
Project Pluto was a United States government program to develop nuclear-powered ramjet engines for use in cruise missiles. Two experimental engines were tested at the Nevada Test Site (NTS) in 1961 and 1964 respectively.
This is a list of aviation-related events from 1927:
This is a list of aviation-related events from 1961:
Hunter-Killer is an unofficial project name based upon an Aviation Week & Space Technology article. The U.S. Air Force's Hunter-Killer program was a tactical unmanned combat air vehicles (UCAV) procurement program. The General Atomics MQ-9 Reaper, a variant of the MQ-1 Predator won the project and was deployed in Afghanistan.

Ōyodo (大淀) was a light cruiser built for the Imperial Japanese Navy (IJN) during World War II, and was the only ship of her class completed before the end of the war. Designed to command submarine operations, she was obsolete upon completion in 1943. The ship was used as a transport and to escort the navy's capital ships for the rest of the year. Ōyodo was lightly damaged by American aircraft in early January 1944 during one transport mission and returned home several months later to begin conversion to serve as the flagship of the Combined Fleet.

The two Hiyō-class aircraft carriers were built for the Imperial Japanese Navy (IJN) during World War II. Both ships of the class, Hiyō and Jun'yō, were originally laid down as luxury passenger liners before being acquired by the IJN for conversion to aircraft carriers in 1941. Jun'yō was the first of the sister ships to be completed in May 1942 and the ship participated in the invasion of the Aleutian Islands the following month. Both ships participated in several battles during the Guadalcanal Campaign in late 1942. Their aircraft were disembarked several times and used from land bases in a number of battles in the South West Pacific.
The Kronshtadt-class battlecruisers, with the Soviet designation as Project 69 heavy cruisers,, were ordered for the Soviet Navy in the late 1930s. Two ships were started but none were completed due to World War II. These ships had a complex and prolonged design process which was hampered by constantly changing requirements and the Great Purge in 1937.
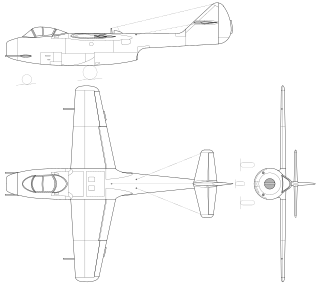
The Lavochkin La-150, was designed by the Lavochkin design bureau (OKB) in response to a 1945 order to build a single-seat jet fighter using a single German turbojet. By this time both the Americans and British, as well as the Germans, had already flown jet fighters and the single Soviet jet engine under development was not yet ready for production. The design was completed quickly, but the construction of the five flying prototypes was protracted by the factory's inexperience in building metal aircraft. The aircraft made its first flight in September 1946, but proved to require extensive modifications to meet the Soviet Air Forces' requirements. These took so long to make and test that the aircraft was essentially obsolete by the time that they were completed. Even one variant with a much more powerful engine was inferior to other aircraft that the OKB had under development and all work was terminated in 1947.

The Le Fantasque class of six large, very fast destroyers was ordered under the French naval programme of 1930. They served in World War II for both Vichy France and the Free French Forces.

The Gnevny class were a group of 29 destroyers built for the Soviet Navy in the late 1930s. They are sometimes known as the Gremyashchiy class and the official Soviet designation was Project 7. These ships fought in World War II.
The Storozhevoyclass were a group of 18 destroyers built for the Soviet Navy in the late 1930s that were officially known as Project 7U. The design was finalised in 1936 after initial disappointments with the Gnevny class. The main changes were unit machinery, a strengthened hull and reduced fuel capacity. The anti-aircraft guns were repositioned to improve firing arcs. The ships fought in World War II.

The Vauquelin class was a group of six large destroyers built for the French Navy in the early 1930s. Entering service in 1933–1934, the sister ships spent most of their careers in the Mediterranean. During the Spanish Civil War of 1936–1939, they helped to enforce the non-intervention agreement. When France declared war on Germany in September 1939, all of the Vauquelins were assigned to the High Sea Forces which was tasked to escort French convoys and support the other commands as needed. Three of the sisters briefly deployed to Scotland in early 1940 to support the Allied forces in the Norwegian Campaign and Maillé Brézé was lost to an accidental explosion. The others returned to the Mediterranean in time to participate in Operation Vado, a bombardment of Italian coastal facilities after Italy entered the war in June.

The Nagato-class battleships were a pair of dreadnought battleships built for the Imperial Japanese Navy (IJN) towards the end of World War I, although they were not completed until after the war. The last of Japan's pre-Treaty capital ships, they were the first class to carry 41 cm (16.1 in) guns, the largest afloat and the first bigger than 15 inches (381 mm). Nagato, the lead ship of the class, frequently served as a flagship. Both ships carried supplies for the survivors of the Great Kantō earthquake in 1923. They were modernized in 1933–1936 with improvements to their armor and machinery and a rebuilt superstructure in the pagoda mast style. Nagato and her sister ship Mutsu briefly participated in the Second Sino-Japanese War in 1937 and Nagato was the flagship of Admiral Isoroku Yamamoto during the attack on Pearl Harbor on 7 December 1941 that began the Pacific War.

Kaiyō was an escort carrier operated by the Imperial Japanese Navy (IJN) during World War II. The ship was originally built as the ocean liner Argentina Maru. She was purchased by the IJN on 9 December 1942, converted into an escort carrier, and renamed Kaiyō. The ship was primarily used as an aircraft transport, escort carrier and training ship during the war. She was badly damaged by repeated air attacks in July 1945 and was scrapped in 1946–48.

The Lavochkin La-152,, and its variants, was a jet fighter prototype designed and manufactured by the Lavochkin Design Bureau (OKB) shortly after the end of World War II. Derived from the Lavochkin La-150, the 152 used several different engines, but the program was canceled as other fighters with more powerful engines and swept wings showed more promise.

The Ibuki-class cruisers were the last class of heavy cruisers built for the Imperial Japanese Navy (IJN). In order to save design time, the ships were essentially repeats of the earlier Mogami class. Begun during World War II, only the lead ship, Ibuki, was launched, but she was in the process of being converted into a light aircraft carrier when construction was suspended in 1945. She was scrapped the following year. The unnamed second ship was scrapped less than a month after being laid down in order to clear her slipway for an aircraft carrier.

The 1927 KLM Fokker F.VIII crash happened on 22 August 1927 when Fokker F.VIII H-NADU of KLM crashed at Underriver, Kent, following structural failure of the tailfin or rudder. The aircraft was operating an international scheduled flight from Croydon, Surrey, to Waalhaven Airport, Rotterdam, the Netherlands. One of the two crew was killed and eight people were injured.

Aeroflot Flight U-505 crashed just after takeoff in Tashkent on 16 January 1987. Flight 505 was an early morning flight from Tashkent to Shahrisabz, both in the Uzbek Soviet Socialist Republic, now the Republic of Uzbekistan. The flight took off just one minute and 28 seconds after an Ilyushin Il-76, thus encountering its wake vortex. The Yakovlev Yak-40 then banked sharply to the right, struck the ground, and caught fire. All 9 people on board died.
The Type 1941 torpedo boats were a group of 15 torpedo boats that were built for Nazi Germany's Kriegsmarine during World War II. Ordered in late 1942, none of the ships were finished before the German surrender on 8/9 May 1945, although four of the ships had been towed west to be completed earlier in that year. They were all either scuttled or demolished in the shipyard in 1945–1946.

The Type 44 torpedo boats were a group of six or nine torpedo boats that were designed for Nazi Germany's Kriegsmarine during World War II. Ordered in 1944, none of the ships were laid down before the German surrender in May 1945.













