
The North American Electric Reliability Corporation (NERC) is a nonprofit corporation based in Atlanta, Georgia, and formed on March 28, 2006, as the successor to the North American Electric Reliability Council. The original NERC was formed on June 1, 1968, by the electric utility industry to promote the reliability and adequacy of bulk power transmission in the electric utility systems of North America. NERC's mission states that it is to "ensure the reliability of the North American bulk power system."

The Electric Reliability Council of Texas (ERCOT) operates Texas's electrical grid, the Texas Interconnection, which supplies power to more than 25 million Texas customers and represents 90 percent of the state's electric load. ERCOT is the first independent system operator (ISO) in the United States and one of nine ISOs in North America. ERCOT works with the Texas Reliability Entity (TRE), one of eight regional entities within the North American Electric Reliability Corporation (NERC) that coordinate to improve reliability of the bulk power grid.

A regional transmission organization (RTO) in the United States is an electric power transmission system operator (TSO) that coordinates, controls, and monitors a multi-state electric grid. The transfer of electricity between states is considered interstate commerce, and electric grids spanning multiple states are therefore regulated by the Federal Energy Regulatory Commission (FERC). The voluntary creation of RTOs was initiated by FERC Order No. 2000, issued on December 20, 1999. The purpose of the RTO is to promote economic efficiency, reliability, and non-discriminatory practices while reducing government oversight.

The Texas Interconnection is an alternating current (AC) power grid – a wide area synchronous grid – that covers most of the state of Texas. The grid is managed by the Electric Reliability Council of Texas (ERCOT).

The Eastern Interconnection is one of the two major alternating-current (AC) electrical grids in the continental U.S. power transmission grid. The other major interconnection is the Western Interconnection. The three minor interconnections are the Quebec, Alaska, and Texas interconnections.

The Western Interconnection is a wide area synchronous grid and one of the two major alternating current (AC) power grids in the continental U.S. power transmission grid. The other major wide area synchronous grid is the Eastern Interconnection. The three minor interconnections are the Québec Interconnection, the Texas Interconnection, and the Alaska Interconnection.

ReliabilityFirst (RF) is one of the eight Federal Energy Regulatory Commission (Commission)-approved Regional Entities responsible for ensuring the reliability of the North American Bulk-Power System, pursuant to the Energy Policy Act of 2005. ReliabilityFirst performs this function pursuant to and under its delegation agreement with North American Electric Reliability Corporation (NERC), which is the Commission-approved electric reliability organization. NERC and the Regional Entities are non-governmental, self-regulatory organizations that were created in recognition of, among other things, the complex, interconnected, and international nature of the North American Bulk Power-System.

The Western Electricity Coordinating Council (WECC) promotes Bulk Electric System (BES) reliability in the Western Interconnection. WECC is the Regional Entity responsible for compliance monitoring and enforcement. In addition, WECC provides an environment for the development of Reliability Standards and the coordination of the operating and planning activities of its members as set forth in the WECC Bylaws.

The Florida Reliability Coordinating Council (FRCC) is one of 8 Regional Entities delegated authority to ensure reliability by North American Electric Reliability Corporation (NERC) in North America and was formed on September 16, 1996. The area served by FRCC was previously served by SERC Reliability Corporation (SERC). NERC and the regional reliability councils were formed following the Northeast Blackout of 1965. FRCC's offices are located in Tampa, Florida.

The Midwest Reliability Organization (MRO) began operations on January 1, 2005, as the successor to the Mid-continent Area Power Pool (MAPP), which was formed in 1965. MRO is one of six regional electric reliability councils under North American Electric Reliability Corporation (NERC) authority. NERC and the regional reliability councils were formed following the Northeast Blackout of 1965. MRO's offices are located in St.Paul, Minnesota. MRO members include municipal utilities, cooperatives, investor-owned utilities, a federal power marketing agency, Canadian Crown Corporations, and independent power producers.

The Northeast Power Coordinating Council (NPCC) was formed January 19, 1966, as a successor to the Canada–United States Eastern Interconnection (CANUSE). NPCC is one of six regional electric reliability councils under North American Electric Reliability Corporation (NERC) authority. NERC and the regional reliability councils were formed following the Northeast Blackout of 1965. NPCC's offices are located in New York City, New York.

The electric grid is vital to our everyday lives. It is fundamental for the health, safety, and well-being of our communities, and provides the platform for our economy and our societal and technological advancements.

Southwest Power Pool (SPP), manages the electric grid and wholesale power market for the central United States. As a regional transmission organization, the nonprofit corporation is mandated by the Federal Energy Regulatory Commission to ensure reliable supplies of power, adequate transmission infrastructure and competitive wholesale electricity prices. Southwest Power Pool and its diverse group of member companies coordinate the flow of electricity across approximately 60,000 miles of high-voltage transmission lines spanning 14 states. The company is headquartered in Little Rock, Arkansas.
A NERC Tag, also commonly referred to as an E-Tag, represents a transaction on the North American bulk electricity market scheduled to flow within, between or across electric utility company territories. The NERC Tag is named for the North American Electric Reliability Corporation (NERC), which is the entity that was responsible for the implementation of the first energy tagging processes. NERC Tags were first introduced in 1997, in response to the need to track the increasingly complicated energy transactions which were produced as a result of the beginning of electric deregulation in North America.
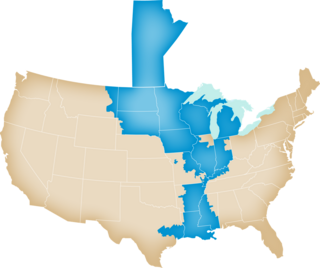
The Midcontinent Independent System Operator, Inc., formerly named Midwest Independent Transmission System Operator, Inc. (MISO) is an Independent System Operator (ISO) and Regional Transmission Organization (RTO) providing open-access transmission service and monitoring the high-voltage transmission system in the Midwest United States and Manitoba, Canada and a southern United States region which includes much of Arkansas, Mississippi, and Louisiana. MISO also operates one of the world's largest real-time energy markets.

An electrical grid, electric grid or power grid, is an interconnected network for delivering electricity from producers to consumers. It consists of:

The New Brunswick System Operator (NBSO) was an independent not-for-profit statutory corporation created under New Brunswick's Electricity Act on October 1, 2004. Under the Act, the NBSO was responsible for the adequacy and reliability of the integrated electricity system, and for facilitating the development and operation of the New Brunswick Electricity Market. These responsibilities took the form of operation of the NBSO-controlled grid and administration of the Open Access Transmission Tariff (Tariff) and the New Brunswick Electricity Market Rules.

The electrical power grid that powers Northern America is not a single grid, but is instead divided into multiple wide area synchronous grids. The Eastern Interconnection and the Western Interconnection are the largest. Three other regions include the Texas Interconnection, the Quebec Interconnection, and the Alaska Interconnection. Each region delivers power at a nominal 60 Hz frequency. The regions are not usually directly connected or synchronized to each other, but there are some HVDC Interconnectors.

The Alaska Interconnection (ASCC) is an AC power transmission grid in North America that serves Central and Southeast Alaska. While the Alaska Interconnection is often referred to as one interconnected grid, its two parts are not connected to each other through interconnectors, nor are the two grids connected to any other interconnection, making the grids in Alaska isolated circuits. Both grids, though, are managed by the Alaska Systems Coordinating Council as if they were one entity like the other interconnections in North America.

The Texas Reliability Entity is one of the regional electric reliability councils under North American Electric Reliability Corporation (NERC) authority. Each Regional Entity is tasked with compliance, monitoring, and enforcement on the behalf of NERC to ensure bulk power system reliability. Texas RE was formed on January 1, 2010 to succeed Texas Regional Entity as the Regional Entity for the Electric Reliability Council of Texas (ERCOT). ERCOT is located in Texas, covering 75% of the state's land area and 90% of its electric load, making it the only Regional Entity that serves both a single interconnection and a single state.










