
Georgia's location, nestled between the Black Sea, Russia, and Turkey, renders it strategically important. It is developing as the gateway from the Black Sea to the Caucasus and the larger Caspian region, but also serves as a buffer between Russia and Turkey. Georgia has a long and tumultuous relationship with Russia, but it is reaching out to its other neighbours and looking to the West in search of alternatives and opportunities. It signed a partnership and cooperation agreement with the European Union, participates in the Partnership for Peace, and encourages foreign investment. France, Germany, South Korea, the United Kingdom, and the United States all have embassies in Tbilisi. Georgia in 2004-2008 sought to become a member of NATO, but did not succeed in the face of strong Russian opposition.

As one of the oldest Euro-Atlantic member states in the region of Southeast Europe, Greece enjoys a prominent geopolitical role as a middle power, due to its political and geographical proximity to Europe, Asia, the Middle East, Africa, the Americas and Australia. Its main allies are the United States, the United Kingdom, France, Italy, Israel, Cyprus and the rest of the European Union, NATO and UN.

The foreign relations of North Macedonia since its independence in 1991 have been characterized by the country's efforts to gain membership in international organizations such as NATO and the European Union and to gain international recognition under its constitutional name, overshadowed by a long-standing, dead-locked dispute with neighboring Greece. Greek objections to the country's name have led to it being admitted to the United Nations and several other international fora only under the provisional designation Former Yugoslav Republic of Macedonia.
Since Slovenia declared independence in 1991, its Governments have underscored their commitment in improving cooperation with neighbouring countries and to actively contribute to international efforts aimed at bringing stability to Southeast Europe. Resource limitations have nevertheless been a problem hindering the efficiency of the Slovenian diplomacy. In the 1990s, foreign relations, especially with Italy, Austria and Croatia, triggered internal political controversies. In the last eight years, however, a wide consensus has been reached among the vast majority of Slovenian political parties to jointly work in the improvement of the country's diplomatic infrastructure and to avoid politicizing the foreign relations by turning them into an issue of internal political debates.
The foreign relations of Albania are its relations with other governments and peoples. Foreign relations are conducted through the Ministry of Foreign Affairs in Tirana. The current minister is Olta Xhaçka. The current Ambassador to the United Nations is Ferit Hoxha.

In many countries, the ministry of foreign affairs is the government department responsible for the state's foreign policy and relations, diplomacy, bilateral, and multilateral relations affairs as well as for providing support for a country's citizens who are abroad. The entity is usually headed by a foreign minister or minister of foreign affairs. The foreign minister typically reports to the head of government.
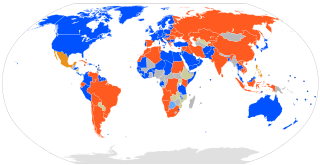
International recognition of Kosovo, since its declaration of independence from Serbia enacted on 17 February 2008, has been mixed, and international governments are divided on the issue.

Cypriot–Georgian relations are foreign relations between Cyprus and Georgia. After the dissolution of the Soviet Union, Cyprus recognized the independence of Georgia in December 1991. The formal Protocol on the Establishment of Diplomatic Relations between the two countries was signed in 1992 and the relations were established on July 9, 1993. Cyprus is represented in Georgia through its embassy in Athens (Greece). Georgia opened an embassy in 2005 in Nicosia and the current ambassador, Vladimir Konstindinidi, presented his credentials in 2009.
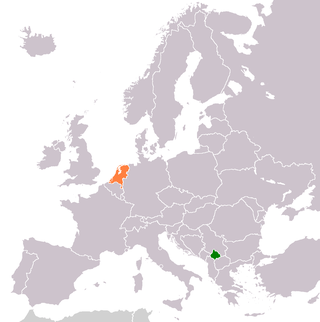
Kosovo–Netherlands relations are foreign relations between Kosovo and the Netherlands. Kosovo declared its independence on 17 February 2008 and the Netherlands recognised it on 4 March 2008. The Netherlands have maintained an embassy in Pristina since 27 June 2008, and Kosovo opened an embassy in The Hague in November 2009. Relations between the two countries are considered to be good and the Netherlands offers support to various projects in Kosovo with the goal of aiding the country in its transition to democracy.

Foreign relations between Austria and Georgia. Both countries established diplomatic relations in 1992 and Georgia opened its embassy in Vienna in 1996. Austria is represented in Georgia through a non resident ambassador based in Vienna, and through an honorary consulate in Tbilisi. Georgia has an embassy in Vienna and an honorary consulate in Graz.

The Ministry of Foreign Affairs is a department of the Government of Kosovo in charge of foreign relations and the admission of Kosovo into the European Union and North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO).

Egyptian–Kosovan relations are foreign relations between Egypt and Kosovo.
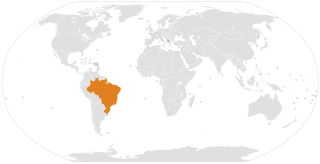
Albania has an embassy in Brasília, and Brazil has an embassy in Tirana.

Albania intends to open an embassy in Baku and Azerbaijan has accredited its ambassador in Athens with the additional position of Ambassador to Albania.

Kosovo–Thailand relations are foreign relations between the Republic of Kosovo and the Kingdom of Thailand. Thailand recognised the Republic of Kosovo as independent state on 24 September 2013.

Georgia–Slovenia relations are the bilateral relations between Georgia and Slovenia, two European nations with a communist past that established their bilateral ties in 1993. Their relations have been highly represented with a close diplomatic partnership, with Slovenia being one of the staunch supporters of Georgia's territorial integrity and pro-Western path.

Cameroonian–Kosovar relations are foreign relations between Cameroon and Kosovo. Formal diplomatic relations between two states are non-existent as Cameroon does not recognize Kosovo as a sovereign state.

Kosovar–Ugandan relations are foreign relations between Kosovo and Uganda. Formal diplomatic relations between two states are non-existent as Uganda does not recognize Kosovo as a sovereign state.

Kosovar–Moroccan relations are foreign relations between Kosovo and Morocco. Formal diplomatic relations between two states are non-existent as Morocco does not recognize Kosovo as a sovereign state.



















