Internet Small Computer Systems Interface or iSCSI is an Internet Protocol-based storage networking standard for linking data storage facilities. iSCSI provides block-level access to storage devices by carrying SCSI commands over a TCP/IP network. iSCSI facilitates data transfers over intranets and to manage storage over long distances. It can be used to transmit data over local area networks (LANs), wide area networks (WANs), or the Internet and can enable location-independent data storage and retrieval.

A network interface controller is a computer hardware component that connects a computer to a computer network.

Network-attached storage (NAS) is a file-level computer data storage server connected to a computer network providing data access to a heterogeneous group of clients. The term "NAS" can refer to both the technology and systems involved, or a specialized device built for such functionality.
TCP offload engine (TOE) is a technology used in some network interface cards (NIC) to offload processing of the entire TCP/IP stack to the network controller. It is primarily used with high-speed network interfaces, such as gigabit Ethernet and 10 Gigabit Ethernet, where processing overhead of the network stack becomes significant. TOEs are often used as a way to reduce the overhead associated with Internet Protocol (IP) storage protocols such as iSCSI and Network File System (NFS).
NetApp, Inc. is an intelligent data infrastructure company that provides unified data storage, integrated data services, and cloud operations (CloudOps) solutions to enterprise customers. The company is based in San Jose, California. It has ranked in the Fortune 500 from 2012 to 2021. Founded in 1992 with an initial public offering in 1995, NetApp offers cloud data services for management of applications and data both online and physically.
A web accelerator is a proxy server that reduces website access time. They can be a self-contained hardware appliance or installable software.
The PowerPC 400 family is a line of 32-bit embedded RISC processor cores based on the PowerPC or Power ISA instruction set architectures. The cores are designed to fit inside specialized applications ranging from system-on-a-chip (SoC) microcontrollers, network appliances, application-specific integrated circuits (ASICs) and field-programmable gate arrays (FPGAs) to set-top boxes, storage devices and supercomputers.
The CXFS file system is a proprietary shared disk file system designed by Silicon Graphics (SGI) specifically to be used in a storage area network (SAN) environment.
Gluster Inc. was a software company that provided an open source platform for scale-out public and private cloud storage. The company was privately funded and headquartered in Sunnyvale, California, with an engineering center in Bangalore, India. Gluster was funded by Nexus Venture Partners and Index Ventures. Gluster was acquired by Red Hat on October 7, 2011.
Grid-oriented Storage (GOS) was a term used for data storage by a university project during the era when the term grid computing was popular.
Panasas is a data storage company that creates network-attached storage for technical computing environments.
StorNext File System (SNFS), colloquially referred to as StorNext is a shared disk file system made by Quantum Corporation. StorNext enables multiple Windows, Linux and Apple workstations to access shared block storage over a Fibre Channel network. With the StorNext file system installed, these computers can read and write to the same storage volume at the same time enabling what is known as a "file-locking SAN." StorNext is used in environments where large files must be shared, and accessed simultaneously by users without network delays, or where a file must be available for access by multiple readers starting at different times. Common use cases include multiple video editor environments in feature film, television and general video post production.
IC Manage is a company that provides design data and IP management, Big Data Analytics, Hybrid Cloud Bursting, and High-Performance Computing software to semiconductors, systems, Internet of Things and artificial intelligence IC companies.

StarWind Software, Inc. is a privately held Beverly, Massachusetts-based computer software and hardware appliance company specializing in storage virtualization and software-defined storage.
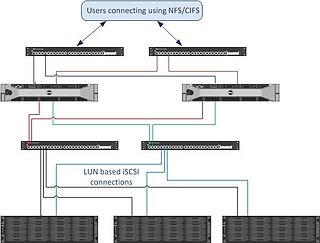
Dell Fluid File System, or FluidFS, is a shared-disk filesystem made by Dell that provides distributed file systems to clients. Customers buy an appliance: a combination of purpose-built network-attached storage (NAS) controllers with integrated primary and backup power supplies attached to block level storage via the iSCSI or Fiber Channel protocol. A single Dell FluidFS appliance consists of two controllers operating in concert connecting to the back-end storage area network (SAN). Depending on the storage capacity requirements and user preference, FluidFS version 4 NAS appliances can be used with Compellent or EqualLogic SAN arrays. The EqualLogic FS7600 and FS7610 connect to the client network and to Dell's EqualLogic arrays with either 1 Gbit/s (FS7600) or 10 Gbit/s (FS7610) iSCSI protocol. For Compellent, FluidFS is available with either 1 Gbit/s or 10 Gbit/s iSCSI connectivity to the client network and connection to the backend Compellent SAN can be either 8 Gbit/s Fibre Channel or 10 Gbit/s iSCSI.
The OpenDataPlane (ODP) is an open-source project which defines application programming interfaces (APIs) for portable high performance networking data plane applications. ODP API design enables various implementation strategies without exposing the application to implementation details. This allows the same application (source code or binary) to run efficiently on various hardware platforms with different levels of HW acceleration. For example, the same application source code may be re-compiled to run on a standard server system or a specialized networking System on a Chip (SoC) device.

Dell Technologies PowerFlex, is a commercial software-defined storage product from Dell Technologies that creates a server-based storage area network (SAN) from local server storage using x86 servers. It converts this direct-attached storage into shared block storage that runs over an IP-based network.
Nasuni is a privately-held hybrid cloud storage company with headquarters in Boston, Massachusetts.
Network Device Interface (NDI) is a software specification developed by the technology company NewTek that enables high-definition video to be delivered, received, and communicated over a computer network in a low-latency, high-quality manner. The specification is royalty-free and allows for frame accurate switching, making it suitable for use in live production environments.
ONTAP or Data ONTAP or Clustered Data ONTAP (cDOT) or Data ONTAP 7-Mode is NetApp's proprietary operating system used in storage disk arrays such as NetApp FAS and AFF, ONTAP Select, and Cloud Volumes ONTAP. With the release of version 9.0, NetApp decided to simplify the Data ONTAP name and removed the word "Data" from it, and remove the 7-Mode image, therefore, ONTAP 9 is the successor of Clustered Data ONTAP 8.




