
The following is a timeline of the Second Yemeni Civil War, which began in September 2014.

The Ma'rib campaign is a campaign for control of the Ma'rib Governorate of Yemen, between the Houthi fighters and Yemeni Army units loyal to Supreme Political Council on one side, and pro-Hadi militiamen and Yemeni Army units loyal to Abdrabbuh Mansur Hadi on the other side.

From late August to late September 2019, a military operation was carried out by Yemeni forces loyal to the Houthi-led Supreme Political Council, under the code name "Victory from God". It targeted Saudi Arabia and allied forces along the Saudi Arabia–Yemen border.
During the Yemeni civil war, Saudi Arabia led an Arab coalition of nine nations from the Middle East and parts of Africa in response to calls from the internationally recognized pro-Saudi president of Yemen Abdrabbuh Mansur Hadi for military support after he was ousted by the Houthi movement due to economic and political grievances, and fled to Saudi Arabia.

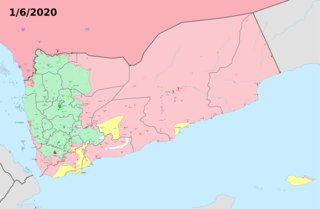
Events of 2020 in Yemen.
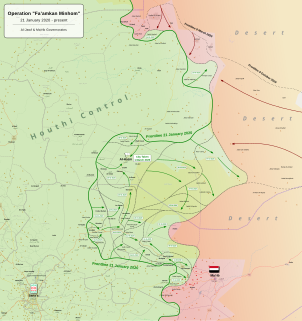
The Al Jawf offensive began in February 2020 with clashes in the Al Jawf Governorate and reached a decisive phase with the capture of the town of Al Hazm by the Houthi movement on 1 March 2020 from the Hadi government, during the Second Yemeni Civil War.

On 28 August 2020, Houthi forces launched a ballistic missile and drone attack at a military camp in Ma'rib governorate, targeting Saudi-led coalition forces supporting the government of Abdrabbuh Mansur Hadi. The attack killed at least 5 Yemeni soldiers, other sources indicate 40 killed, another soldiers were reported injured.