Related Research Articles

The Baltimore and Ohio Railroad was the first common carrier railroad and the oldest railroad in the United States. It operated as B&O from 1830 until 1987, when it was merged into the Chessie System; its lines are today controlled by CSX Transportation.

The Shay locomotive is a geared steam locomotive that originated and was primarily used in North America. The locomotives were built to the patents of Ephraim Shay, who has been credited with the popularization of the concept of a geared steam locomotive. Although the design of Ephraim Shay's early locomotives differed from later ones, there is a clear line of development that joins all Shays. Shay locomotives were especially suited to logging, mining and industrial operations and could operate successfully on steep or poor quality track.

A 2-8-8-4 steam locomotive, under the Whyte notation, has two leading wheels, two sets of eight driving wheels, and a four-wheel trailing truck. The type was generally named the Yellowstone, a name given it by the first owner, the Northern Pacific Railway, whose lines ran near Yellowstone National Park. Seventy-two Yellowstone-type locomotives were built for four U.S. railroads.

The Virginian Railway was a Class I railroad located in Virginia and West Virginia in the United States. The VGN was created to transport high quality "smokeless" bituminous coal from southern West Virginia to port at Hampton Roads.

The Western Maryland Railway was an American Class I railroad (1852–1983) that operated in Maryland, West Virginia, and Pennsylvania. It was primarily a coal hauling and freight railroad, with a small passenger train operation.
Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives by wheel arrangement, a 2-6-6-2 is a locomotive with one pair of unpowered leading wheels, followed by two sets of three pairs of powered driving wheels and one pair of trailing wheels. The wheel arrangement was principally used on Mallet-type articulated locomotives, although some tank locomotive examples were also built. A Garratt locomotive or Golwé locomotive with the same wheel arrangement is designated 2-6-0+0-6-2 since both engine units are pivoting.
The Wheeling and Lake Erie Railway is a Class II regional railroad that provides freight service, mainly in the areas of Northern Ohio and Western Pennsylvania. It took its name from the former Wheeling and Lake Erie Railway, most of which it bought from the Norfolk and Western Railway in 1990.

Cass Scenic Railroad State Park is a state park and heritage railroad located in Cass, Pocahontas County, West Virginia.

The Winchester and Western Railroad is a shortline railroad operating from Gore, Virginia to Hagerstown, Maryland. It also operates several lines in southern New Jersey, connecting to Conrail Shared Assets Operations at Millville and Vineland.
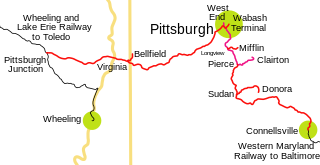
The Pittsburgh and West Virginia Railway was a railroad in the Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, and Wheeling, West Virginia, areas. Originally built as the Wabash Pittsburgh Terminal Railway, a Pittsburgh extension of George J. Gould's Wabash Railroad, the venture entered receivership in 1908, and the line was cut loose. An extension completed in 1931 connected it to the Western Maryland Railway at Connellsville, Pennsylvania, forming part of the Alphabet Route, a coalition of independent lines between the Northeastern United States and the Midwest. It was leased by the Norfolk and Western Railway in 1964 in conjunction with the N&W acquiring several other sections of the former Alphabet Route but was leased to the new spinoff Wheeling and Lake Erie Railway in 1990, just months before the N&W was merged into the Norfolk Southern Railway.

The Argentine Central Railway was a 3 ft narrow gauge railroad in the United States built from the Colorado and Southern Railway at Silver Plume, Colorado, to Waldorf, Colorado, and onward to the summit of Mount McClellan. Construction began on August 1, 1905, and the line was opened to Waldorf a year later on August 1, 1906, a distance of about 16 miles. It was financed and organised by Edward J. Wilcox, owner of 65 mining properties in the Argentine region that were consolidated into the Waldorf Mining and Milling Company in 1902. His headquarters at Waldorf was accessible only by pack mule for much of the year.
The Richmond and Petersburg Railroad moved passengers and goods between Richmond and Petersburg from 1838 to 1898. It survived the American Civil War and eventually merged into the Atlantic Coast Line Railroad in 1900.
The Hempfield Railroad was chartered May 15, 1850 and was a line that originally was to run from Wheeling, West Virginia to Greensburg, Pennsylvania for a distance of 76 miles.
The Hetch Hetchy Railroad (HHRR) was a 68-mile (109 km) standard gauge Class III railroad constructed by the City of San Francisco to support the construction and expansion of the O'Shaughnessy Dam across Hetch Hetchy Valley.
The Wheeling and Lake Erie Railway was a Class I railroad mostly within the U.S. state of Ohio. It was leased to the New York, Chicago and St. Louis Railroad in 1949, and merged into the Norfolk and Western Railway in 1988. A new regional railroad reused the Wheeling and Lake Erie Railway name in 1990 when it acquired most of the former W&LE from the N&W.

The Buffalo and Susquehanna Railroad was a railroad company that formerly operated in western and north central Pennsylvania and western New York. It was created in 1893 by the merger and consolidation of several smaller logging railroads. It operated independently until 1929, when a majority of its capital stock was purchased by the Baltimore and Ohio Railroad. At the same time, the B&O also purchased control of the neighboring Buffalo, Rochester, and Pittsburgh Railway. The Baltimore and Ohio officially took over operations of both roads in 1932.
The Greenbrier, Cheat and Elk Railroad (GC&E) was a logging railroad in West Virginia operating in the early 20th century. Its main line ran from Bergoo to Cheat Junction, where it connected with the Western Maryland Railway (WM).

The Lancaster, Oxford and Southern Railway (LO&S) was a 3 ft narrow gauge railway that operated in southeastern Pennsylvania between 1912 and 1918, as a successor company following the bankruptcy of the Lancaster, Oxford and Southern Railroad. The main line connected Oxford and Peach Bottom, Pennsylvania.
The North Western Virginia Railroad was chartered by the Virginia General Assembly as the Northwestern Virginia Railroad on February 14, 1851, in order to build track from Grafton, West Virginia to Parkersburg, West Virginia. Future statehood advocate and U.S. Senator Peter G. Van Winkle of Parkersburg began as the Northwestern Railroad's secretary in 1852 and served as its president through the American Civil War.

The Bell's Gap Railroad was a 8+1⁄2 miles (13.7 km) long railroad in Pennsylvania. It was inaugurated in 1873 and consolidated in 1874. The original construction was narrow-gauge.
References
- ↑ Poor’s Manual of the Railroads of The United States 1900, page 402-403.
- ↑ Poor’s Manual of the Railroad of the United States 1902, page 248.
- ↑ Poor’s Manual of the Railroads of the United States 1903, page 1533
- ↑ The Official Railway Guide, North America Freight Edition, 1905 page 538.
- ↑ Source is the 1914 West Virginia Public Service Commission Report, page 17.