Related Research Articles

The Marine Biological Laboratory (MBL) is an international center for research and education in biological and environmental science. Founded in Woods Hole, Massachusetts, in 1888, the MBL is a private, nonprofit institution that was independent for most of its history, but became officially affiliated with the University of Chicago on July 1, 2013. It also collaborates with numerous other institutions.

Gene Elden Likens is an American limnologist and ecologist. He co-founded the Hubbard Brook Ecosystem Study at the Hubbard Brook Experimental Forest in 1963, and founded the Cary Institute of Ecosystem Studies in Millbrook, New York in 1983.

Carl Henry Eigenmann was a German-American ichthyologist of the late nineteenth and early twentieth centuries, who, along with his wife Rosa Smith Eigenmann, and his zoology students is credited with identifying and describing for the first time 195 genera containing nearly 600 species of fishes of North America and South America. Especially notable among his published papers are his studies of the freshwater fishes of South America, the evolution and systematics of South American fishes, and for his analysis of degenerative evolution based on his studies of blind cave fishes found in parts of North America and in Cuba. His most notable works are The American Characidae (1917–1929) and A revision of the South American Nematognathi or cat-fishes (1890), in addition to numerous published papers such as "Cave Vertebrates of North America, a study of degenerative evolution" (1909) and "The fresh-water fishes of Patagonia and an examination of the Archiplata-Archelenis theory" (1909).
Simon Asher Levin is an American ecologist and the James S. McDonnell Distinguished University Professor in Ecology and Evolutionary Biology and the director of the Center for BioComplexity at Princeton University. He specializes in using mathematical modeling and empirical studies in the understanding of macroscopic patterns of ecosystems and biological diversities.

The Stazione Zoologica Anton Dohrn is a research institute in Naples, Italy, devoted to basic research in biology. Research is largely interdisciplinary involving the fields of evolution, biochemistry, molecular biology, neurobiology, cell biology, biological oceanography, marine botany, molecular plant biology, benthic ecology, and ecophysiology.

The Oregon Institute of Marine Biology is the marine station of the University of Oregon. This 100-acre (0.40 km2) marine station is located in Charleston, Oregon at the mouth of Coos Bay. Currently, OIMB is home to several permanent faculty members and a number of graduate students. OIMB is a member of the National Association of Marine Laboratories (NAML). In addition to graduate research, undergraduate classes are offered year round, including marine birds and mammals, estuarine biology, marine ecology, invertebrate zoology, molecular biology, biology of fishes, biological oceanography, and embryology.
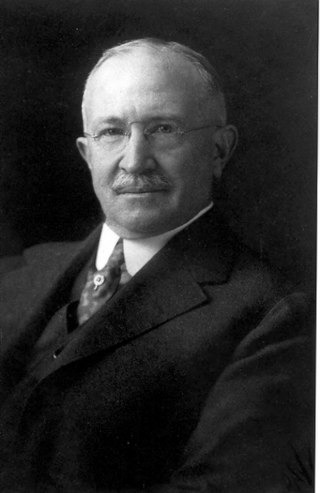
Charles Henry Gilbert was a pioneer ichthyologist and fishery biologist of particular significance to natural history of the western United States. He collected and studied fishes from Central America north to Alaska and described many new species. Later he became an expert on Pacific salmon and was a noted conservationist of the Pacific Northwest. He is considered by many as the intellectual founder of American fisheries biology. He was one of the 22 "pioneer professors" of Stanford University.

Scott E. Fraser is an American biophysicist and Provost Professor of Biological Sciences and Biomedical Engineering at the University of Southern California (USC). He is also the Elizabeth Garrett Chair in Convergent Bioscience and Director of Science Initiatives, where he is helping to launch USC’s Initiative in Convergent Bioscience. In addition, he holds joint appointments in the Departments of Physiology and Biophysics, Stem Cell Biology and Regenerative Medicine, Pediatrics, Radiology, and Ophthalmology.

The Marine Biological Association of the United Kingdom (MBA) is a learned society with a scientific laboratory that undertakes research in marine biology. The organisation was founded in 1884 and has been based in Plymouth since the Citadel Hill Laboratory was opened on 30 June 1888.

The UPLB Limnological Research Station traces its root from the Department of Entomology, of the then UP College of Agriculture. Since its conception, the station contributed immensely to the understanding of the bounties of Laguna de Bay and helped establish the duck farming industry on Los Baňos foreshores and pioneered in aquarium fish production in the country. It serves as the base for studies on limnology and biology of aquatic organisms aimed at developing strategies for the optimum utilization and sustained production of aquatic resources; developing, adapting or improving conventional technologies used to increase fish production; and promoting environment friendly approaches for effective water management.
Samuel M. Nabrit, became the first African American to be awarded a doctoral degree from Brown University, the first Morehouse College graduate to earn a Ph.D. and the first African American appointed to the U.S. Atomic Energy Commission . He was also the first African American to serve on the Brown University Board of Trustees.

The Kerala University of Fisheries and Ocean Studies (KUFOS) is a university established by the Government of Kerala devoted to studies in fisheries and ocean sciences. The bill seeking to establish the university was passed by the Kerala Legislative Assembly on 30 December 2010. KUFOS has its headquarters in the premises of the College of Fisheries, Panangad, near Madavana Junction along the Kochi Bypass. The College of Fisheries, established in 1979, was a constituent college of the Kerala Agricultural University. KUFOS is the first university in India exclusively dedicated to studies in fisheries and allied disciplines. The university was inaugurated and dedicated to the nation in a function held at the campus of the College of Fisheries, Panangad, on 20 February 2011.

Mary Dora Rogick was an American zoologist. In 1935 she joined the College of New Rochelle in New York, where she spent her career as a professor and researcher. She was a specialist in the taxonomy and ecology of bryozoa, a phylum of aquatic invertebrate animals.
John Ernest "Jack" Randall was an American ichthyologist and a leading authority on coral reef fishes. Randall described over 800 species and authored 11 books and over 900 scientific papers and popular articles. He spent most of his career working in Hawaii. He died in April 2020 at the age of 95.
John Dow Fisher Gilchrist (1866–1926) was a Scottish ichthyologist, who established ichthyology as a scientific discipline in South Africa. He was instrumental in the development of marine biology in South Africa and of a scientifically based local fishing industry.

Sarah Preston Monks (1841–1926) was an American naturalist, educator, scientific illustrator, and poet, based for much of her career in San Pedro, California. Monks was the first zoology instructor at Los Angeles State Normal School, a precursor to the University of California, Los Angeles, where she taught for over 20 years, and published on diverse topics including reptiles, amphibians, spiders, and marine biology.

Charles Lincoln Edwards was an American zoologist. His research included studies of development in reptiles and sea cucumbers, chromosomes of Ascaris roundworms, and taxonomy of sea cucumbers and copepods, naming at least five species of copepods found in sea cucumber body cavities.
Walter Kenrick Fisher was an American zoologist, evolutionary biologist, illustrator and painter. He taught in Stanford University before eventually becoming Emeritus Professor in Zoology until his retirement in 1943. Fisher was the son of ornithologist Albert Kenrick Fisher.
Melvin Amos Brannon was a biological scientist, university dean and (briefly) coach at University of North Dakota for athletics and American football.

Dr. Effa Funk Muhse was an American biologist. She was the first woman to obtain a PhD from Indiana University. While at Indiana, she studied glands in toads. After earning her degree, she went on to promote the National Woman's Party in Pennsylvania, Idaho, and Chicago. Later she became a biology teacher at Chevy Chase School and Junior College. Chevy Chase School and Junior College later named a science building after her.
References
- ↑ Proceedings of the Indiana Academy of Science, Volumes 83-84 (1974) By Indiana Academy of Science, 335.
- 1 2 Albert B. Ulrey, Ancestry.com.
- ↑ “A. B. Ulrey, First Biology Instructor Manchester College,” Manchester College Archives and Brethren Historical Collection.
- ↑ USC Wrigley Institute Archived 2010-05-18 at the Wayback Machine .
- ↑ Dr. Herbert R. Axelrod and Dr. Leonard P. Schultz, Handbook of Tropical Aquarium Fishes (Neptune City: T.F.H. Publications, Inc., 1983), 226.