Alexander Gottschalk is Professor of Cellular and Molecular Neurobiology at the Goethe University in Frankfurt, Germany.
Alexander Gottschalk is Professor of Cellular and Molecular Neurobiology at the Goethe University in Frankfurt, Germany.
Alexander Gottschalk studied chemistry, biochemistry and immunology at Goethe University in Frankfurt, Philipps University in Marburg and University of Edinburgh, UK. His PhD thesis (Dr. rer. nat.) was conducted in the laboratory of Reinhard Lührmann at the University of Marburg. As a postdoctoral fellow, he worked with William R. Schafer at UC San Diego to study the nervous system of Caenorhabditis elegans . In 2004, he became an independent research group leader in Frankfurt. In 2010, he was awarded a Heisenberg-Professor position and became Full Professor for Molecular Cell Biology and Neurobiochemistry in 2016. His research group is located at the Buchmann Institute for Molecular Life Sciences.
Alexander Gottschalk studies the neuronal control of behavior in the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans . In 2005, he demonstrated that neuronal expression of the light-gated channel Channelrhodpsin-2 allows controlling the movement of an intact animal with blue light, making him one of the pioneers of Optogenetics. [1] [2] Working with Georg Nagel, he developed optogenetic tools to modulate the second messenger cGMP. [3] He is the coordinator of Priority Programme SPP1926, 'Next Generation Optogenetics' of the German Research Foundation. [4]

Guanylate cyclase is a lyase enzyme that converts guanosine triphosphate (GTP) to cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP) and pyrophosphate:

Behavioral neuroscience, also known as biological psychology, biopsychology, or psychobiology, is the application of the principles of biology to the study of physiological, genetic, and developmental mechanisms of behavior in humans and other animals.

Howard Robert Horvitz ForMemRS NAS AAA&S APS NAM is an American biologist best known for his research on the nematode worm Caenorhabditis elegans, for which he was awarded the 2002 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine, together with Sydney Brenner and John E. Sulston, whose "seminal discoveries concerning the genetic regulation of organ development and programmed cell death" were "important for medical research and have shed new light on the pathogenesis of many diseases".
Channelrhodopsins are a subfamily of retinylidene proteins (rhodopsins) that function as light-gated ion channels. They serve as sensory photoreceptors in unicellular green algae, controlling phototaxis: movement in response to light. Expressed in cells of other organisms, they enable light to control electrical excitability, intracellular acidity, calcium influx, and other cellular processes. Channelrhodopsin-1 (ChR1) and Channelrhodopsin-2 (ChR2) from the model organism Chlamydomonas reinhardtii are the first discovered channelrhodopsins. Variants that are sensitive to different colors of light or selective for specific ions have been cloned from other species of algae and protists.

The Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz Prize, or Leibniz Prize, is awarded by the German Research Foundation to "exceptional scientists and academics for their outstanding achievements in the field of research". Since 1986, up to ten prizes have been awarded annually to individuals or research groups working at a research institution in Germany or at a German research institution abroad. It is considered the most important research award in Germany.
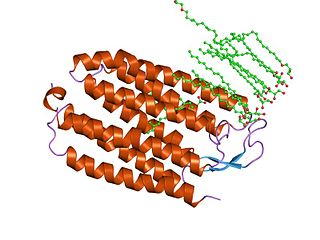
Halorhodopsin is a seven-transmembrane retinylidene protein from microbial rhodopsin family. It is a chloride-specific light-gated ion pump found in archaea known as halobacteria. It is activated by green light wavelengths of approximately 578nm. Halorhodopsin also shares sequence similarity to channelrhodopsin, another light-driven ion channel.
Retinylidene proteins, or rhodopsins in a broad sense, are proteins that use retinal as a chromophore for light reception. They are the molecular basis for a variety of light-sensing systems from phototaxis in flagellates to eyesight in animals. Retinylidene proteins include all forms of opsin and rhodopsin. While rhodopsin in the narrow sense refers to a dim-light visual pigment found in vertebrates, usually on rod cells, rhodopsin in the broad sense refers to any molecule consisting of an opsin and a retinal chromophore in the ground state. When activated by light, the chromophore is isomerized, at which point the molecule as a whole is no longer rhodopsin, but a related molecule such as metarhodopsin. However, it remains a retinylidene protein. The chromophore then separates from the opsin, at which point the bare opsin is a retinylidene protein. Thus, the molecule remains a retinylidene protein throughout the phototransduction cycle.
Light-gated ion channels are a family of ion channels regulated by electromagnetic radiation. Other gating mechanisms for ion channels include voltage-gated ion channels, ligand-gated ion channels, mechanosensitive ion channels, and temperature-gated ion channels. Most light-gated ion channels have been synthesized in the laboratory for study, although two naturally occurring examples, channelrhodopsin and anion-conducting channelrhodopsin, are currently known. Photoreceptor proteins, which act in a similar manner to light-gated ion channels, are generally classified instead as G protein-coupled receptors.

Gero Andreas Miesenböck is an Austrian scientist. He is currently Waynflete Professor of Physiology and Director of the Centre for Neural Circuits and Behaviour (CNCB) at the University of Oxford and a fellow of Magdalen College, Oxford.
Optogenetics is a biological technique to control the activity of neurons or other cell types with light. This is achieved by expression of light-sensitive ion channels, pumps or enzymes specifically in the target cells. On the level of individual cells, light-activated enzymes and transcription factors allow precise control of biochemical signaling pathways. In systems neuroscience, the ability to control the activity of a genetically defined set of neurons has been used to understand their contribution to decision making, learning, fear memory, mating, addiction, feeding, and locomotion. In a first medical application of optogenetic technology, vision was partially restored in a blind patient.

Karl Alexander Deisseroth is an American scientist. He is the D.H. Chen Professor of Bioengineering and of psychiatry and behavioral sciences at Stanford University.

Feng Zhang is a Chinese-American biochemist. Zhang currently holds the James and Patricia Poitras Professorship in Neuroscience at the McGovern Institute for Brain Research and in the departments of Brain and Cognitive Sciences and Biological Engineering at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology. He also has appointments with the Broad Institute of MIT and Harvard. He is most well known for his central role in the development of optogenetics and CRISPR technologies.

Peter Hegemann is a Hertie Senior Research Chair for Neurosciences and a Professor of Experimental Biophysics at the Department of Biology, Faculty of Life Sciences, Humboldt University of Berlin, Germany. He is known for his discovery of channelrhodopsin, a type of ion channels regulated by light, thereby serving as a light sensor. This created the field of optogenetics, a technique that controls the activities of specific neurons by applying light. He has received numerous accolades, including the Rumford Prize, the Shaw Prize in Life Science and Medicine, and the Albert Lasker Award for Basic Medical Research.

Herwig Baier is a German neurobiologist with dual German and US-American citizenship. He is Director at the Max Planck Institute for Biological Intelligence and head of the department Genes – Circuits – Behavior. Herwig Baier's research aims to understand how animal brains convert sensory inputs into behavioral responses.

William Ronald Schafer is a neuroscientist and geneticist who has made important contributions to understanding the molecular and neural basis of behaviour. His work, principally in the nematode C. elegans, has used an interdisciplinary approach to investigate how small groups of neurons generate behavior, and he has pioneered methodological approaches, including optogenetic neuroimaging and automated behavioural phenotyping, that have been widely influential in the broader neuroscience field. He has made significant discoveries on the functional properties of ionotropic receptors in sensory transduction and on the roles of gap junctions and extrasynaptic modulation in neuronal microcircuits. More recently, he has applied theoretical ideas from network science and control theory to investigate the structure and function of simple neuronal connectomes, with the goal of understanding conserved computational principles in larger brains. He is an EMBO member, Welcome Investigator and Fellow of the Academy of Medical Sciences.

Georg Nagel is a biophysicist and professor at the Department for Neurophysiology at the University of Würzburg in Germany. His research is focused on microbial photoreceptors and the development of optogenetic tools.
Ernst Bamberg is a German biophysicist and director emeritus of the Department of Biophysical Chemistry at the Max Planck Institute of Biophysics.

Photoactivated adenylyl cyclase (PAC) is a protein consisting of an adenylyl cyclase enzyme domain directly linked to a BLUF type light sensor domain. When illuminated with blue light, the enzyme domain becomes active and converts ATP to cAMP, an important second messenger in many cells. In the unicellular flagellate Euglena gracilis, PACα and PACβ (euPACs) serve as a photoreceptor complex that senses light for photophobic responses and phototaxis. Small but potent PACs were identified in the genome of the bacteria Beggiatoa (bPAC) and Oscillatoria acuminata (OaPAC). While natural bPAC has some enzymatic activity in the absence of light, variants with no dark activity have been engineered (PACmn).
The Cluster of Excellence Frankfurt "Macromolecular Complexes" (CEF) was established in 2006 by Goethe University Frankfurt together with the Max Planck Institute of Biophysics and the Max Planck Institute for Brain Research in the context of the German Universities Excellence Initiative. Funding by the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG) endet in October 2019. CEF grew out of the long-standing collaborative research on membrane proteins and RNA molecules and strengthened research efforts in these fields by recruiting further scientists to Frankfurt/Main. CEF brought together the research activities of up to 45 research groups, the majority of which were based on Riedberg Campus in Frankfurt/Main. CEF founded the Buchmann Institute for Molecular Life Sciences (BMLS).

Ikue Mori is a Japanese scientist. She is known for her work on molecular, cellular and neural circuit analyses of thermotaxis behavior in C. elegans. She is Director of Neuroscience Institute and Professor of Molecular Neurobiology of the Graduate School of Science in Nagoya University, Japan. In 2013, she became the first woman to receive Tokizane Award, the most prestigious neuroscience award in Japan, and in 2017, was awarded Medal of Honor with Purple Ribbon.